Arrays
An array is a consecutive group of memory locations that all have the same type. To refer to a particular location or element in the array, we specify the name of the array and the position number of the particular element in the array.
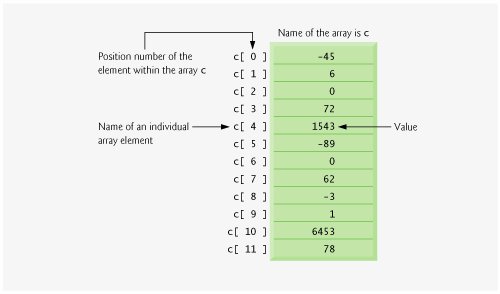
Figure 7.1 shows an integer array called c. This array contains 12 elements. A program refers to any one of these elements by giving the name of the array followed by the position number of the particular element in square brackets ([]). The position number is more formally called a subscript or index (this number specifies the number of elements from the beginning of the array). The first element in every array has subscript 0 (zero) and is sometimes called the zeroth element. Thus, the elements of array c are c[ 0 ] (pronounced "c sub zero"), c[ 1 ], c[ 2 ] and so on. The highest subscript in array c is 11, which is 1 less than 12the number of elements in the array. Array names follow the same conventions as other variable names, i.e., they must be identifiers.
Figure 7.1. Array of 12 elements
A subscript must be an integer or integer expression (using any integral type). If a program uses an expression as a subscript, then the program evaluates the expression to determine the subscript. For example, if we assume that variable a is equal to 5 and that variable b is equal to 6, then the statement
c[ a + b ] += 2;
adds 2 to array element c[ 11 ]. Note that a subscripted array name is an lvalueit can be used on the left side of an assignment, just as non-array variable names can.
Let us examine array c in Fig. 7.1 more closely. The name of the entire array is c. The 12 elements of array c are referred to as c[ 0 ], c[ 1 ], c[ 2 ], ..., c[ 11 ]. The value of c[ 0 ] is -45, the value of c[ 1 ] is 6, the value of c[ 2 ] is 0, the value of c[ 7 ] is 62, and the value of c[ 11 ] is 78. To print the sum of the values contained in the first three elements of array c, we would write
cout << c[ 0 ] + c[ 1 ] + c[ 2 ] << endl;
To divide the value of c[ 6 ] by 2 and assign the result to the variable x, we would write
x = c[ 6 ] / 2;
Common Programming Error 7.1
 |
It is important to note the difference between the "seventh element of the array" and "array element 7." Array subscripts begin at 0, so the "seventh element of the array" has a subscript of 6, while "array element 7" has a subscript of 7 and is actually the eighth element of the array. Unfortunately, this distinction frequently is a source of off-by-one errors. To avoid such errors, we refer to specific array elements explicitly by their array name and subscript number (e.g., c[ 6 ] or c[ 7 ]). |
The brackets used to enclose the subscript of an array are actually an operator in C++. Brackets have the same level of precedence as parentheses. Figure 7.2 shows the precedence and associativity of the operators introduced so far. Note that brackets ([]) have been added to the first row of Fig. 7.2. The operators are shown top to bottom in decreasing order of precedence with their associativity and type.
|
Operators |
Associativity |
Type |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
() |
[] |
left to right |
highest |
|||||
|
++ |
-- |
static_cast<type>( operand ) |
left to right |
unary (postfix) |
||||
|
++ |
-- |
+ |
- |
! |
right to left |
unary (prefix) |
||
|
* |
/ |
% |
left to right |
multiplicative |
||||
|
+ |
- |
left to right |
additive |
|||||
|
<< |
>> |
left to right |
insertion/extraction |
|||||
|
< |
<= |
> |
>= |
left to right |
relational |
|||
|
== |
!= |
left to right |
equality |
|||||
|
&& |
left to right |
logical AND |
||||||
|
|| |
left to right |
logical OR |
||||||
|
?: |
right to left |
conditional |
||||||
|
= |
+= |
-= |
*= |
/= |
%= |
right to left |
assignment |
|
|
, |
left to right |
comma |
||||||
Introduction to Computers, the Internet and World Wide Web
- Introduction
- What Is a Computer?
- Computer Organization
- Early Operating Systems
- Personal, Distributed and Client/Server Computing
- The Internet and the World Wide Web
- Machine Languages, Assembly Languages and High-Level Languages
- History of C and C++
- C++ Standard Library
- History of Java
- FORTRAN, COBOL, Pascal and Ada
- Basic, Visual Basic, Visual C++, C# and .NET
- Key Software Trend: Object Technology
- Typical C++ Development Environment
- Notes About C++ and C++ How to Program, 5/e
- Test-Driving a C++ Application
- Software Engineering Case Study: Introduction to Object Technology and the UML (Required)
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to C++ Programming
- Introduction
- First Program in C++: Printing a Line of Text
- Modifying Our First C++ Program
- Another C++ Program: Adding Integers
- Memory Concepts
- Arithmetic
- Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Examining the ATM Requirements Document
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to Classes and Objects
- Introduction
- Classes, Objects, Member Functions and Data Members
- Overview of the Chapter Examples
- Defining a Class with a Member Function
- Defining a Member Function with a Parameter
- Data Members, set Functions and get Functions
- Initializing Objects with Constructors
- Placing a Class in a Separate File for Reusability
- Separating Interface from Implementation
- Validating Data with set Functions
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying the Classes in the ATM Requirements Document
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Control Statements: Part 1
- Introduction
- Algorithms
- Pseudocode
- Control Structures
- if Selection Statement
- if...else Double-Selection Statement
- while Repetition Statement
- Formulating Algorithms: Counter-Controlled Repetition
- Formulating Algorithms: Sentinel-Controlled Repetition
- Formulating Algorithms: Nested Control Statements
- Assignment Operators
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Class Attributes in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Control Statements: Part 2
- Introduction
- Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition
- for Repetition Statement
- Examples Using the for Statement
- do...while Repetition Statement
- switch Multiple-Selection Statement
- break and continue Statements
- Logical Operators
- Confusing Equality (==) and Assignment (=) Operators
- Structured Programming Summary
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Objects States and Activities in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Functions and an Introduction to Recursion
- Introduction
- Program Components in C++
- Math Library Functions
- Function Definitions with Multiple Parameters
- Function Prototypes and Argument Coercion
- C++ Standard Library Header Files
- Case Study: Random Number Generation
- Case Study: Game of Chance and Introducing enum
- Storage Classes
- Scope Rules
- Function Call Stack and Activation Records
- Functions with Empty Parameter Lists
- Inline Functions
- References and Reference Parameters
- Default Arguments
- Unary Scope Resolution Operator
- Function Overloading
- Function Templates
- Recursion
- Example Using Recursion: Fibonacci Series
- Recursion vs. Iteration
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Class Operations in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Arrays and Vectors
- Introduction
- Arrays
- Declaring Arrays
- Examples Using Arrays
- Passing Arrays to Functions
- Case Study: Class GradeBook Using an Array to Store Grades
- Searching Arrays with Linear Search
- Sorting Arrays with Insertion Sort
- Multidimensional Arrays
- Case Study: Class GradeBook Using a Two-Dimensional Array
- Introduction to C++ Standard Library Class Template vector
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Collaboration Among Objects in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Recursion Exercises
- vector Exercises
Pointers and Pointer-Based Strings
- Introduction
- Pointer Variable Declarations and Initialization
- Pointer Operators
- Passing Arguments to Functions by Reference with Pointers
- Using const with Pointers
- Selection Sort Using Pass-by-Reference
- sizeof Operators
- Pointer Expressions and Pointer Arithmetic
- Relationship Between Pointers and Arrays
- Arrays of Pointers
- Case Study: Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation
- Function Pointers
- Introduction to Pointer-Based String Processing
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Building Your Own Computer
- More Pointer Exercises
- String-Manipulation Exercises
- Special Section: Advanced String-Manipulation Exercises
- A Challenging String-Manipulation Project
Classes: A Deeper Look, Part 1
- Introduction
- Time Class Case Study
- Class Scope and Accessing Class Members
- Separating Interface from Implementation
- Access Functions and Utility Functions
- Time Class Case Study: Constructors with Default Arguments
- Destructors
- When Constructors and Destructors Are Called
- Time Class Case Study: A Subtle TrapReturning a Reference to a private Data Member
- Default Memberwise Assignment
- Software Reusability
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Starting to Program the Classes of the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Classes: A Deeper Look, Part 2
- Introduction
- const (Constant) Objects and const Member Functions
- Composition: Objects as Members of Classes
- friend Functions and friend Classes
- Using the this Pointer
- Dynamic Memory Management with Operators new and delete
- static Class Members
- Data Abstraction and Information Hiding
- Container Classes and Iterators
- Proxy Classes
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Operator Overloading; String and Array Objects
- Introduction
- Fundamentals of Operator Overloading
- Restrictions on Operator Overloading
- Operator Functions as Class Members vs. Global Functions
- Overloading Stream Insertion and Stream Extraction Operators
- Overloading Unary Operators
- Overloading Binary Operators
- Case Study: Array Class
- Converting between Types
- Case Study: String Class
- Overloading ++ and --
- Case Study: A Date Class
- Standard Library Class string
- explicit Constructors
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Object-Oriented Programming: Inheritance
- Introduction
- Base Classes and Derived Classes
- protected Members
- Relationship between Base Classes and Derived Classes
- Constructors and Destructors in Derived Classes
- public, protected and private Inheritance
- Software Engineering with Inheritance
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Object-Oriented Programming: Polymorphism
- Introduction
- Polymorphism Examples
- Relationships Among Objects in an Inheritance Hierarchy
- Type Fields and switch Statements
- Abstract Classes and Pure virtual Functions
- Case Study: Payroll System Using Polymorphism
- (Optional) Polymorphism, Virtual Functions and Dynamic Binding Under the Hood
- Case Study: Payroll System Using Polymorphism and Run-Time Type Information with Downcasting, dynamic_cast, typeid and type_info
- Virtual Destructors
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Incorporating Inheritance into the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Templates
- Introduction
- Function Templates
- Overloading Function Templates
- Class Templates
- Nontype Parameters and Default Types for Class Templates
- Notes on Templates and Inheritance
- Notes on Templates and Friends
- Notes on Templates and static Members
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Stream Input/Output
- Introduction
- Streams
- Stream Output
- Stream Input
- Unformatted I/O using read, write and gcount
- Introduction to Stream Manipulators
- Stream Format States and Stream Manipulators
- Stream Error States
- Tying an Output Stream to an Input Stream
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Exception Handling
- Introduction
- Exception-Handling Overview
- Example: Handling an Attempt to Divide by Zero
- When to Use Exception Handling
- Rethrowing an Exception
- Exception Specifications
- Processing Unexpected Exceptions
- Stack Unwinding
- Constructors, Destructors and Exception Handling
- Exceptions and Inheritance
- Processing new Failures
- Class auto_ptr and Dynamic Memory Allocation
- Standard Library Exception Hierarchy
- Other Error-Handling Techniques
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
File Processing
- Introduction
- The Data Hierarchy
- Files and Streams
- Creating a Sequential File
- Reading Data from a Sequential File
- Updating Sequential Files
- Random-Access Files
- Creating a Random-Access File
- Writing Data Randomly to a Random-Access File
- Reading from a Random-Access File Sequentially
- Case Study: A Transaction-Processing Program
- Input/Output of Objects
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Class string and String Stream Processing
- Introduction
- string Assignment and Concatenation
- Comparing strings
- Substrings
- Swapping strings
- string Characteristics
- Finding Strings and Characters in a string
- Replacing Characters in a string
- Inserting Characters into a string
- Conversion to C-Style Pointer-Based char * Strings
- Iterators
- String Stream Processing
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Web Programming
- Introduction
- HTTP Request Types
- Multitier Architecture
- Accessing Web Servers
- Apache HTTP Server
- Requesting XHTML Documents
- Introduction to CGI
- Simple HTTP Transactions
- Simple CGI Scripts
- Sending Input to a CGI Script
- Using XHTML Forms to Send Input
- Other Headers
- Case Study: An Interactive Web Page
- Cookies
- Server-Side Files
- Case Study: Shopping Cart
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Searching and Sorting
- Introduction
- Searching Algorithms
- Sorting Algorithms
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Data Structures
- Introduction
- Self-Referential Classes
- Dynamic Memory Allocation and Data Structures
- Linked Lists
- Stacks
- Queues
- Trees
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Building Your Own Compiler
Bits, Characters, C-Strings and structs
- Introduction
- Structure Definitions
- Initializing Structures
- Using Structures with Functions
- typedef
- Example: High-Performance Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation
- Bitwise Operators
- Bit Fields
- Character-Handling Library
- Pointer-Based String-Conversion Functions
- Search Functions of the Pointer-Based String-Handling Library
- Memory Functions of the Pointer-Based String-Handling Library
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Standard Template Library (STL)
- Introduction to the Standard Template Library (STL)
- Sequence Containers
- Associative Containers
- Container Adapters
- Algorithms
- Class bitset
- Function Objects
- Wrap-Up
- STL Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Recommended Reading
Other Topics
- Introduction
- const_cast Operator
- namespaces
- Operator Keywords
- mutable Class Members
- Pointers to Class Members (.* and ->*)
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance and virtual Base Classes
- Wrap-Up
- Closing Remarks
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Appendix A. Operator Precedence and Associativity Chart
Appendix B. ASCII Character Set
Appendix C. Fundamental Types
Appendix D. Number Systems
- D.1. Introduction
- D.2. Abbreviating Binary Numbers as Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers
- D.3. Converting Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers to Binary Numbers
- D.4. Converting from Binary, Octal or Hexadecimal to Decimal
- D.5. Converting from Decimal to Binary, Octal or Hexadecimal
- D.6. Negative Binary Numbers: Twos Complement Notation
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Appendix E. C Legacy Code Topics
- E.1. Introduction
- E.2. Redirecting Input/Output on UNIX/LINUX/Mac OS X and Windows Systems
- E.3. Variable-Length Argument Lists
- E.4. Using Command-Line Arguments
- E.5. Notes on Compiling Multiple-Source-File Programs
- E.6. Program Termination with exit and atexit
- E.7. The volatile Type Qualifier
- E.8. Suffixes for Integer and Floating-Point Constants
- E.9. Signal Handling
- E.10. Dynamic Memory Allocation with calloc and realloc
- E.11. The Unconditional Branch: goto
- E.12. Unions
- E.13. Linkage Specifications
- E.14. Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Appendix F. Preprocessor
- F.1. Introduction
- F.2. The #include Preprocessor Directive
- F.3. The #define Preprocessor Directive: Symbolic Constants
- F.4. The #define Preprocessor Directive: Macros
- F.5. Conditional Compilation
- F.6. The #error and #pragma Preprocessor Directives
- F.7. The # and ## Operators
- F.8. Predefined Symbolic Constants
- F.9. Assertions
- F.10. Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Appendix G. ATM Case Study Code
- Appendix G. ATM Case Study Code
- G.1. ATM Case Study Implementation
- G.2. Class ATM
- G.3. Class Screen
- G.4. Class Keypad
- G.5. Class CashDispenser
- G.6. Class DepositSlot
- G.7. Class Account
- G.8. Class BankDatabase
- G.9. Class Transaction
- G.10. Class BalanceInquiry
- G.11. Class Withdrawal
- G.12. Class Deposit
- G.13. Test Program ATMCaseStudy.cpp
- G.14. Wrap-Up
Appendix H. UML 2: Additional Diagram Types
Appendix I. C++ Internet and Web Resources
- Appendix I. C++ Internet and Web Resources
- I.1. Resources
- I.2. Tutorials
- I.3. FAQs
- I.4. Visual C++
- I.5. Newsgroups
- I.6. Compilers and Development Tools
- I.7. Standard Template Library
Appendix J. Introduction to XHTML
- J.1. Introduction
- J.2. Editing XHTML
- J.3. First XHTML Example
- J.4. Headers
- J.5. Linking
- J.6. Images
- J.7. Special Characters and More Line Breaks
- J.8. Unordered Lists
- J.9. Nested and Ordered Lists
- J.10. Basic XHTML Tables
- J.11. Intermediate XHTML Tables and Formatting
- J.12. Basic XHTML Forms
- J.13. More Complex XHTML Forms
- J.14. Internet and World Wide Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
Appendix K. XHTML Special Characters
Appendix L. Using the Visual Studio .NET Debugger
- L.1. Introduction
- L.2. Breakpoints and the Continue Command
- L.3. The Locals and Watch Windows
- L.4. Controlling Execution Using the Step Into, Step Over, Step Out and Continue Commands
- L.5. The Autos Window
- L.6. Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
Appendix M. Using the GNU C++ Debugger
- M.1. Introduction
- M.2. Breakpoints and the run, stop, continue and print Commands
- M.3. The print and set Commands
- M.4. Controlling Execution Using the step, finish and next Commands
- M.5. The watch Command
- M.6. Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
Bibliography
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 627
