G.2. Navigating the Java API
The Java API documentation can be downloaded to your local hard disk or viewed on line. To download the Java API documentation, go to java.sun.com/j2se/5.0/download.jsp and locate the DOWNLOAD link in the J2SE v 1.5.0 Documentation section. You will be asked to accept a license agreement. To do this, click Accept, then click Continue. Click the Java(TM) 2 SDK, Standard Edition Documentation 1.5.0, English link to begin the download. After downloading the file, you can use a ZIP file-extraction program, such as WinZip (www.winzip.com), to extract the files. If you are using Windows, extract the contents to your jdk1.5.0 directory or the directory where you installed Java. (See the Before You Begin section of this book for information on installing Java.) To view the API documentation on your local hard disk in Microsoft Windows, open C:Program FilesJavajdk1.5.0docsapiindex.html page in your browser. To view the API documentation on line, go to java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/api/index.html (Fig. G.1).
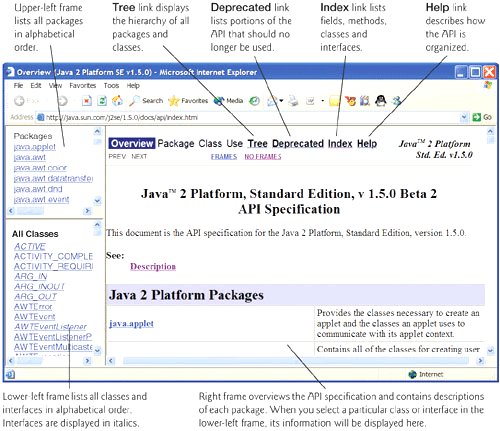
Figure G.1. Java API overview. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
Frames in the API Documentation's index.html Page
The API documentation is divided into three frames (see Fig. G.1). The upper-left frame lists all of the Java API's packages in alphabetical order. The lower-left frame initially lists the Java API's classes and interfaces in alphabetical order. Interface names are displayed in italic. When you click a specific package in the upper-left frame, the lower-left frame lists the classes and interfaces of the selected package. The right frame initially provides a brief description of each package of the Java API specificationread this overview to become familiar wth the general capabilities of the Java APIs. If you select a class or interface in the lower-left frame, the right frame displays information about that class or interface.
Important Links in the index.html Page
At the top of the right frame (Fig. G.1), there are four linksTree, Deprecated, Index and Help. The Tree link displays the hierarchy of all packages, classes and interfaces in a tree structure. The Deprecated link displays interfaces, classes, exceptions, fields, constructors and methods that should no longer be used. The Index link displays classes, interfaces, fields, constructors and methods in alphabetical order. The Help link describes how the API documentation is organized. You should probably begin by reading the Help page.
Viewing the Index Page
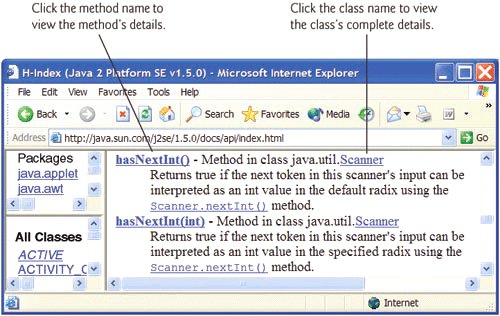
If you do not know the name of the class you are looking for, but you do know the name of a method or field, you can use the documentation's index to locate the class. The Index link is located near the upper-right corner of the right frame. The index page (Fig. G.2) displays fields, constructors, methods, interfaces and classes in alphabetical order. For example, if you are looking for Scanner method hasNextInt, but do not know the class name, you can click the H link to go to the alphabetical listing of all items in the Java API that begin with "h". Scroll to method hasNextInt (Fig. G.3). Once there, each method named hasNextInt is listed with the package name and class to which the method belongs. From there, you can click the class name to view the class's complete details, or you can click the method name to view the method's details.
Figure G.2. Viewing the Index page. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1429 in the print version)
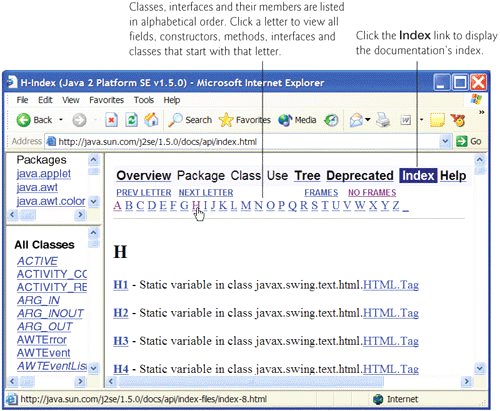
Figure G.3. Scroll to method hasNextInt. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
Viewing a Specific Package
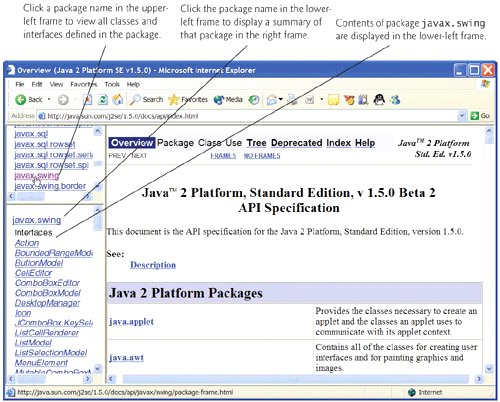
When you click the package name in the upper-left frame, all classes and interfaces from that package are displayed in the lower-left frame and are divided into five subsectionsInterfaces, Classes, Enums, Exceptions and Errorseach listed alphabetically. For example, when you click javax.swing in the upper-left frame, the contents of package javax.swing are displayed in the lower-left frame (Fig. G.4). You can click the package name in the lower-left frame to get an overview of the package. If you think that a package contains several classes that could be useful in your application, the package overview can be especially helpful.
Figure G.4. Clicking a package name in the upper-left frame to view all classes and interfaces declared in this package. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1431 in the print version)
Viewing the Details of a Class
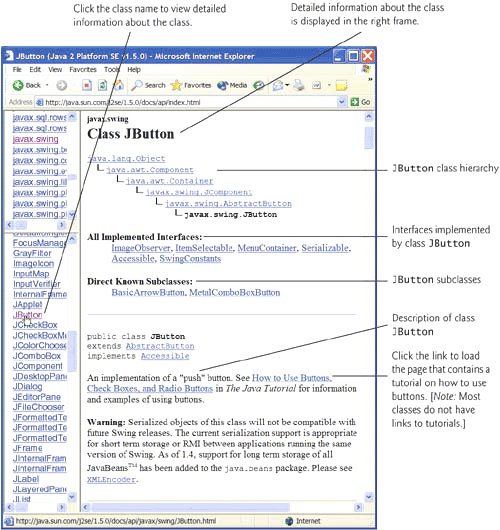
When you click a class name or interface name in the lower-left frame, the right frame displays the details of that class or interface. First you will see the class's package name followed by a hierarchy that shows the class's relationship to other classes. You will also see a list of the interfaces implemented by the class and the class's known subclasses. Figure G.5 shows the beginning of the documentation page for class JButton from the javax.swing package. The page first shows the package name in which the class appears. This is followed by the class hierarchy that leads to class JButton, the interfaces class JButton implements and the subclasses of class JButton. The bottom of the right frame shows the beginning of class JButton's description. Note that when you look at the documentation for an interface, the right frame does not display a hierarchy for that interface. Instead, the right frame lists the interface's superinterfaces, known subinterfaces and known implementing classes.
Figure G.5. Clicking a class name to view detailed information about the class. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1432 in the print version)
Summary Sections in a Class's Documentation Page
Other parts of each API page are listed below. Each part is presented only if the class contains or inherits the items specified. Class members shown in the summary sections are public unless they are explicitly marked as protected. A class's private members are not shown in the documentation, because they cannot be used directly in your programs.
- The Nested Class Summary section summarizes the class's public and protected nested classesi.e., classes that are defined inside the class. Unless explicitly specified, these classes are public and non-static.
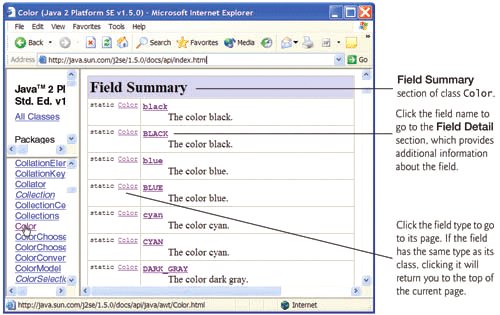
- The Field Summary section summarizes the class's public and protected fields. Unless explicitly specified, these fields are public and non-static. Figure G.6 shows the Field Summary section of class Color.
Figure G.6. Field Summary section of class Color. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1433 in the print version)
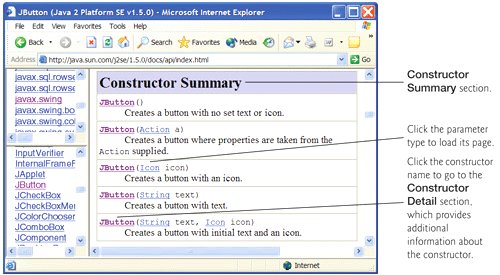
- The Constructor Summary section summarizes the class's constructors. Constructors are not inherited, so this section appears in the documentation for a class only if the class declares one or more constructors. Figure G.7 shows the Constructor Summary section of class JButton.
Figure G.7. Constructor Summary section of class JButton. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1433 in the print version)
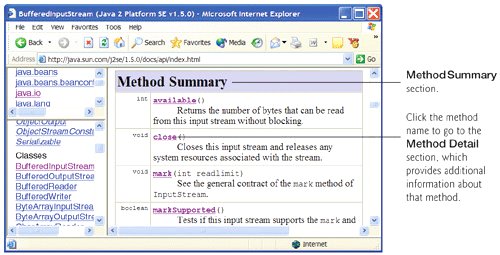
- The Method Summary section summarizes the class's public and protected methods. Unless explicitly specified, these methods are public and non-static. Figure G.8 shows the Method Summary section of class BufferedInputStream.
Figure G.8. Method Summary section of class BufferedInputStream. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1434 in the print version)
Note that the summary sections typically provide only a one-sentence description of a class member. Additional details are presented in the detail sections discussed next.
Detail Sections in a Class's Documentation Page
After the summary sections are detail sections that normally provide more discussion of particular class members. There is not a detail section for nested classes. When you click the link in the Nested Class Summary for a particular nested class, a documentation page describing that nested class is displayed. The detail sections are described below.
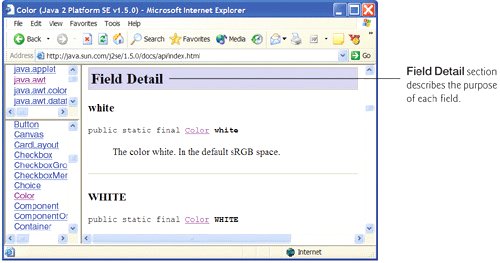
- The Field Detail section provides the declaration of each field. It also discusses each field, including the field's modifiers and meaning. Figure G.9 shows the Field Detail section of class Color.
Figure G.9. Field Detail section of class Color. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1435 in the print version)
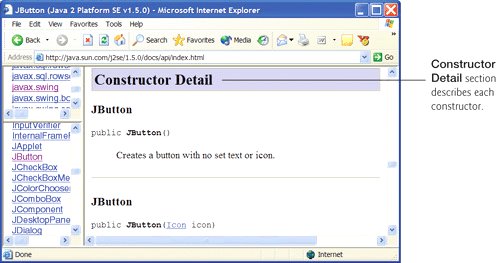
- The Constructor Detail section provides the first line of each constructor's declaration and discusses the constructors. The discussion includes the modifiers of each constructor, a description of each constructor, each constructor's parameters and any exceptions thrown by each constructor. Figure G.10 shows the Constructor Detail section of class JButton.
Figure G.10. Constructor Detail section of class JButton. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1435 in the print version)
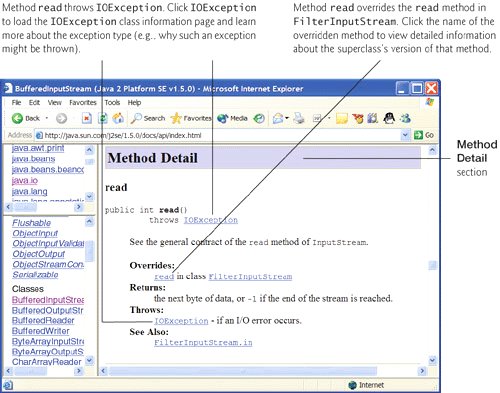
- The Method Detail section provides the first line of each method. The discussion of each method includes its modifiers, a more complete method description, the method's parameters, the method's return type and any exceptions thrown by the method. Figure G.11 shows the Method Detail section of class BufferedInputStream. The method details show you other methods that might be of interest (labeled as See Also). If the method overrides a method of the superclass, the name of the superclass method and the name of the superclass are provided so you can link to the method or superclass for more information.
Figure G.11. Method Detail section of class BufferedInputStream. (Courtesy of Sun Microsystems, Inc.)
(This item is displayed on page 1436 in the print version)
As you look through the documentation, you will notice that there are often links to other fields, methods, nested-classes and top-level classes. These links enable you to jump from the class you are looking at to another relevant portion of the documentation.
Introduction to Computers, the Internet and the World Wide Web
- Introduction
- What Is a Computer?
- Computer Organization
- Early Operating Systems
- Personal, Distributed and Client/Server Computing
- The Internet and the World Wide Web
- Machine Languages, Assembly Languages and High-Level Languages
- History of C and C++
- History of Java
- Java Class Libraries
- FORTRAN, COBOL, Pascal and Ada
- BASIC, Visual Basic, Visual C++, C# and .NET
- Typical Java Development Environment
- Notes about Java and Java How to Program, Sixth Edition
- Test-Driving a Java Application
- Software Engineering Case Study: Introduction to Object Technology and the UML (Required)
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to Java Applications
- Introduction
- First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
- Modifying Our First Java Program
- Displaying Text with printf
- Another Java Application: Adding Integers
- Memory Concepts
- Arithmetic
- Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Examining the Requirements Document
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to Classes and Objects
- Introduction
- Classes, Objects, Methods and Instance Variables
- Declaring a Class with a Method and Instantiating an Object of a Class
- Declaring a Method with a Parameter
- Instance Variables, set Methods and get Methods
- Primitive Types vs. Reference Types
- Initializing Objects with Constructors
- Floating-Point Numbers and Type double
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Using Dialog Boxes
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying the Classes in a Requirements Document
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Control Statements: Part I
- Introduction
- Algorithms
- Pseudocode
- Control Structures
- if Single-Selection Statement
- if...else Double-Selection Statement
- while Repetition Statement
- Formulating Algorithms: Counter-Controlled Repetition
- Formulating Algorithms: Sentinel-Controlled Repetition
- Formulating Algorithms: Nested Control Statements
- Compound Assignment Operators
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Primitive Types
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Creating Simple Drawings
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Class Attributes
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Control Statements: Part 2
- Introduction
- Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition
- for Repetition Statement
- Examples Using the for Statement
- do...while Repetition Statement
- switch Multiple-Selection Statement
- break and continue Statements
- Logical Operators
- Structured Programming Summary
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Drawing Rectangles and Ovals
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Objects States and Activities
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Methods: A Deeper Look
- Introduction
- Program Modules in Java
- static Methods, static Fields and Class Math
- Declaring Methods with Multiple Parameters
- Notes on Declaring and Using Methods
- Method Call Stack and Activation Records
- Argument Promotion and Casting
- Java API Packages
- Case Study: Random-Number Generation
- Case Study: A Game of Chance (Introducing Enumerations)
- Scope of Declarations
- Method Overloading
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Colors and Filled Shapes
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Class Operations
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Arrays
- Introduction
- Arrays
- Declaring and Creating Arrays
- Examples Using Arrays
- Case Study: Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation
- Enhanced for Statement
- Passing Arrays to Methods
- Case Study: Class GradeBook Using an Array to Store Grades
- Multidimensional Arrays
- Case Study: Class GradeBook Using a Two-Dimensional Array
- Variable-Length Argument Lists
- Using Command-Line Arguments
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Drawing Arcs
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Collaboration Among Objects
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Building Your Own Computer
Classes and Objects: A Deeper Look
- Introduction
- Time Class Case Study
- Controlling Access to Members
- Referring to the Current Objects Members with the this Reference
- Time Class Case Study: Overloaded Constructors
- Default and No-Argument Constructors
- Notes on Set and Get Methods
- Composition
- Enumerations
- Garbage Collection and Method finalize
- static Class Members
- static Import
- final Instance Variables
- Software Reusability
- Data Abstraction and Encapsulation
- Time Class Case Study: Creating Packages
- Package Access
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Using Objects with Graphics
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Starting to Program the Classes of the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Object-Oriented Programming: Inheritance
- Introduction
- Superclasses and Subclasses
- protected Members
- Relationship between Superclasses and Subclasses
- Constructors in Subclasses
- Software Engineering with Inheritance
- Object Class
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Displaying Text and Images Using Labels
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Object-Oriented Programming: Polymorphism
- Introduction
- Polymorphism Examples
- Demonstrating Polymorphic Behavior
- Abstract Classes and Methods
- Case Study: Payroll System Using Polymorphism
- final Methods and Classes
- Case Study: Creating and Using Interfaces
- (Optional) GUI and Graphics Case Study: Drawing with Polymorphism
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Incorporating Inheritance into the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
GUI Components: Part 1
- Introduction
- Simple GUI-Based Input/Output with JOptionPane
- Overview of Swing Components
- Displaying Text and Images in a Window
- Text Fields and an Introduction to Event Handling with Nested Classes
- Common GUI Event Types and Listener Interfaces
- How Event Handling Works
- JButton
- Buttons that Maintain State
- JComboBox and Using an Anonymous Inner Class for Event Handling
- JList
- Multiple-Selection Lists
- Mouse Event Handling
- Adapter Classes
- JPanel Subclass for Drawing with the Mouse
- Key-Event Handling
- Layout Managers
- Using Panels to Manage More Complex Layouts
- JTextArea
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Graphics and Java 2D™
- Introduction
- Graphics Contexts and Graphics Objects
- Color Control
- Font Control
- Drawing Lines, Rectangles and Ovals
- Drawing Arcs
- Drawing Polygons and Polylines
- Java 2D API
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Exception Handling
- Introduction
- Exception-Handling Overview
- Example: Divide By Zero Without Exception Handling
- Example: Handling ArithmeticExceptions and InputMismatchExceptions
- When to Use Exception Handling
- Java Exception Hierarchy
- finally block
- Stack Unwinding
- printStackTrace, getStackTrace and getMessage
- Chained Exceptions
- Declaring New Exception Types
- Preconditions and Postconditions
- Assertions
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Files and Streams
- Introduction
- Data Hierarchy
- Files and Streams
- Class File
- Sequential-Access Text Files
- Object Serialization
- Random-Access Files
- Additional java.io Classes
- Opening Files with JFileChooser
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Recursion
- Introduction
- Recursion Concepts
- Example Using Recursion: Factorials
- Example Using Recursion: Fibonacci Series
- Recursion and the Method Call Stack
- Recursion vs. Iteration
- String Permutations
- Towers of Hanoi
- Fractals
- Recursive Backtracking
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Searching and Sorting
- Introduction
- Searching Algorithms
- Sorting Algorithms
- Invariants
- Wrap-up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Data Structures
- Introduction
- Type-Wrapper Classes for Primitive Types
- Autoboxing and Auto-Unboxing
- Self-Referential Classes
- Dynamic Memory Allocation
- Linked Lists
- Stacks
- Queues
- Trees
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Building Your Own Compiler
Generics
- Introduction
- Motivation for Generic Methods
- Generic Methods: Implementation and Compile-Time Translation
- Additional Compile-Time Translation Issues: Methods That Use a Type Parameter as the Return Type
- Overloading Generic Methods
- Generic Classes
- Raw Types
- Wildcards in Methods That Accept Type Parameters
- Generics and Inheritance: Notes
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Collections
- Introduction
- Collections Overview
- Class Arrays
- Interface Collection and Class Collections
- Lists
- Collections Algorithms
- Stack Class of Package java.util
- Class PriorityQueue and Interface Queue
- Sets
- Maps
- Properties Class
- Synchronized Collections
- Unmodifiable Collections
- Abstract Implementations
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to Java Applets
- Introduction
- Sample Applets Provided with the JDK
- Simple Java Applet: Drawing a String
- Applet Life-Cycle Methods
- Initializing an Instance Variable with Method init
- Sandbox Security Model
- Internet and Web Resources
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Multimedia: Applets and Applications
- Introduction
- Loading, Displaying and Scaling Images
- Animating a Series of Images
- Image Maps
- Loading and Playing Audio Clips
- Playing Video and Other Media with Java Media Framework
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Challenging Multimedia Projects
GUI Components: Part 2
- Introduction
- JSlider
- Windows: Additional Notes
- Using Menus with Frames
- JPopupMenu
- Pluggable Look-and-Feel
- JDesktopPane and JInternalFrame
- JTabbedPane
- Layout Managers: BoxLayout and GridBagLayout
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Multithreading
- Introduction
- Thread States: Life Cycle of a Thread
- Thread Priorities and Thread Scheduling
- Creating and Executing Threads
- Thread Synchronization
- Producer/Consumer Relationship without Synchronization
- Producer/Consumer Relationship with Synchronization
- Producer/Consumer Relationship: Circular Buffer
- Producer/Consumer Relationship: ArrayBlockingQueue
- Multithreading with GUI
- Other Classes and Interfaces in java.util.concurrent
- Monitors and Monitor Locks
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Networking
- Introduction
- Manipulating URLs
- Reading a File on a Web Server
- Establishing a Simple Server Using Stream Sockets
- Establishing a Simple Client Using Stream Sockets
- Client/Server Interaction with Stream Socket Connections
- Connectionless Client/Server Interaction with Datagrams
- Client/Server Tic-Tac-Toe Using a Multithreaded Server
- Security and the Network
- Case Study: DeitelMessenger Server and Client
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Accessing Databases with JDBC
- Introduction
- Relational Databases
- Relational Database Overview: The books Database
- SQL
- Instructions to install MySQL and MySQL Connector/J
- Instructions on Setting MySQL User Account
- Creating Database books in MySQL
- Manipulating Databases with JDBC
- Stored Procedures
- RowSet Interface
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Recommended Readings
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Servlets
- Introduction
- Servlet Overview and Architecture
- Setting Up the Apache Tomcat Server
- Handling HTTP get Requests
- Handling HTTP get Requests Containing Data
- Handling HTTP post Requests
- Redirecting Requests to Other Resources
- Multitier Applications: Using JDBC from a Servlet
- Welcome Files
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
JavaServer Pages (JSP)
- Introduction
- JavaServer Pages Overview
- First JSP Example
- Implicit Objects
- Scripting
- Standard Actions
- Directives
- Case Study: Guest Book
- Wrap-Up
- Internet and Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Formatted Output
- Introduction
- Streams
- Formatting Output with printf
- Printing Integers
- Printing Floating-Point Numbers
- Printing Strings and Characters
- Printing Dates and Times
- Other Conversion Characters
- Printing with Field Widths and Precisions
- Using Flags in the printf Format String
- Printing with Argument Indices
- Printing Literals and Escape Sequences
- Formatting Output with Class Formatter
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Strings, Characters and Regular Expressions
- Introduction
- Fundamentals of Characters and Strings
- Class String
- Class StringBuffer
- Class Character
- Class StringTokenizer
- Regular Expressions, Class Pattern and Class Matcher
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Advanced String-Manipulation Exercises
- Special Section: Challenging String-Manipulation Projects
Appendix A. Operator Precedence Chart
Appendix B. ASCII Character Set
Appendix C. Keywords and Reserved Words
Appendix D. Primitive Types
Appendix E. (On CD) Number Systems
Appendix F. (On CD) Unicode®
Appendix G. Using the Java API Documentation
Appendix H. (On CD) Creating Documentation with javadoc
Appendix I. (On CD) Bit Manipulation
Appendix J. (On CD) ATM Case Study Code
Appendix K. (On CD) Labeled break and continue Statements
Appendix L. (On CD) UML 2: Additional Diagram Types
Appendix M. (On CD) Design Patterns
Appendix N. Using the Debugger
Inside Back Cover
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 615
- Challenging the Unpredictable: Changeable Order Management Systems
- The Second Wave ERP Market: An Australian Viewpoint
- Distributed Data Warehouse for Geo-spatial Services
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality
- Development of Interactive Web Sites to Enhance Police/Community Relations
