Menu Bar and Toolbar
Commands for managing the IDE and for developing, maintaining and executing programs are contained in menus, which are located on the menu bar of the IDE (Fig. 2.7). Note that the set of menus displayed in Fig. 2.7 changes based on what you are currently doing in the IDE.
Figure 2.7. Visual Studio menu bar.

Menus contain groups of related commands (also called menu items) that, when selected, cause the IDE to perform specific actions (e.g., open a window, save a file, print a file and execute a program). For example, new projects can be created by selecting File > New Project.... The menus depicted in Fig. 2.7 are summarized in Fig. 2.8. In Chapter 14, Graphical User Interface Concepts: Part 2, we discuss how to create and add your own menus and menu items to your programs.
|
Menu |
Description |
|---|---|
|
File |
Contains commands for opening, closing, adding and saving projects, as well as printing project data and exiting Visual Studio. |
|
Edit |
Contains commands for editing programs, such as cut, copy, paste, undo, redo, delete, find and select. |
|
View |
Contains commands for displaying windows (e.g., Solution Explorer, Toolbox, Properties window) and for adding toolbars to the IDE. |
|
Project |
Contains commands for managing projects and their files. |
|
Build |
Contains commands for compiling a program. |
|
Debug |
Contains commands for debugging (i.e., identifying and correcting problems in a program) and running a program. Debugging is discussed in detail in Appendix C. |
|
Data |
Contains commands for interacting with databases (i.e., organized collections of data stored on computers), which we discuss in Chapter 20, Database, SQL and ADO.NET). |
|
Format |
Contains commands for arranging and modifying a form's controls. Note that the Format menu appears only when a GUI component is selected in Design view. |
|
Tools |
Contains commands for accessing additional IDE tools (e.g., the Toolbox) and options that enable you to customize the IDE. |
|
Window |
Contains commands for arranging and displaying windows. |
|
Community |
Contains commands for sending questions directly to Microsoft, checking question status, sending feedback on Visual C# and searching the CodeZone developer center and the Microsoft developers community site. |
|
Help |
Contains commands for accessing the IDE's help features. |
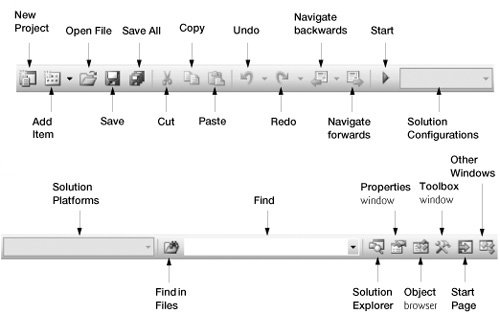
Rather than navigating the menus from the menu bar, you can access many of the more common commands from the toolbar (Fig. 2.9), which contains graphics, called icons, that graphically represent commands. [Note: Figure 2.9 divides the toolbar into two parts so that we can illustrate the graphics more clearlythe toolbar appears on one line inside the IDE.] By default, the standard toolbar is displayed when you run Visual Studio for the first time; it contains icons for the most commonly used commands, such as opening a file, adding an item to a project, saving and running (Fig. 2.9). Some commands are initially disabled (i.e., unavailable to use). These commands, which are initially grayed out, are enabled by Visual Studio only when they are necessary. For example, Visual Studio enables the command for saving a file once you begin editing the file.
Figure 2.9. Standard toolbar in Visual Studio.
(This item is displayed on page 44 in the print version)
a)
b)
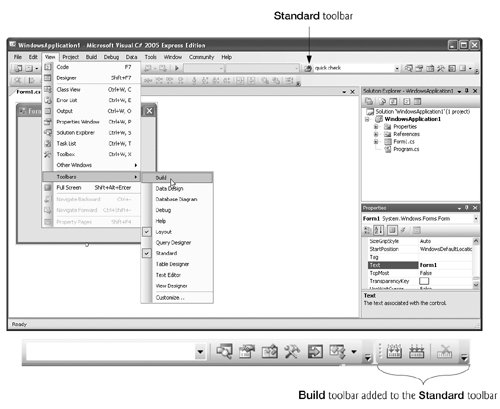
You can customize the IDE by adding more toolbars. Select View > Toolbars (Fig. 2.10). Each toolbar you select will be displayed with the other toolbars at the top of the Visual Studio window (Fig. 2.10). Another way in which you can add toolbars to your IDE (which we do not show in this chapter) is through selecting Tools > Customize. Then, under the Toolbars tab, select the additional toolbars you would like to have appear in the IDE.
Figure 2.10. Adding the Build toolbar to the IDE.
(This item is displayed on page 44 in the print version)
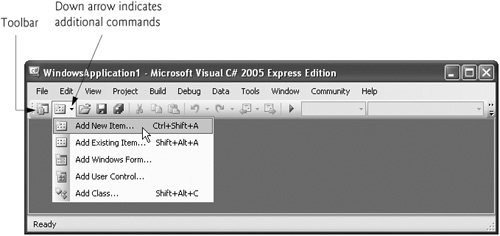
To execute a command via the toolbar, click its icon. Some icons contain a down arrow that, when clicked, displays a related command or commands, as shown in Fig. 2.11.
Figure 2.11. IDE toolbar icon showing additional commands.
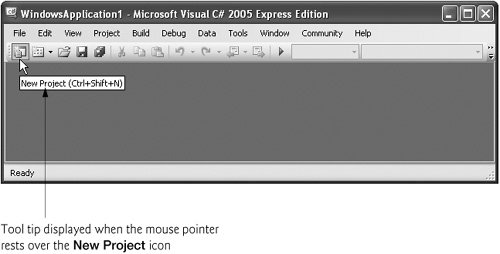
It is difficult to remember what each of the icons on the toolbar represents. Positioning the mouse pointer over an icon highlights it and, after a brief delay, displays a description of the icon called a tool tip (Fig. 2.12). Tool tips help novice programmers become familiar with the IDE's features and serve as useful reminders of each toolbar icon's functionality.
Figure 2.12. Tool tip demonstration.
Preface
Index
Introduction to Computers, the Internet and Visual C#
- Introduction
- What Is a Computer?
- Computer Organization
- Early Operating Systems
- Personal Computing, Distributed Computing and Client/Server Computing
- Hardware Trends
- Microsofts Windows® Operating System
- Machine Languages, Assembly Languages and High-Level Languages
- C#
- C, C++, Java and Visual Basic
- Other High-Level Languages
- The Internet and the World Wide Web
- Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- Microsofts .NET
- The .NET Framework and the Common Language Runtime
- Test-Driving a C# Application
- Software Engineering Case Study: Introduction to Object Technology and the UML
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to the Visual C# 2005 Express Edition IDE
- Introduction
- Overview of the Visual Studio 2005 IDE
- Menu Bar and Toolbar
- Navigating the Visual Studio 2005 IDE
- Using Help
- Using Visual Programming to Create a Simple Program Displaying Text and an Image
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to C# Applications
- Introduction
- A Simple C# Application: Displaying a Line of Text
- Creating Your Simple Application in Visual C# Express
- Modifying Your Simple C# Application
- Formatting Text with Console.Write and Console.WriteLine
- Another C# Application: Adding Integers
- Memory Concepts
- Arithmetic
- Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Examining the ATM Requirements Document
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Introduction to Classes and Objects
- Introduction
- Classes, Objects, Methods, Properties and Instance Variables
- Declaring a Class with a Method and Instantiating an Object of a Class
- Declaring a Method with a Parameter
- Instance Variables and Properties
- UML Class Diagram with a Property
- Software Engineering with Properties and set and get Accessors
- Value Types vs. Reference Types
- Initializing Objects with Constructors
- Floating-Point Numbers and Type decimal
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying the Classes in the ATM Requirements Document
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Control Statements: Part 1
- Introduction
- Algorithms
- Pseudocode
- Control Structures
- if Single-Selection Statement
- if...else Double-Selection Statement
- while Repetition Statement
- Formulating Algorithms: Counter-Controlled Repetition
- Formulating Algorithms: Sentinel-Controlled Repetition
- Formulating Algorithms: Nested Control Statements
- Compound Assignment Operators
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Simple Types
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Class Attributes in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Control Statements: Part 2
- Introduction
- Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition
- for Repetition Statement
- Examples Using the for Statement
- do...while Repetition Statement
- switch Multiple-Selection Statement
- break and continue Statements
- Logical Operators
- Structured Programming Summary
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Objects States and Activities in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Methods: A Deeper Look
- Introduction
- Packaging Code in C#
- static Methods, static Variables and Class Math
- Declaring Methods with Multiple Parameters
- Notes on Declaring and Using Methods
- Method Call Stack and Activation Records
- Argument Promotion and Casting
- The Framework Class Library
- Case Study: Random-Number Generation
- Case Study: A Game of Chance (Introducing Enumerations)
- Scope of Declarations
- Method Overloading
- Recursion
- Passing Arguments: Pass-by-Value vs. Pass-by-Reference
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Identifying Class Operations in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Arrays
- Introduction
- Arrays
- Declaring and Creating Arrays
- Examples Using Arrays
- Case Study: Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation
- foreach Statement
- Passing Arrays and Array Elements to Methods
- Passing Arrays by Value and by Reference
- Case Study: Class GradeBook Using an Array to Store Grades
- Multidimensional Arrays
- Case Study: Class GradeBook Using a Rectangular Array
- Variable-Length Argument Lists
- Using Command-Line Arguments
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Collaboration Among Objects in the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
- Special Section: Building Your Own Computer
Classes and Objects: A Deeper Look
- Introduction
- Time Class Case Study
- Controlling Access to Members
- Referring to the Current Objects Members with the this Reference
- Indexers
- Time Class Case Study: Overloaded Constructors
- Default and Parameterless Constructors
- Composition
- Garbage Collection and Destructors
- static Class Members
- readonly Instance Variables
- Software Reusability
- Data Abstraction and Encapsulation
- Time Class Case Study: Creating Class Libraries
- internal Access
- Class View and Object Browser
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Starting to Program the Classes of the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Object-Oriented Programming: Inheritance
- Introduction
- Base Classes and Derived Classes
- protected Members
- Relationship between Base Classes and Derived Classes
- Constructors in Derived Classes
- Software Engineering with Inheritance
- Class object
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Polymorphism, Interfaces & Operator Overloading
- Introduction
- Polymorphism Examples
- Demonstrating Polymorphic Behavior
- Abstract Classes and Methods
- Case Study: Payroll System Using Polymorphism
- sealed Methods and Classes
- Case Study: Creating and Using Interfaces
- Operator Overloading
- (Optional) Software Engineering Case Study: Incorporating Inheritance and Polymorphism into the ATM System
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Exception Handling
- Introduction
- Exception Handling Overview
- Example: Divide by Zero Without Exception Handling
- Example: Handling DivideByZeroExceptions and FormatExceptions
- .NET Exception Hierarchy
- finally Block
- Exception Properties
- User-Defined Exception Classes
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Graphical User Interface Concepts: Part 1
- Introduction
- Windows Forms
- Event Handling
- Control Properties and Layout
- Labels, TextBoxes and Buttons
- GroupBoxes and Panels
- CheckBoxes and RadioButtons
- PictureBoxes
- ToolTips
- NumericUpDown Control
- Mouse-Event Handling
- Keyboard-Event Handling
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Answers To Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Graphical User Interface Concepts: Part 2
- Introduction
- Menus
- MonthCalendar Control
- DateTimePicker Control
- LinkLabel Control
- ListBox Control
- CheckedListBox Control
- ComboBox Control
- TreeView Control
- ListView Control
- TabControl Control
- Multiple Document Interface (MDI) Windows
- Visual Inheritance
- User-Defined Controls
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Multithreading
- Introduction
- Thread States: Life Cycle of a Thread
- Thread Priorities and Thread Scheduling
- Creating and Executing Threads
- Thread Synchronization and Class Monitor
- Producer/Consumer Relationship without Thread Synchronization
- Producer/Consumer Relationship with Thread Synchronization
- Producer/Consumer Relationship: Circular Buffer
- Multithreading with GUIs
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Strings, Characters and Regular Expressions
- Introduction
- Fundamentals of Characters and Strings
- string Constructors
- string Indexer, Length Property and CopyTo Method
- Comparing strings
- Locating Characters and Substrings in strings
- Extracting Substrings from strings
- Concatenating strings
- Miscellaneous string Methods
- Class StringBuilder
- Length and Capacity Properties, EnsureCapacity Method and Indexer of Class StringBuilder
- Append and AppendFormat Methods of Class StringBuilder
- Insert, Remove and Replace Methods of Class StringBuilder
- Char Methods
- Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation
- Regular Expressions and Class Regex
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Graphics and Multimedia
- Introduction
- Drawing Classes and the Coordinate System
- Graphics Contexts and Graphics Objects
- Color Control
- Font Control
- Drawing Lines, Rectangles and Ovals
- Drawing Arcs
- Drawing Polygons and Polylines
- Advanced Graphics Capabilities
- Introduction to Multimedia
- Loading, Displaying and Scaling Images
- Animating a Series of Images
- Windows Media Player
- Microsoft Agent
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Files and Streams
- Introduction
- Data Hierarchy
- Files and Streams
- Classes File and Directory
- Creating a Sequential-Access Text File
- Reading Data from a Sequential-Access Text File
- Serialization
- Creating a Sequential-Access File Using Object Serialization
- Reading and Deserializing Data from a Sequential-Access Text File
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- Introduction
- XML Basics
- Structuring Data
- XML Namespaces
- Document Type Definitions (DTDs)
- W3C XML Schema Documents
- (Optional) Extensible Stylesheet Language and XSL Transformations
- (Optional) Document Object Model (DOM)
- (Optional) Schema Validation with Class XmlReader
- (Optional) XSLT with Class XslCompiledTransform
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Database, SQL and ADO.NET
- Introduction
- Relational Databases
- Relational Database Overview: Books Database
- SQL
- ADO.NET Object Model
- Programming with ADO.NET: Extracting Information from a Database
- Querying the Books Database
- Programming with ADO.NET: Address Book Case Study
- Using a DataSet to Read and Write XML
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
ASP.NET 2.0, Web Forms and Web Controls
- Introduction
- Simple HTTP Transactions
- Multitier Application Architecture
- Creating and Running a Simple Web-Form Example
- Web Controls
- Session Tracking
- Case Study: Connecting to a Database in ASP.NET
- Case Study: Secure Books Database Application
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Web Services
- Introduction
- .NET Web Services Basics
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
- Publishing and Consuming Web Services
- Session Tracking in Web Services
- Using Web Forms and Web Services
- User-Defined Types in Web Services
- Wrap-Up
- Web Resources
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Networking: Streams-Based Sockets and Datagrams
- Introduction
- Connection-Oriented vs. Connectionless Communication
- Protocols for Transporting Data
- Establishing a Simple TCP Server (Using Stream Sockets)
- Establishing a Simple TCP Client (Using Stream Sockets)
- Client/Server Interaction with Stream-Socket Connections
- Connectionless Client/Server Interaction with Datagrams
- Client/Server Tic-Tac-Toe Using a Multithreaded Server
- WebBrowser Control
- .NET Remoting
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Searching and Sorting
- Introduction
- Searching Algorithms
- Sorting Algorithms
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Data Structures
- Introduction
- Simple-Type structs, Boxing and Unboxing
- Self-Referential Classes
- Linked Lists
- Stacks
- Queues
- Trees
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Generics
- Introduction
- Motivation for Generic Methods
- Generic Method Implementation
- Type Constraints
- Overloading Generic Methods
- Generic Classes
- Notes on Generics and Inheritance
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Collections
- Introduction
- Collections Overview
- Class Array and Enumerators
- Non-Generic Collections
- Generic Collections
- Synchronized Collections
- Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Appendix A. Operator Precedence Chart
Appendix B. Number Systems
- B.1. Introduction
- B.2. Abbreviating Binary Numbers as Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers
- B.3. Converting Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers to Binary Numbers
- B.4. Converting from Binary, Octal or Hexadecimal to Decimal
- B.5. Converting from Decimal to Binary, Octal or Hexadecimal
- B.6. Negative Binary Numbers: Twos Complement Notation
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Exercises
Appendix C. Using the Visual Studio 2005 Debugger
- C.1. Introduction
- C.2. Breakpoints and the Continue Command
- C.3. The Locals and Watch Windows
- C.4. Controlling Execution Using the Step Into, Step Over, Step Out and Continue Commands
- C.5. Other Features
- C.6. Wrap-Up
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
Appendix D. ASCII Character Set
Appendix E. Unicode®
- E.1. Introduction
- E.2. Unicode Transformation Formats
- E.3. Characters and Glyphs
- E.4. Advantages/Disadvantages of Unicode
- E.5. Using Unicode
- E.6. Character Ranges
- Summary
- Terminology
- Self-Review Exercises
- Answers to Self-Review exercises
- Exercises
Appendix F. Introduction to XHTML: Part 1
- F.1. Introduction
- F.2. Editing XHTML
- F.3. First XHTML Example
- F.4. W3C XHTML Validation Service
- F.5. Headers
- F.6. Linking
- F.7. Images
- F.8. Special Characters and More Line Breaks
- F.9. Unordered Lists
- F.10. Nested and Ordered Lists
- F.11. Web Resources
Appendix G. Introduction to XHTML: Part 2
- G.1. Introduction
- G.2. Basic XHTML Tables
- G.3. Intermediate XHTML Tables and Formatting
- G.4. Basic XHTML Forms
- G.5. More Complex XHTML Forms
- G.6. Internal Linking
- G.7. Creating and Using Image Maps
- G.8. meta Elements
- G.9. frameset Element
- G.10. Nested framesets
- G.11. Web Resources
Appendix H. HTML/XHTML Special Characters
Appendix I. HTML/XHTML Colors
Appendix J. ATM Case Study Code
- Appendix J. ATM Case Study Code
- J.1. ATM Case Study Implementation
- J.2. Class ATM
- J.3. Class Screen
- J.4. Class Keypad
- J.5. Class CashDispenser
- J.6. Class DepositSlot
- J.7. Class Account
- J.8. Class BankDatabase
- J.9. Class Transaction
- J.10. Class BalanceInquiry
- J.11. Class Withdrawal
- J.12. Class Deposit
- J.13. Class ATMCaseStudy
- J.14. Wrap-Up
Appendix K. UML 2: Additional Diagram Types
Appendix L. Simple Types
Index
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 600
