Failover
The failover feature on Cisco ASA ensures that the secondary Cisco ASA takes over the connections if the primary device fails to respond. The security Cisco ASA also supports Active/Active failover, in which both Cisco ASA are active and standby at the same time.
For this example, SecureMe is trying to set up two security Cisco ASA in failover mode. There are two security contexts configured: Cubs and Bears. The requirements for the Cisco ASA devices are as follows:
- The primary Cisco ASA will act as an active unit for the Cubs context while the secondary Cisco ASA will act as an active unit for the Bears context. These Cisco ASA will act as a backup for the other context.
- Use GigabitEthernet0/3 for both LAN failover and stateful failover updates.
To achieve the preceding listed requirements, use the following steps:
|
Step 1. |
Enable failover. Figure 19-27. Enabling Failover 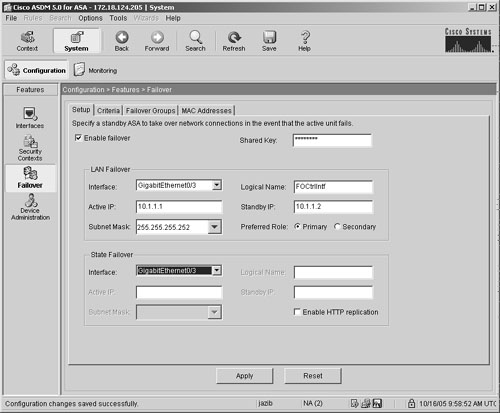
|
|
Step 2. |
Define failover groups. Figure 19-28. Setting Failover Groups 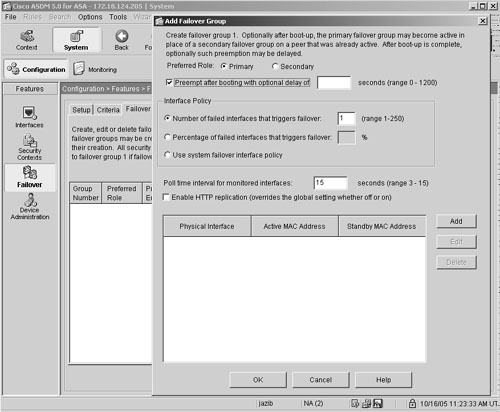
Similarly, add another failover group to be in the Secondary role with the preempt option enabled. |
|
Step 3. |
Map failover groups to security contexts. Figure 19-29. Mapping of Failover Group to Security Context 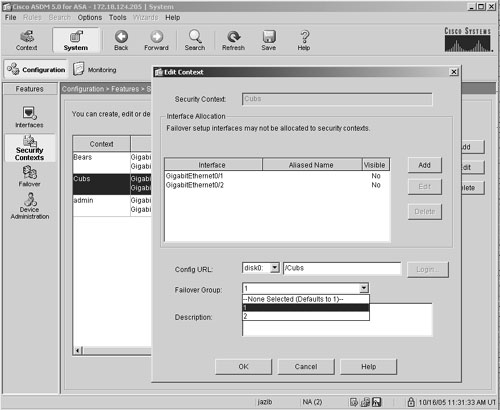
|
Example 19-9 shows the complete configuration of failover as generated by ASDM.
Example 19-9. Failover Configuration Generated by ASDM
failover group 1 primary polltime interface 15 interface-policy 1 failover group 2 secondary polltime interface 15 interface-policy 1 failover context Cubs join-failover-group 1 context Bears join-failover-group 2 failover active
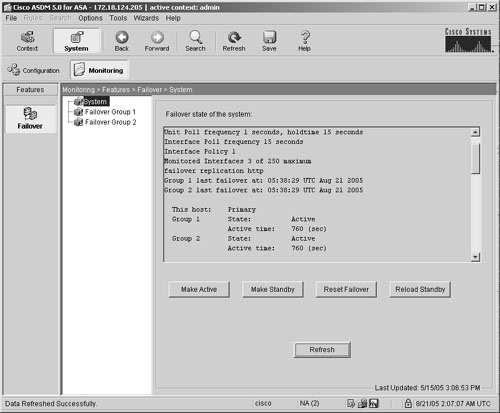
If you navigate to Monitoring > Features > Failover > System under the System context, ASDM displays the output of show failover in the GUI. You can choose to make an Cisco ASA active or standby, reset failover, and reload the standby Cisco ASA, as shown in Figure 19-30.
Figure 19-30. Monitoring Failover
Part I: Product Overview
Introduction to Network Security
- Introduction to Network Security
- Firewall Technologies
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Technologies
- Network-Based Attacks
- Virtual Private Networks
- Summary
Product History
- Product History
- Cisco Firewall Products
- Cisco IDS Products
- Cisco VPN Products
- Cisco ASA All-in-One Solution
- Summary
Hardware Overview
Part II: Firewall Solution
Initial Setup and System Maintenance
- Initial Setup and System Maintenance
- Accessing the Cisco ASA Appliances
- Managing Licenses
- Initial Setup
- IP Version 6
- Setting Up the System Clock
- Configuration Management
- Remote System Management
- System Maintenance
- System Monitoring
- Summary
Network Access Control
- Network Access Control
- Packet Filtering
- Advanced ACL Features
- Content and URL Filtering
- Deployment Scenarios Using ACLs
- Monitoring Network Access Control
- Understanding Address Translation
- DNS Doctoring
- Monitoring Address Translations
- Summary
IP Routing
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA)
- Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA)
- AAA Protocols and Services Supported by Cisco ASA
- Defining an Authentication Server
- Configuring Authentication of Administrative Sessions
- Authenticating Firewall Sessions (Cut-Through Proxy Feature)
- Configuring Authorization
- Configuring Accounting
- Deployment Scenarios
- Troubleshooting AAA
- Summary
Application Inspection
- Application Inspection
- Enabling Application Inspection Using the Modular Policy Framework
- Selective Inspection
- Computer Telephony Interface Quick Buffer Encoding Inspection
- Domain Name System
- Extended Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- File Transfer Protocol
- General Packet Radio Service Tunneling Protocol
- H.323
- HTTP
- ICMP
- ILS
- MGCP
- NetBIOS
- PPTP
- Sun RPC
- RSH
- RTSP
- SIP
- Skinny
- SNMP
- SQL*Net
- TFTP
- XDMCP
- Deployment Scenarios
- Summary
Security Contexts
- Security Contexts
- Architectural Overview
- Configuration of Security Contexts
- Deployment Scenarios
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting the Security Contexts
- Summary
Transparent Firewalls
- Transparent Firewalls
- Architectural Overview
- Transparent Firewalls and VPNs
- Configuration of Transparent Firewall
- Deployment Scenarios
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting the Transparent Firewall
- Summary
Failover and Redundancy
- Failover and Redundancy
- Architectural Overview
- Failover Configuration
- Deployment Scenarios
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting Failovers
- Summary
Quality of Service
- Quality of Service
- Architectural Overview
- Configuring Quality of Service
- QoS Deployment Scenarios
- Monitoring QoS
- Summary
Part III: Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) Solution
Intrusion Prevention System Integration
- Intrusion Prevention System Integration
- Adaptive Inspection Prevention Security Services Module Overview (AIP-SSM)
- Directing Traffic to the AIP-SSM
- AIP-SSM Module Software Recovery
- Additional IPS Features
- Summary
Configuring and Troubleshooting Cisco IPS Software via CLI
- Configuring and Troubleshooting Cisco IPS Software via CLI
- Cisco IPS Software Architecture
- Introduction to the CIPS 5.x Command-Line Interface
- User Administration
- AIP-SSM Maintenance
- Advanced Features and Configuration
- Summary
Part IV: Virtual Private Network (VPN) Solution
Site-to-Site IPSec VPNs
- Site-to-Site IPSec VPNs
- Preconfiguration Checklist
- Configuration Steps
- Advanced Features
- Optional Commands
- Deployment Scenarios
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting Site-to-Site IPSec VPNs
- Summary
Remote Access VPN
- Remote Access VPN
- Cisco IPSec Remote Access VPN Solution
- Advanced Cisco IPSec VPN Features
- Deployment Scenarios of Cisco IPSec VPN
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting Cisco Remote Access VPN
- Cisco WebVPN Solution
- Advanced WebVPN Features
- Deployment Scenarios of WebVPN
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting WebVPN
- Summary
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Introduction to PKI
- Enrolling the Cisco ASA to a CA Using SCEP
- Manual (Cut-and-Paste) Enrollment
- Configuring CRL Options
- Configuring IPSec Site-to-Site Tunnels Using Certificates
- Configuring the Cisco ASA to Accept Remote-Access VPN Clients Using Certificates
- Troubleshooting PKI
- Summary
Part V: Adaptive Security Device Manager
Introduction to ASDM
- Introduction to ASDM
- Setting Up ASDM
- Initial Setup
- Functional Screens
- Interface Management
- System Clock
- Configuration Management
- Remote System Management
- System Maintenance
- System Monitoring
- Summary
Firewall Management Using ASDM
- Firewall Management Using ASDM
- Access Control Lists
- Address Translation
- Routing Protocols
- AAA
- Application Inspection
- Security Contexts
- Transparent Firewalls
- Failover
- QoS
- Summary
IPS Management Using ASDM
- IPS Management Using ASDM
- Accessing the IPS Device Management Console from ASDM
- Configuring Basic AIP-SSM Settings
- Advanced IPS Configuration and Monitoring Using ASDM
- Summary
VPN Management Using ASDM
- VPN Management Using ASDM
- Site-to-Site VPN Setup Using Preshared Keys
- Site-to-Site VPN Setup Using PKI
- Cisco Remote-Access IPSec VPN Setup
- WebVPN
- VPN Monitoring
- Summary
Case Studies
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 231
