QMainWindow and QSettings
Most QApplications manage a single QMainWindow. As Figure 11.4 shows, the QMainWindow has some features that are common to most desktop applications:
- A central widget
- Menu bar
- Status bar
- Dock regions
Figure 11.4. A main window
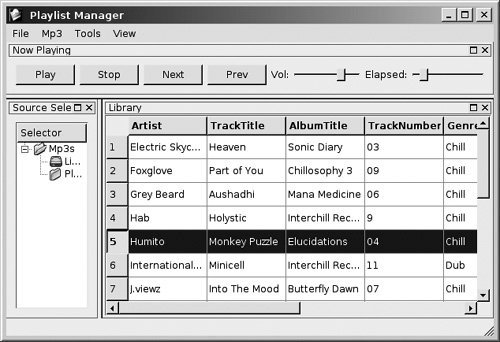
Because the QMainWindow is the parent of all other widgets (in that main window), it is common practice to extend that class for some applications, as shown in Example 11.1.
Example 11.1. src/widgets/mainwindow/mymainwindow.h
[ . . . . ]
class MyMainWindow : public QMainWindow {
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyMainWindow();
void closeEvent(QCloseEvent *event); <-- 1
protected slots:
virtual void newFile();
virtual void open();
virtual bool save();
[ . . . . ]
|
11.2.1. QSettings: Saving and Restoring Application State
All modern desktop applications have a way for users to configure the settings. The settings/preferences/options need to be persistent. The mechanism for that is included with QSettings. As you develop a new QMainWindow application, the first persistent settings you may want to save will probably be the window size and position. You may also want to save the names of the most recent documents that were opened by the application.
QSettings is a persistent map of key/value pairs. It is a QObject and uses QObject's property interface, setValue() and value(), to set and get its values. It can be used to store any data that needs to be remembered across multiple executions.
The QSettings constructor has two QString parameters: one for the organization name and one for the application name. You can establish defaults for these values with the two QCoreApplication functions, setOrganizationName() and setApplicationName(), after which you can use the default QSettings constructor. Each combination of names defines a unique persistent map that does not clash with settings from other-named Qt applications.
The actual mechanism for the persistent storage of QSettings data is implementation dependent and quite flexible. Some possibilities for its storage include the Win32 registry (in Windows) and your $HOME/.qt directory (in Linux). For more detailed information, see the Qt QSettings API documentation.
QMainWindow::saveState() returns a QByteArray that contains information about the main window's toolbars and dockwidgets. To do this it makes use of the objectName property for each of those subwidgets, thus making it important that each name be unique. saveState() has an optional int versionNumber parameter. The QSettings object stores that QByteArray with the key string "state".
QMainWindow::restoreState() takes a QByteArray, presumably created by saveState(), and uses the information that it holds to put the toolbars and dockwidgets into a prior arrangement. It too has an optional versionNumber parameter. We show the use of these functions in Example 11.2.
Example 11.2. src/widgets/mainwindow/mymainwindow.cpp
[ . . . . ]
void MyMainWindow::readSettings() {
QSettings settings("objectlearning.net", "Qt4 Sample Main"); <-- 1
QPoint pos = settings.value("pos", QPoint(200, 200)).toPoint();
QSize size = settings.value("size", QSize(400, 400)).toSize();
QByteArray state = settings.value("state", QByteArray()).toByteArray();
restoreState(state);
resize(size);
move(pos);
}
void MyMainWindow::writeSettings() {
/* Save postion/size of main window */
QSettings settings("objectlearning.net", "Qt4 Sample Main");
settings.setValue("pos", pos());
settings.setValue("size", size());
settings.setValue("state", saveState());
}
|
By placing the "root program logic" in a derived class of QMainWindow or QApplication, the main() becomes quite simple, as shown in Example 11.3.
Example 11.3. src/widgets/mainwindow/mainwindow-main.cpp
#include "mymainwindow.h"
#include
int main( int argc, char ** argv ) {
QApplication a( argc, argv );
MyMainWindow mw;
mw.show();
return a.exec();
}
|
Dialogs |
Part I: Introduction to C++ and Qt 4
C++ Introduction
- C++ Introduction
- Overview of C++
- A Brief History of C++
- Setup: Open-Source Platforms
- Setup: Win32
- C++ First Example
- Input and Output
- Identifiers, Types, and Literals
- C++ Simple Types
- C++ Standard Library Strings
- Streams
- The Keyword const
- Pointers and Memory Access
- const* and *const
- Reference Variables
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Classes
- Classes
- Structs
- Class Definitions
- Member Access Specifiers
- Encapsulation
- Introduction to UML
- Friends of a Class
- Constructors
- Subobjects
- Destructors
- The Keyword static
- Copy Constructors and Assignment Operators
- Conversions
- const Member Functions
- Review Questions
Introduction to Qt
- Introduction to Qt
- Example Project: Using QApplication and QLabel
- Makefile, qmake, and Project Files
- Getting Help Online
- Style Guidelines and Naming Conventions
- The Qt Core Module
- Streams and Dates
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Lists
Functions
- Functions
- Function Declarations
- Overloading Functions
- Optional Arguments
- Operator Overloading
- Parameter Passing by Value
- Parameter Passing by Reference
- References to const
- Function Return Values
- Returning References from Functions
- Overloading on const-ness
- Inline Functions
- Inlining versus Macro Expansion
- Review Questions
Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Simple Derivation
- Derivation with Polymorphism
- Derivation from an Abstract Base Class
- Inheritance Design
- Overloading, Hiding, and Overriding
- Constructors, Destructors, and Copy Assignment Operators
- Processing Command-Line Arguments
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Part II: Higher-Level Programming
Libraries
- Libraries
- Code Containers
- Reusing Other Libraries
- Organizing Libraries: Dependency Management
- Installing Libraries: A Lab Exercise
- Frameworks and Components
- Review Questions
Introduction to Design Patterns
QObject
- QObject
- QObjects Child Managment
- Composite Pattern: Parents and Children
- QApplication and the Event Loop
- Q_OBJECT and moc: A Checklist
- Values and Objects
- tr() and Internationalization
- Point of Departure
- Review Questions
Generics and Containers
- Generics and Containers
- Generics and Templates
- Containers
- Managed Containers, Composites, and Aggregates
- Implicitly Shared Classes
- Generics, Algorithms, and Operators
- Serializer Pattern
- Sorted Map Example
- Review Questions
Qt GUI Widgets
- Qt GUI Widgets
- Widget Categories
- QMainWindow and QSettings
- Dialogs
- Images and Resources
- Layout of Widgets
- QActions, QMenus, and QMenuBars
- QActions, QToolbars, and QActionGroups
- Regions and QDockWidgets
- Views of a QStringList
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Concurrency
- Concurrency
- QProcess and Process Control
- Threads and QThread
- Summary: QProcess and QThread
- Review Questions
Validation and Regular Expressions
- Validation and Regular Expressions
- Validators
- Regular Expressions
- Regular Expression Validation
- Review Questions
Parsing XML
Meta Objects, Properties, and Reflective Programming
- Meta Objects, Properties, and Reflective Programming
- Anti-patterns
- QMetaObject: The MetaObject Pattern
- Type Identification and qobject_cast
- Q_PROPERTY Macro: Describing QObject Properties
- QVariant Class: Accessing Properties
- DataObject: An Extension of QObject
- Property Containers: PropsMap
- Review Questions
More Design Patterns
- More Design Patterns
- Creational Patterns
- Serializer Pattern Revisited
- The Façade Pattern
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Models and Views
- Models and Views
- M-V-C: What about the Controller?
- Dynamic Form Models
- Qt 4 Models and Views
- Table Models
- Tree Models
- Review Questions
Qt SQL Classes
Part III: C++ Language Reference
Types and Expressions
- Types and Expressions
- Operators
- Evaluation of Logical Expressions
- Enumerations
- Signed and Unsigned Integral Types
- Standard Expression Conversions
- Explicit Conversions
- Safer Typecasting Using ANSI C++ Typecasts
- Run-Time Type Identification (RTTI)
- Member Selection Operators
- Point of Departure
- Review Questions
Scope and Storage Class
- Scope and Storage Class
- Declarations and Definitions
- Identifier Scope
- Storage Class
- Namespaces
- Review Questions
Statements and Control Structures
Memory Access
- Memory Access
- Pointer Pathology
- Further Pointer Pathology with Heap Memory
- Memory Access Summary
- Introduction to Arrays
- Pointer Arithmetic
- Arrays, Functions, and Return Values
- Different Kinds of Arrays
- Valid Pointer Operations
- What Happens If new Fails?
Chapter Summary
Inheritance in Detail
- Inheritance in Detail
- Virtual Pointers and Virtual Tables
- Polymorphism and virtual Destructors
- Multiple Inheritance
- Point of Departure
- public, protected, and private Derivation
- Review Questions
Miscellaneous Topics
Part IV: Programming Assignments
MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- Data Model: Mp3File
- Visitor: Generating Playlists
- Preference: An Enumerated Type
- Reusing id3lib
- PlayListModel Serialization
- Testing Mp3File Related Classes
- Simple Queries and Filters
- Mp3PlayerView
- Models and Views: PlayList
- Source Selector
- Persistent Settings
- Edit Form View for FileTagger
- Points of Departure
Part V: Appendices
MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- Appendix A. C++ Reserved Keywords
- Appendix B. Standard Headers
- Appendix C. The Development Environment
- Section C.1. The Preprocessor: For #including Files
- Section C.2. Understanding the Linker
- Section C.3. Debugging
- Section C.4. Qt Assistant and Designer
- Section C.5. Open-Source IDEs and Development Tools
Bibliography
MP3 Jukebox Assignments
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 268
