Managed Containers, Composites, and Aggregates
Value containers are containers of uniform (same-typed) values, for example, QString, byte, int, float, etc. Pointer containers are containers of pointers to (polymorphic commonly typed) objects. They can be managed or unmanaged.
Both kinds of containers can grow at runtime by allocating additional heap memory as needed. This is always done in an exception-safe way, so you don't need to worry about possible memory leaks.
In the case of pointer containers to heap objects, however, one must decide which class is responsible for managing the heap objects. UML diagrams can distinguish between managed and unmanaged containers by using composite (filled diamond) and aggregate (empty diamond) connectors, as shown in Figure 10.2.
Figure 10.2. Aggregates and compositions
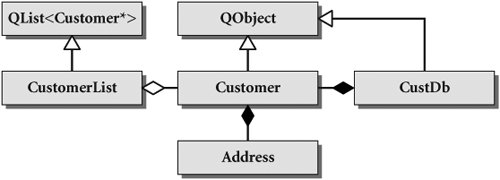
In general, we can say that a managed container is a composite, because the container manages its pointed-to objects. In other words, when a composite is destroyed, it destroys (cleans up) its entire self (because the smaller objects are part of its composition).
When one object embeds another as a sub-object, it is also considered a composition.
In Figure 10.2, there are two kinds of Customer containers, CustomerList and CustDb. CustDb and CustomerList both reuse template containers. CustomerList objects are aggregatestemporary structures to hold the results of a query, or a user selection. CustDb, on the other hand, is a singleton composite that manages all of the Customer objects that exist.
In the case of the Customer and Address relationship, this diagram indicates that one or more Address objects should be associated with a particular Customer. When the Customer object is destroyed, it is reasonable to destroy all of its Address objects at the same time. Thus, the Customer object manages its Addresses, which gives us another example of a composite relationship.
 |
This suggested design does impose some limitations on possible use of Address; in particular, there is no easy way to find all customers at a particular address. If Address and Customer were independently managed, then we could form bidirectional relationships between the classes. |
Typically, a managed container deletes any heap objects it "owns" when the container itself is destroyed. With a Qt container of pointers, one can use qDeleteAll(container), an algorithm that calls delete on each element in the container.
Copying a managed container can be defined in a number of ways:
- For some containers, the feature might be disabled.
- For others, it might be called a deep copy, where all contained objects are cloned and placed in the new container.
- Another approach, taken with the design of Qt containers, is implicit sharing, explained in the next section.
When a container only provides an indexing or reference navigation mechanism to its objects we call it an aggregate container.
In this case, the container does not manage its objects, it only provides a convenient way to access them. When an aggregate container is copied, only references to the collected objects are copied. When an aggregate container is deleted, only the references are removed. There is no impact on the underlying objects in the container.
 |
A managed container is a composition, and an unmanaged container of objects is usually (but not always) represented in a UML diagram as aggregation. |
Exercise: Managed Containers, Compositions and Aggregates
This exercise involves designing some data types to represent a deck and a hand of cards. The following UML diagram suggests one way of representing them.
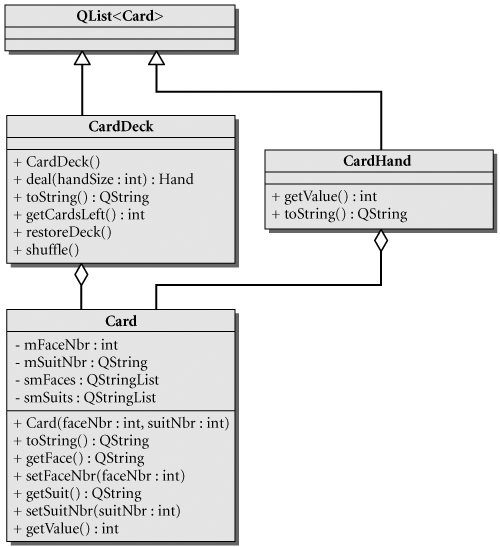
Here are some hints:
- The CardDeck constructor generates a complete deck of 52 cards in a convenient order.
- CardDeck::deal(int k) should use the random() function from to pick k cards from the deck (removing each one from the deck after it is picked) to fill a CardHand object.
- Initialize the random() function from the system clock so that the results will be different each time you run the app. The syntax is
srandom(time(0));
- Evaluate the hand using the rules of the game of bridge: Ace =4, King =3, Queen =2, Jack =1; all other cards have zero value. Use this formula to calculate the return values for the getValue() functions.
- Example 10.6 gives a piece of client code that you can start with for testing.
Example 10.6. src/cardgame/datastructure/cardgame-client.cpp
#include "carddeck.h" #include using namespace qstd; <-- 1 int main() { CardDeck deck; CardHand hand; int handSize, playerScore, progScore; cout << "How many cards in a hand? " << flush; handSize = promptInt(); do { hand = deck.deal(handSize); cout << "Here is your hand:" << endl; cout << hand.toString() << endl; playerScore = hand.getValue(); cout << QString("Your score is: %1 points.") .arg(playerScore) << endl; // Now a hand for the dealer: hand = deck.deal(handSize); progScore = hand.getValue(); cout << "Here is my hand:" << endl; cout << hand.toString() << endl; cout << QString("My score is: %1 points.") .arg(progScore) << endl; cout << QString("%1 win!!") .arg((playerScore > progScore)?"You":"I") << endl; } while(more("hand")); }(1)for cout, endl, and more()
Part I: Introduction to C++ and Qt 4
C++ Introduction
- C++ Introduction
- Overview of C++
- A Brief History of C++
- Setup: Open-Source Platforms
- Setup: Win32
- C++ First Example
- Input and Output
- Identifiers, Types, and Literals
- C++ Simple Types
- C++ Standard Library Strings
- Streams
- The Keyword const
- Pointers and Memory Access
- const* and *const
- Reference Variables
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Classes
- Classes
- Structs
- Class Definitions
- Member Access Specifiers
- Encapsulation
- Introduction to UML
- Friends of a Class
- Constructors
- Subobjects
- Destructors
- The Keyword static
- Copy Constructors and Assignment Operators
- Conversions
- const Member Functions
- Review Questions
Introduction to Qt
- Introduction to Qt
- Example Project: Using QApplication and QLabel
- Makefile, qmake, and Project Files
- Getting Help Online
- Style Guidelines and Naming Conventions
- The Qt Core Module
- Streams and Dates
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Lists
Functions
- Functions
- Function Declarations
- Overloading Functions
- Optional Arguments
- Operator Overloading
- Parameter Passing by Value
- Parameter Passing by Reference
- References to const
- Function Return Values
- Returning References from Functions
- Overloading on const-ness
- Inline Functions
- Inlining versus Macro Expansion
- Review Questions
Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Simple Derivation
- Derivation with Polymorphism
- Derivation from an Abstract Base Class
- Inheritance Design
- Overloading, Hiding, and Overriding
- Constructors, Destructors, and Copy Assignment Operators
- Processing Command-Line Arguments
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Part II: Higher-Level Programming
Libraries
- Libraries
- Code Containers
- Reusing Other Libraries
- Organizing Libraries: Dependency Management
- Installing Libraries: A Lab Exercise
- Frameworks and Components
- Review Questions
Introduction to Design Patterns
QObject
- QObject
- QObjects Child Managment
- Composite Pattern: Parents and Children
- QApplication and the Event Loop
- Q_OBJECT and moc: A Checklist
- Values and Objects
- tr() and Internationalization
- Point of Departure
- Review Questions
Generics and Containers
- Generics and Containers
- Generics and Templates
- Containers
- Managed Containers, Composites, and Aggregates
- Implicitly Shared Classes
- Generics, Algorithms, and Operators
- Serializer Pattern
- Sorted Map Example
- Review Questions
Qt GUI Widgets
- Qt GUI Widgets
- Widget Categories
- QMainWindow and QSettings
- Dialogs
- Images and Resources
- Layout of Widgets
- QActions, QMenus, and QMenuBars
- QActions, QToolbars, and QActionGroups
- Regions and QDockWidgets
- Views of a QStringList
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Concurrency
- Concurrency
- QProcess and Process Control
- Threads and QThread
- Summary: QProcess and QThread
- Review Questions
Validation and Regular Expressions
- Validation and Regular Expressions
- Validators
- Regular Expressions
- Regular Expression Validation
- Review Questions
Parsing XML
Meta Objects, Properties, and Reflective Programming
- Meta Objects, Properties, and Reflective Programming
- Anti-patterns
- QMetaObject: The MetaObject Pattern
- Type Identification and qobject_cast
- Q_PROPERTY Macro: Describing QObject Properties
- QVariant Class: Accessing Properties
- DataObject: An Extension of QObject
- Property Containers: PropsMap
- Review Questions
More Design Patterns
- More Design Patterns
- Creational Patterns
- Serializer Pattern Revisited
- The Façade Pattern
- Points of Departure
- Review Questions
Models and Views
- Models and Views
- M-V-C: What about the Controller?
- Dynamic Form Models
- Qt 4 Models and Views
- Table Models
- Tree Models
- Review Questions
Qt SQL Classes
Part III: C++ Language Reference
Types and Expressions
- Types and Expressions
- Operators
- Evaluation of Logical Expressions
- Enumerations
- Signed and Unsigned Integral Types
- Standard Expression Conversions
- Explicit Conversions
- Safer Typecasting Using ANSI C++ Typecasts
- Run-Time Type Identification (RTTI)
- Member Selection Operators
- Point of Departure
- Review Questions
Scope and Storage Class
- Scope and Storage Class
- Declarations and Definitions
- Identifier Scope
- Storage Class
- Namespaces
- Review Questions
Statements and Control Structures
Memory Access
- Memory Access
- Pointer Pathology
- Further Pointer Pathology with Heap Memory
- Memory Access Summary
- Introduction to Arrays
- Pointer Arithmetic
- Arrays, Functions, and Return Values
- Different Kinds of Arrays
- Valid Pointer Operations
- What Happens If new Fails?
Chapter Summary
Inheritance in Detail
- Inheritance in Detail
- Virtual Pointers and Virtual Tables
- Polymorphism and virtual Destructors
- Multiple Inheritance
- Point of Departure
- public, protected, and private Derivation
- Review Questions
Miscellaneous Topics
Part IV: Programming Assignments
MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- Data Model: Mp3File
- Visitor: Generating Playlists
- Preference: An Enumerated Type
- Reusing id3lib
- PlayListModel Serialization
- Testing Mp3File Related Classes
- Simple Queries and Filters
- Mp3PlayerView
- Models and Views: PlayList
- Source Selector
- Persistent Settings
- Edit Form View for FileTagger
- Points of Departure
Part V: Appendices
MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- MP3 Jukebox Assignments
- Appendix A. C++ Reserved Keywords
- Appendix B. Standard Headers
- Appendix C. The Development Environment
- Section C.1. The Preprocessor: For #including Files
- Section C.2. Understanding the Linker
- Section C.3. Debugging
- Section C.4. Qt Assistant and Designer
- Section C.5. Open-Source IDEs and Development Tools
Bibliography
MP3 Jukebox Assignments
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 268
