Carrier Supporting Carriers Overview
Carrier supporting carriers (CSC) is implemented in circumstances in which one service provider needs to use the transport services provided by another service provider. The service provider providing the transport is called the backbone carrier and the service provider using the services provided by the backbone carrier is called a customer carrier. The customer carrier can either be an ISP provider or an MPLS VPN service provider.
Figure 8-1 shows a network topology in which ISPX is the customer carrier and has two POP sites, ISPX-POP1 and ISPX-POP2.
Figure 8-1. CSC Architecture
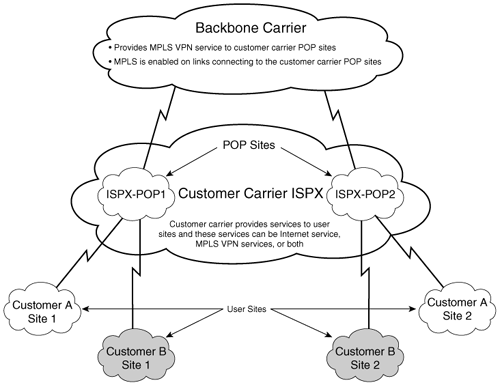
The customer carrier ISPX is using MPLS VPN services provided by the backbone carrier to route traffic between user sites. In the CSC model, the links between the backbone and customer carrier are MPLS enabled to provide an end-to-end LSP path between the two POP sites located in the customer carrier network. In the CSC model, the backbone carrier providing MPLS VPN services to the customer carrier has knowledge of only the customer carrier's internal routes. These routes are relevant for building the LSP path between the two POP sites and for forming the iBGP or MP-iBGP session between the POP sites. User networks will then be transported across this iBGP or MP-iBGP session.
Label Exchange Methods in CSC Architecture
There are two ways of exchanging IGP labels in an MPLS VPN network:
- Using IGP for label exchange
- Using BGP for label exchange
Using IGP for Label Exchange
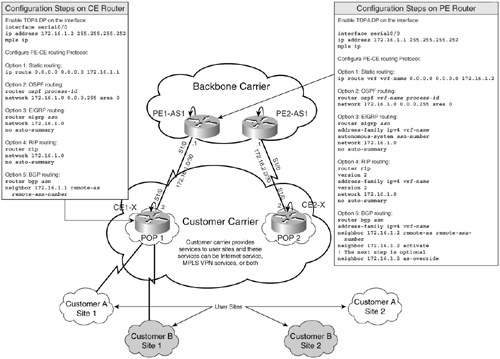
This method employs the traditional approach of using an IGP to exchange routes between PE-CE routers. Label exchange is performed using TDP/LDP protocols. Figure 8-2 shows the configuration steps for enabling MPLS on PE-CE routers.
Figure 8-2. Label Exchange by Enabling MPLS on the Interface
Using BGP for Label Exchange
In this method, BGP is used for routing and for label exchange. When using EBGP for label exchange, mpls bgp forwarding is automatically configured under the interface. Prior to that, ensure that TDP/LDP Protocol (mpls ip) is not enabled on the interface.
Figure 8-3 shows the steps to configure BGP for IPv4 label distribution.
Figure 8-3. Using BGP for IPv4 Label Distribution
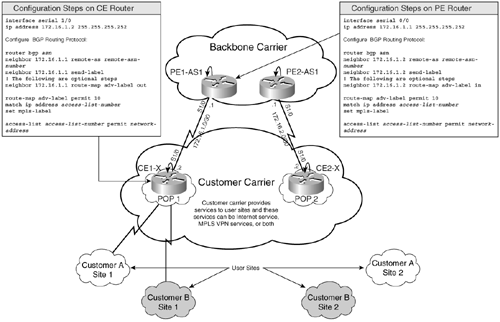
Note
Check Cisco.com for IOS versions supporting this method.
MPLS Overview
- MPLS Overview
- Unicast IP Forwarding in Traditional IP Networks
- Overview of MPLS Forwarding
- MPLS Terminology
- MPLS Control and Data Plane Components
- MPLS Operation
- Special Outgoing Label Types
- Penultimate Hop Popping
- Frame-Mode MPLS
- Cell-Mode MPLS
Basic MPLS Configuration
- Basic MPLS Configuration
- Frame-Mode MPLS Configuration and Verification
- Cell-Mode MPLS over ATM Overview, Configuration, and Verification
- Command Reference
Basic MPLS VPN Overview and Configuration
- Basic MPLS VPN Overview and Configuration
- VPN Categories
- MPLS VPN Architecture and Terminology
- MPLS VPN Routing Model
- MPLS VPN Basic Configuration
- Outbound Route Filters
- Command Reference
PE-CE Routing Protocol-Static and RIP
- PE-CE Routing Protocol-Static and RIP
- Static PE-CE Routing Overview, Configuration, and Verification
- Static PE-CE Routing Command Reference
- RIPv2 PE-CE Routing Overview, Configuration, and Verification
- RIPv1 PE-CE Routing Configuration and Verification
- RIP PE-CE Routing Command Reference
PE-CE Routing Protocol-OSPF and EIGRP
- PE-CE Routing Protocol-OSPF and EIGRP
- OSPF PE-CE Routing Protocol Overview, Configuration and Verification
- EIGRP PE-CE Routing Protocol Overview, Configuration, and Verification
Implementing BGP in MPLS VPNs
- Implementing BGP in MPLS VPNs
- BGP PE-CE Routing Protocol Overview, Configuration, and Verification
- Implementing Route-Reflectors in MPLS VPN Networks
- Case Study-Hub and Spoke MPLS VPN Network Using BGP PE-CE Routing for Sites Using Unique AS Numbers
- Case Study-Hub and Spoke MPLS VPN Network with Sites Using Same AS Numbers
- Command Reference
Inter-Provider VPNs
- Inter-Provider VPNs
- Overview of Inter-Provider VPNs
- Option 1: Inter-Provider VPN Using Back-to-Back VRF Method
- Option 2: Inter-Provider VPNs Using ASBR-to-ASBR Approach
- Option 3: Multi-Hop MP-eBGP Between RR and eBGP Between ASBRs
- Option 4: Non-VPN Transit Provider
- Case Study-Inter-AS Implementing Route-Reflector and BGP Confederation in Provider Networks
- Case Study-Multi-Homed Inter-AS Provider Network
- Command Reference
Carrier Supporting Carriers
- Carrier Supporting Carriers
- Carrier Supporting Carriers Overview
- Deployment Scenarios with CSC Architecture
- CSC Architecture Benefits
- Command Reference
MPLS Traffic Engineering
- MPLS Traffic Engineering
- TE Basics
- MPLS TE Theory
- Constraint-Based Routing and Operation in MPLS TE
- Configuring MPLS TE
- Command Reference
Implementing VPNs with Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol Version 3
- Implementing VPNs with Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol Version 3
- L2TPv3 Overview
- Configuring L2TPv3 Tunnels for Layer 2 VPN
- Configuring L2TPv3 Static Tunnels
- Configuring L2TPv3 Dynamic Tunnels
- Implementing Layer 3 VPNs over L2TPv3 Tunnels
- Command Reference
Any Transport over MPLS (AToM)
- Any Transport over MPLS (AToM)
- Introduction to Layer 2 VPNs
- Implementing AToM for Like to Like Circuits
- L2 VPN-Any to Any Interworking
- Local Switching
- Command Reference
Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS)
- Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS)
- VPLS Overview
- VPLS Topology-Single PE or Direct Attachment
- Hierarchical VPLS-Distributed PE Architecture
- Command Reference
Implementing Quality of Service in MPLS Networks
- Implementing Quality of Service in MPLS Networks
- Introduction to QoS-Classification and Marking
- MPLS QoS Implementation
- MPLS QoS Operating Modes
- Modular QoS CLI: Configuration of QoS on Cisco Routers
- Configuration and Implementation of MPLS QoS in Uniform Mode and Short Pipe Mode Operation
- Implementing MPLS QoS for Layer 2 VPN Implementations
- Command Reference
MPLS Features and Case Studies
- MPLS Features and Case Studies
- Case Study 1: Implementing Multicast Support for MPLS VPNs
- Case Study 2: Implementing Multi-VRF CE, VRF Selection Using Source IP Address, VRF Selection Using Policy-Based Routing, NAT and HSRP Support in MPLS VPN, and Multicast VPN Support over Multi-VRF CE
- Case Study 3: Implementing Layer 2 VPNs over Inter-AS Topologies Using Layer 2 VPN Pseudo-Wire Switching
- Case Study 4: Implementing Layer 3 VPNs over Layer 2 VPN Topologies and Providing L2 VPN Redundancy
- Case Study 5: Implementing Dynamic Layer 3 VPNs Using mGRE Tunnels
- Case Study 6: Implementing Class-Based Tunnel Selection with MPLS Traffic Engineering
- Case Study 7: Implementing Hub and Spoke Topologies with OSPF
- Case Study 8: Implementing Hub and Spoke Topologies with EIGRP
- Case Study 9: Implementing VPLS Services with the GSR 12000 Series
- Case Study 10: BGP Site of Origin
- Command Reference
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 130
- Chapter I e-Search: A Conceptual Framework of Online Consumer Behavior
- Chapter III Two Models of Online Patronage: Why Do Consumers Shop on the Internet?
- Chapter VIII Personalization Systems and Their Deployment as Web Site Interface Design Decisions
- Chapter X Converting Browsers to Buyers: Key Considerations in Designing Business-to-Consumer Web Sites
- Chapter XI User Satisfaction with Web Portals: An Empirical Study
