The Role of IP-to-IP Gateways
A voice gateway joins a VoIP network and the PSTN. A gatekeeper joins separate segments of the same VoIP network. An IP-to-IP gateway (IPIPGW), often called a Session Border Controller, joins independent VoIP or Video over IP networks. It acts as a border device, allowing users in different administrative domains to exchange voice and video using IP, rather than through the PSTN. The call media can either flow through the gateway, or directly between endpoints.
For example, an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP) can use IPIPGWs to route IP voice traffic through another ITSP network. An IPIPGW can provide billing information to the ITSP. IPIPGWs can allow an ITSP to offer its customers end-to-end VoIP service between each other, or between remote offices of the same company. This would allow the exchange of IP calls between CallManager, H.323, and SIP networks.
Figure 1-3 shows an example of two companies that frequently conduct videoconferences between them. They use an IPIPGW to hide the details of each network, while still allowing communication. The H.323 video systems at each location communicate with the IPIPGW, rather than with each other directly. To each network, it looks as if the call signaling originates at the IPIPGW. The IPIPGW acts as a Session Border Controller (SBC) between the two islands, controlling video conferencing between them.
Figure 1-3. IP-to-IP Gateway Example
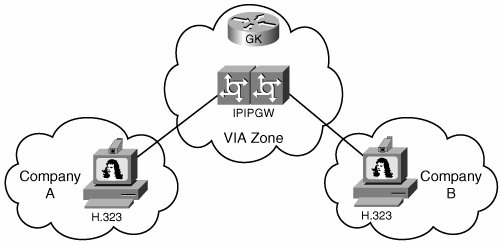
In Figure 1-3, a Voice Infrastructure and Applications (VIA) zone is used, along with a gatekeeper. This zone acts as a transit zone between the two networks. The gatekeeper is especially configured to route calls appropriately to the IPIPGW.
You can install the IP-to-IP gateway Cisco IOS feature set on many Cisco multiservice routers. The following are some features of an IP-to-IP gateway:
- Interconnecting segments of the same or different VoIP networks using different signaling types, such as H.323 and SIP
- Interconnecting segments of the same or different VoIP networks using different media types
- Billing abilities
- Coder/decoder (codec) control
- Call admission control
- Security
Part I: Voice Gateways and Gatekeepers
Gateways and Gatekeepers
- Gateways and Gatekeepers
- The Role of Voice Gateways
- The Role of Voice Gatekeepers
- The Role of IP-to-IP Gateways
- Introduction to Voice Protocols
- Call Control Agents
- Deployment Scenarios
- Case Study: Introduction
- Chapter Review Questions
Part II: Gateways
Media Gateway Control Protocol
- Media Gateway Control Protocol
- Introduction to MGCP
- MGCP Operation
- Call Flow with MGCP
- Dial Plan Considerations
- Implementing MGCP Gateways
- Securing MGCP Gateways
- Troubleshooting Tools
- Case Study: Configuring an MGCP Gateway
- Review Questions
H.323
- H.323
- H.323 Specifications
- H.323 Network Components
- Call Flow
- H.323 Protocol Pros and Cons
- When to Use H.323
- Dial Plan Considerations
- Implementing H.323 Gateways
- Securing H.323 Gateways
- Troubleshooting Tools
- Case Study: Configuring an H.323 Gateway
- Review Questions
Session Initiation Protocol
- Session Initiation Protocol
- Description of SIP
- SIP Call Flow
- SIP Pros and Cons
- When to Use SIP
- Dial Plan Considerations
- Implementing SIP Gateways
- Securing SIP Gateways
- Allowing H.323 to SIP Connections
- Troubleshooting Tools
- Case Study: Configuring SIP Between a Gateway and CallManager 5.x
- Review Questions
Circuit Options
Connecting to the PSTN
- Connecting to the PSTN
- PSTN Circuit Selection Overview
- Analog Trunks
- Digital Trunks
- Case Study: Add an E1 R2 Connection to the Leeds Gateway
- Review Questions
Connecting to PBXs
- Connecting to PBXs
- Analog Trunks
- Digital Trunks
- Configuring Transparent Common Channel Signaling
- Case Study: Implementing a Cisco Voice Gateway at the Shanghai Office
- Review Questions
Connecting to an IP WAN
- Connecting to an IP WAN
- Applications for Connecting to an IP WAN
- Design Considerations
- Quality of Service
- Providing Fax and Modem Services
- Security
- Case Study: Using a T1 Link as a Tie Line
- Review Questions
Dial Plans
- Dial Plans
- Numbering Plans
- Overlapping Numbering Plans
- Building a Scalable Dial Plan
- Dial Peers
- Dial Peer Matching
- Case Study: Configuring PSTN Access
- Review Questions
Digit Manipulation
- Digit Manipulation
- Basic Digit Manipulation
- Number Expansion
- Voice Translation Rules and Profiles
- Manipulating Caller ID
- Order of Operation in Digit Manipulation
- Troubleshooting Digit Manipulation
- Case Study
- Review Questions
Influencing Path Selection
- Influencing Path Selection
- Hunt Groups
- Using Trunk Groups
- Tail-End Hop-Off
- Call Admission Control
- POTS-to-POTS Call Routing Considerations
- Case Study: Implementing Gateway-Controlled RSVP
- Review Questions
Configuring Class of Restrictions
- Configuring Class of Restrictions
- COR Overview
- COR Operation
- Implementing COR
- Assigning COR Lists with SRST
- Assigning COR Lists with Cisco CallManager Express
- Restricting Inbound Calls
- Case Study: Implementing COR for Miami
- Review Questions
SRST and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- SRST and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- SRST Overview
- Configuring SRST
- Dial Plan Considerations
- SRST Features
- SIP SRST
- Call Preservation
- Secure SRST
- MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Configuring MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Verifying and Troubleshooting SRST
- Verifying and Troubleshooting MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Case Study: Integrating SRST with an Analog Voice-Mail System
- Review Questions
DSP Resources
- DSP Resources
- Need for DSP Resources
- Determining the DSP Resources Required
- Configuring DSP Resources
- Transcoding for CallManager Express
- Case Study: Add DSP Resources to the Miami Gateway
- Review Questions
Using Tcl Scripts and VoiceXML
- Using Tcl Scripts and VoiceXML
- Tcl IVR and VoiceXML Application Overview
- Sample Applications
- Downloading Tcl Scripts from Cisco.com
- Configuring the Gateway to Use a Tcl Script
- Implementing the AA Tcl Script
- Creating Audio Files
- Restrictions and Caveats
- Case Study: Implementing ACD Application
- Review Questions
Part III: Gatekeepers
Deploying Gatekeepers
- Deploying Gatekeepers
- Gatekeeper Functionality
- Gatekeeper Signaling
- E.164 Number Resolution
- Call Admission Control
- Gatekeeper Deployment Models
- Gatekeepers with CallManager
- Security with Gatekeepers
- Review Questions
Gatekeeper Configuration
- Gatekeeper Configuration
- Configuring Basic Gatekeeper Functionality
- Multiple Gatekeeper Configurations
- Configuring Directory Gatekeepers
- Troubleshooting Gatekeepers
- CallManager and Gatekeepers
- Gatekeeper Redundancy
- Configuring Resource Availability Indicator
- Configuring Gatekeeper Security
- Case Study: Deploying Gatekeepers to Assist in Migration to VoIP
- Review Questions
Part IV: IP-to-IP Gateways
Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway
- Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway
- IP-to-IP Gateway Overview
- Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway
- Basic Configuration
- IP-to-IP Gateway Features
- Case Study: Providing Enterprise VoIP Trunking to VoIP Service of the Service Provider
- Review Questions
Appendix A. Answers to Chapter-Ending Review Questions
Index
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 218
