Refined Requirements for Online Photo Shop
5.2.1 Refined Use Case Diagram
|
The first task in refining the requirements is to reevaluate the use case diagram. Based on the initial requirements, analysis, and design decisions described in Chapter 4, we update the use case diagram as shown in Figure 5.1. |
Figure 5.1. Refined Use Case Diagram for Online Photo Shop
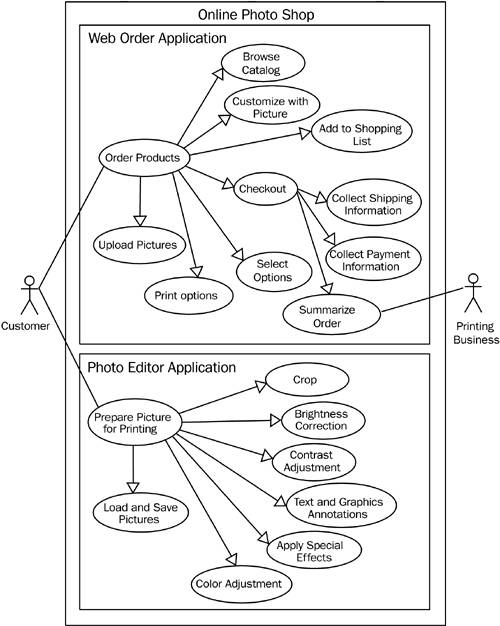
The refined use case diagram clearly distinguishes the different parts of Online Photo Shop, as discussed in Chapter 4. Online Photo Shop provides a Web-based interface for ordering products, whereas the photo editor application is used to edit pictures on the local computer. Because of that, the photo editor and the Web order application are in different processes. This also means that they are two independent applications and have no anticipated dependencies. In addition, the new diagram shows additional use cases for loading and saving pictures in the photo editor, as well as a use case for uploading images to the Web application.
5.2.2 Refined Requirements List
The next task is to update the requirements. In addition to adding the new requirements, it is important to put more details into the requirements. These extra details include pre- and postconditions, functional descriptions, and constraints. Refinement of requirements will not be finished in this iteration, but the goal is to put all details of the use cases known at this point into the requirements to support the following activities:
- Negotiating the deliverable functionality with the customer, including the constraints
- Analyzing the requirements and developing a good design for the implementation
- Planning the project and providing reasonably accurate effort estimates (the effort estimates will be refined throughout development)
- Enabling project management to develop an accurate contract agreement with the customer
Table 5.1 shows the refined requirements for the current iteration.
For the remainder of the book, we show only the requirements that are to be implemented in the described iteration. The alternative would be to refine all the requirements in the first construction iteration, but we have not chosen that approach for several reasons. First, it is easier to focus on the functionality that needs to be implemented in the specified iteration. Second, if requirements must be changed because of design or implementation issues, the changes usually will affect only the current iteration's requirements, and the requirements in later iterations can take all these changes into account from the beginning. (If complete planning is done up front, it is like the Waterfall model. Changes in later phases could trigger many changes.) For reference, the complete list of refined requirements can be found in the Requirement Specification XML file of each chapter on the accompanying CD.
The refined requirements include more details on the actual use case functionality and consider known constraints. In every iteration, we refine the requirements that are to be implemented in that iteration. This allows us to choose the best possible design and therefore the best possible implementation for the system.
|
Requirement |
Type |
Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
F:photo_editor |
Functional |
Customers shall be able to perform basic photo postprocessing on their digital images. The GUI shall be similar to the GUI model provided in the file PhotoEditorGUI.vsd. The GUI model shows the screen layout and the approximate position of the necessary buttons. The buttons to be used are not defined. The buttons should be chosen so that they can be used intuitively. |
|
F:error_handling |
Functional |
Errors shall be reported via exceptions. The exception-handling mechanism is based on the Microsoft Exception Management Application Block (described in detail later in this chapter) and needs to be extended to show error messages in a window on the screen. Every exception shall be displayed on the screen within a dialog window. A meaningful error message shall be displayed. For fatal errors, from which the application is not able to recover, the exception is written into the event log and the application is shut down. |
|
F:picture_load_and_save |
Functional |
It shall be possible to load pictures into the photo editor application, alter them, and save them either to the same or to a new file. An error message is displayed if the image format is not known (see also image_format). |
|
F:image_crop |
Functional |
If an image is loaded, then the photo editor shall provide functionality to select a region of interest and crop the image to that region. |
|
F:image_rotate |
Functional |
If an image is loaded, the photo editor shall be able to rotate an image by 90 degrees in both directions. |
|
F:image_flip |
Functional |
If an image is loaded, the photo editor shall be able to flip an image vertically and horizontally. |
|
F:image_format |
Functional |
The supported image formats are JPG and GIF. The supported image sizes range from 100 pixels to 2,048 pixels for both width and height. An error is reported if the image format is not known. |
|
C:platform_os |
Constraint |
The target platform operating system is Windows XP Professional. No special hardware requirement is necessary. |
Introducing .NET
- Introducing .NET
- The Need for .NET
- The .NET Framework
- The C# Language
- Debugging and the IDE
- References for Further Reading
Introducing Software Engineering
- Introducing Software Engineering
- Introducing Software Engineering Practices
- Choosing a Software Development Model
- Commonly Used Software Development Models
- Conclusion
- References for Further Reading
A .NET Prototype
- Getting Started
- Evaluating .NET for Windows Client Applications
- Our First .NET Application
- Prototyping
- Implementing the SmartNotes Application
- Visual Studio.NET: Platform of Choice
- References for Further Reading
Project Planning
- Project Planning
- The Project Vision and Business Case
- The Initial Use Case Model
- Project Requirements
- Initial Project Planning
- Initial Risk Analysis
- Initial Requirements Analysis and Design
- Conclusion
- References for Further Reading
The Photo Editor Application
- The Photo Editor Application
- The Refined Project Vision and Business Case
- Refined Requirements for Online Photo Shop
- Analysis of the Photo Editor Requirements
- Design of the Photo Editor Application
- The Detailed Project Schedule
- Implementation of the Photo Editor Application
- Unit Tests
- Conclusion
- References for Further Reading
GDI+ Graphics Extensions
- GDI+ Graphics Extensions
- Requirements for the GDI+ Extensions
- Analysis of the GDI+ Extensions Requirements
- Design of the GDI+ Extensions
- Project Management Issues
- GDI+ Programming
- Drawing GDI+ Primitives
- Unit Tests
- Conclusion
- References for Further Reading
Advanced GDI+ Operations
- Advanced GDI+ Operations
- Advanced GDI+ Extensions
- Analysis of the Advanced GDI+ Extensions Requirements
- Design of the Advanced GDI+ Extensions
- Project Management Issues
- Using Pens and Brushes in GDI+
- Implementation of Regions, Pens, and Brushes
- Unit Tests
- Conclusion
Dynamic Loading of Components
- Dynamic Loading of Components
- Requirements for Image Postprocessing Components
- Analysis of the Image Postprocessing Requirements
- Design of the Image-Processing Components Using Late Binding
- Project Management Issues
- Implementing Dynamically Loadable Image Postprocessing Plugins
- Unit Tests
- Conclusion
- References for Further Reading
Accessing System Resources
- Accessing System Resources
- Refining Requirements for 3D Text Display
- Three-Dimensional Rendering Technologies
- Analyzing User Interface Needs
- Using OpenGL.NET
- Adding 3D Text to the Photo Editor Application
- Conclusion: Dont Reinvent the Wheel
- References for Further Reading
Performance Optimization, Multithreading, and Profiling
- Performance Optimization, Multithreading, and Profiling
- Requirements for Performance Optimization
- Analysis of the Editor Optimization Requirement
- Design of the Optimizations
- Project Management Issues
- Multithreading and Optimization Implementation
- Unit Tests
- Conclusion
- References for Further Reading
Building the Web Application with ASP.NET
- Building the Web Application with ASP.NET
- Online Store Requirements
- Analyzing Interfaces and Activities
- Breakdown of the Code Modules
- Implementation of Online Photo Shop
- Conclusion
Security and Database Access
- Security and Database Access
- Secure Checkout
- Integrating Externally Supplied Software
- E-mail, Password, Credit Card: Creating a Customer Profile
- Secure Web Applications
- Database Access with ADO.NET
- Putting It All Together
- No Longer under Construction
- References for Further Reading
Product Release
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 123
