File System Information
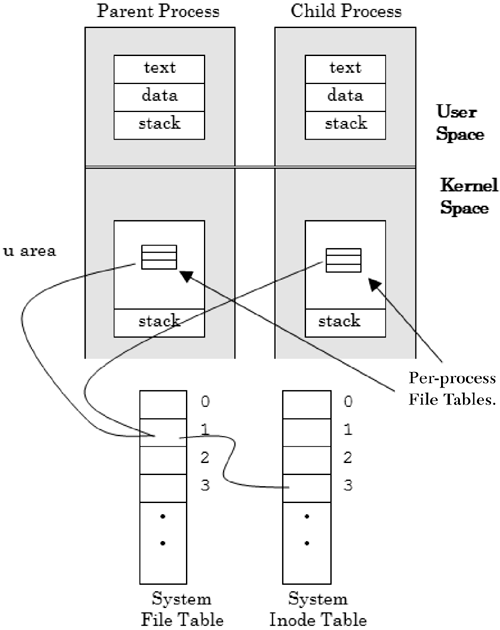
In addition to process ID information, the process environment contains file system information. Associated with each open file is an integer file descriptor value that the operating system uses as an index to a 1,024-entry file descriptor table located in the u ( user ) area for the process. The per-process file descriptor table references a system file table , which is located in kernel space. In turn , the system file table maps to a system inode table that contains a reference to a more complete internal description of the file.
When a child process is generated, it receives a copy of its parent's file descriptor table (this includes the three descriptors stdin , stdout , and stderr ) with the file pointer offset associated with each open file. If a file is marked as shareable, the operating system will need to save each file pointer offset separately. The relationship of process and system tables are shown in Figure 2.10.
Figure 2.10. Process/system file table relationships.
Programs and Processes
- Introduction
- Library Functions
- System Calls
- Linking Object Code
- Managing Failures
- Executable File Format
- System Memory
- Process Memory
- The u Area
- Process Memory Addresses
- Creating a Process
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Processing Environment
- Introduction
- Process ID
- Parent Process ID
- Process Group ID
- Permissions
- Real and Effective User and Group IDs
- File System Information
- File Information
- Process Resource Limits
- Signaling Processes
- Command-Line Values
- Environment Variables
- The /proc Filesystem
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Using Processes
- Introduction
- The fork System Call Revisited
- exec s Minions
- Using fork and exec Together
- Ending a Process
- Waiting on Processes
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Primitive Communications
- Introduction
- Lock Files
- Locking Files
- More About Signals
- Signal and Signal Management Calls
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Pipes
Message Queues
- Introduction
- IPC System Calls: A Synopsis
- Creating a Message Queue
- Message Queue Control
- Message Queue Operations
- A ClientServer Message Queue Example
- Message Queue Class
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Semaphores
- Introduction
- Creating and Accessing Semaphore Sets
- Semaphore Control
- Semaphore Operations
- Semaphore Class
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Shared Memory
- Introduction
- Creating a Shared Memory Segment
- Shared Memory Control
- Shared Memory Operations
- Using a File as Shared Memory
- Shared Memory Class
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Remote Procedure Calls
- Introduction
- Executing Remote Commands at a System Level
- Executing Remote Commands in a Program
- Transforming a Local Function Call into a Remote Procedure
- Debugging RPC Applications
- Using RPCGEN to Generate Templates and a MAKEFILE
- Encoding and Decoding Arbitrary Data Types
- Using Broadcasting to Search for an RPC Service
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Sockets
- Introduction
- Communication Basics
- IPC Using Socketpair
- Sockets: The Connection-Oriented Paradigm
- Sockets: The Connectionless Paradigm
- Multiplexing I/O with select
- Peeking at Data
- Out of Band Messages
- Summary
- Key Terms and Concepts
Threads
- Introduction
- Creating a Thread
- Exiting a Thread
- Basic Thread Management
- Thread Attributes
- Scheduling Threads
- Using Signals in Threads
- Thread Synchronization
- Thread-Specific Data
- Debugging Multithreaded Programs
- Summary
- Nomenclature and Key Concepts
Appendix A. Using Linux Manual Pages
Appendix B. UNIX Error Messages
Appendix C. RPC Syntax Diagrams
Appendix D. Profiling Programs
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 136
