Preventing Call Forward and Voice-Mail Toll Fraud Using Calling Search Spaces
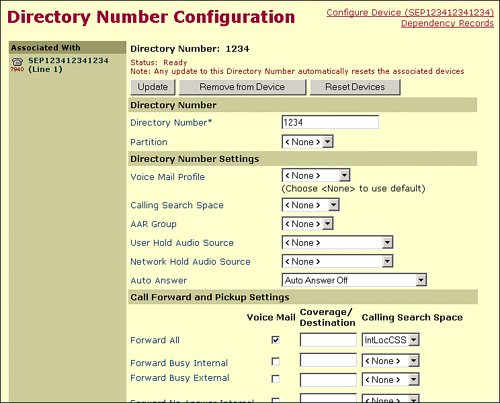
Call Forward All (CFA) is a feature in Cisco CallManager that allows an internal number (for example, an employee office number) to be forwarded to an external number (for example, an international number, mobile number, or premium number). For example, an employee can call the office number, which is then forwarded to the number specified in the forwarding field. This number can be an international or premium number. The user can configure the setting using the web interface, so the forwarding configuration can be set up and removed very easily from home or elsewhere. CFA exploits can be avoided by applying a calling search space to the CFA feature. As shown in Figure 22-2, the administrator has applied a calling search space named IntLocCSS (which allows only internal and local PSTN calls) to the CFA field.
Figure 22-2. Restricting Call Forward All
Note
The only call forwarding ability available to the user (from either the CCMUser pages or the IP phone) is Call Forward All. By applying the calling search space to only this field, you have effectively restricted user forwarding.
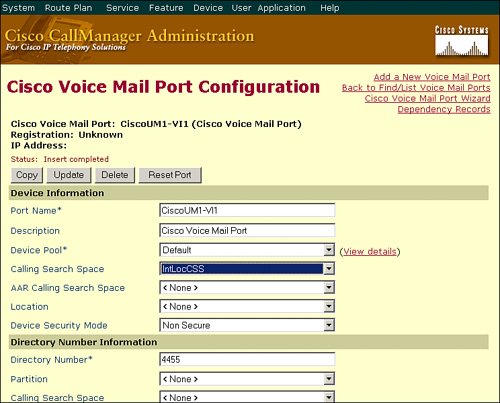
Voice-mail systems, which can transfer a call to an extension, can be misused in a similar way if they are configured to allow transfer of calls when the called party is not available. If such transfers are not limited, a caller could connect to the voice-mail system by a local call and then transfer to the public telephony network (for example, a long-distance number). Voice-mail forwarding exploits can be avoided by applying a calling search space to the voice-mail port in the Cisco CallManager configuration. As shown in Figure 22-3, the administrator has applied the same IntLocCSS calling search space to the voice-mail port.
Figure 22-3. Restricting Voice-Mail Forwarding
Blocking Commonly Exploited Area Codes |
Part I: Cisco CallManager Fundamentals
Introduction to Cisco Unified Communications and Cisco Unified CallManager
Cisco Unified CallManager Clustering and Deployment Options
- Cisco Unified CallManager Clustering and Deployment Options
- The Two Sides of the Cisco Unified CallManager Cluster
- Cluster Redundancy Designs
- Call-Processing Deployment Models
- Summary
- Review Questions
Cisco Unified CallManager Installation and Upgrades
- Cisco Unified CallManager Installation and Upgrades
- Cisco Unified CallManager 4.x Clean Installation Process
- Upgrading Prior Cisco Unified CallManager Versions
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part II: IPT Devices and Users
Cisco IP Phones and Other User Devices
Configuring Cisco Unified CallManager to Support IP Phones
- Configuring Cisco Unified CallManager to Support IP Phones
- Configuring Intracluster IP Phone Communication
- IP Phone Configuration
- Case Study: Device Pool Design
- Summary
- Review Questions
Cisco IP Telephony Users
- Cisco IP Telephony Users
- Cisco CallManager User Database
- Cisco CallManager User Configuration
- User Logon and Device Configuration
- Summary
- Review Questions
Cisco Bulk Administration Tool
- Cisco Bulk Administration Tool
- The Cisco Bulk Administration Tool
- Using the Tool for Auto-Registered Phone Support
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part III: IPT Network Integration and Route Plan
Cisco Catalyst Switches
- Cisco Catalyst Switches
- Catalyst Switch Role in IP Telephony
- Powering the Cisco IP Phone
- Data and Voice VLANs
- Configuring Class of Service
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Cisco Gateways and Trunks
- Configuring Cisco Gateways and Trunks
- Cisco Gateway Concepts
- Configuring Access Gateways
- Cisco Trunk Concepts
- Configuring Intercluster Trunks
- SIP and Cisco CallManager
- Summary
- Review Questions
Cisco Unified CallManager Route Plan Basics
- Cisco Unified CallManager Route Plan Basics
- External Call Routing
- Route Plan Configuration Process
- Summary
- Review Questions
Cisco Unified CallManager Advanced Route Plans
- Cisco Unified CallManager Advanced Route Plans
- Route Filters
- Discard Digit Instructions
- Transformation Masks
- Translation Patterns
- Route Plan Report
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Hunt Groups and Call Coverage
- Configuring Hunt Groups and Call Coverage
- Call Distribution Components
- Configuring Line Groups, Hunt Lists, and Hunt Pilots
- Summary
- Review Questions
Implementing Telephony Call Restrictions and Control
- Implementing Telephony Call Restrictions and Control
- Class of Service Overview
- Partitions and Calling Search Spaces Overview
- Time-of-Day Routing Overview
- Configuring Time-of-Day Routing
- Time-of-Day Routing Usage Scenario
- Summary
- Review Questions
Implementing Multiple-Site Deployments
- Implementing Multiple-Site Deployments
- Call Admission Control
- Survivable Remote Site Telephony
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part IV: VoIP Features
Media Resources
- Media Resources
- Introduction to Media Resources
- Conference Bridge Resources
- Media Termination Point Resources
- Annunciator Resources
- Transcoder Resources
- Music on Hold Resources
- Media Resource Management
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring User Features, Part 1
- Configuring User Features, Part 1
- Basic IP Phone Features
- Softkey Templates
- Enhanced IP Phone Features
- Barge and Privacy
- IP Phone Services
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring User Features, Part 2
- Configuring User Features, Part 2
- Cisco CallManager Extension Mobility
- Client Matter Codes and Forced Authentication Codes
- Call Display Restrictions
- Malicious Call Identification
- Multilevel Precedence and Preemption
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Cisco Unified CallManager Attendant Console
- Configuring Cisco Unified CallManager Attendant Console
- Introduction to Cisco CallManager Attendant Console
- Call Routing and Call Queuing
- Server and Administration Configuration
- Cisco Attendant Console Features
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Cisco IP Manager Assistant
- Configuring Cisco IP Manager Assistant
- Cisco IP Manager Assistant Overview
- Cisco IP Manager Assistant Architecture
- Configuring Cisco IPMA for Shared-Line Support
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part V: IPT Security
Securing the Windows Operating System
- Securing the Windows Operating System
- Threats Targeting the Operating System
- Security and Hot Fix Policy
- Operating System Hardening
- Antivirus Protection
- Cisco Security Agent
- Administrator Password Policy
- Common Windows Exploits
- Security Taboos
- Summary
- Review Questions
Securing Cisco Unified CallManager Administration
- Securing Cisco Unified CallManager Administration
- Threats Targeting Remote Administration
- Securing CallManager Communications Using HTTPS
- Multilevel Administration
- Summary
- Review Questions
Preventing Toll Fraud
- Preventing Toll Fraud
- Toll Fraud Exploits
- Preventing Call Forward and Voice-Mail Toll Fraud Using Calling Search Spaces
- Blocking Commonly Exploited Area Codes
- Using Time-of-Day Routing
- Using FAC and CMC
- Restricting External Transfers
- Dropping Conference Calls
- Summary
- Review Questions
Hardening the IP Phone
Understanding Cryptographic Fundamentals
- Understanding Cryptographic Fundamentals
- What Is Cryptography?
- Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
- Hash Functions
- Digital Signatures
- Summary
- Review Questions
Understanding the Public Key Infrastructure
- Understanding the Public Key Infrastructure
- The Need for a PKI
- PKI as a Trusted Third-Party Protocol
- PKI Entities
- PKI Enrollment
- PKI Revocation and Key Storage
- PKI Example
- Summary
- Review Questions
Understanding Cisco IP Telephony Authentication and Encryption Fundamentals
- Understanding Cisco IP Telephony Authentication and Encryption Fundamentals
- Threats Targeting the IP Telephony System
- How CallManager Protects Against Threats
- PKI Topologies in Cisco IP Telephony
- PKI Enrollment in Cisco IP Telephony
- Keys and Certificate Storage in Cisco IP Telephony
- Authentication and Integrity
- Encryption
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Cisco IP Telephony Authentication and Encryption
- Configuring Cisco IP Telephony Authentication and Encryption
- Authentication and Encryption Configuration Overview
- Enabling Services Required for Security
- Using the CTL Client
- Working with Locally Significant Certificates
- Configuring the Device Security Mode
- Negotiating Device Security Mode
- Generating a CAPF Report
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part VI: IP Video
Introducing IP Video Telephony
- Introducing IP Video Telephony
- IP Video Telephony Solution Components
- Video Call Concepts
- Video Protocols Supported in Cisco CallManager
- Bandwidth Management
- Call Admission Control Within a Cluster
- Call Admission Control Between Clusters
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Cisco VT Advantage
- Configuring Cisco VT Advantage
- Cisco VT Advantage Overview
- How Calls Work with Cisco VT Advantage
- Configuring Cisco CallManager for Video
- Configuring Cisco IP Phones for Cisco VT Advantage
- Installing Cisco VT Advantage on a Client
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part VII: IPT Management
Introducing Database Tools and Cisco Unified CallManager Serviceability
- Introducing Database Tools and Cisco Unified CallManager Serviceability
- Database Management Tools
- Cisco CallManager Serviceability Overview
- Tools Overview
- Summary
- Review Questions
Monitoring Performance
- Monitoring Performance
- Performance Counters
- Microsoft Event Viewer
- Microsoft Performance Monitor
- Real-Time Monitoring Tool Overview
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring Alarms and Traces
- Configuring Alarms and Traces
- Alarm Overview
- Alarm Configuration
- Trace Configuration
- Trace Analysis
- Trace Collection
- Bulk Trace Analysis
- Additional Trace Tools
- Summary
- Review Questions
Configuring CAR
- Configuring CAR
- CAR Overview
- CAR Configuration
- Report Scheduling
- System Database Configuration
- User Report Configuration
- Summary
- Review Questions
Using Additional Management and Monitoring Tools
- Using Additional Management and Monitoring Tools
- Remote Management Tools
- Dependency Records
- Password Changer Tool
- Cisco Dialed Number Analyzer
- Quality Report Tool
- Summary
- Review Questions
Part VIII: Appendix
Appendix A. Answers to Review Questions
Index
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 329
- Chapter I e-Search: A Conceptual Framework of Online Consumer Behavior
- Chapter II Information Search on the Internet: A Causal Model
- Chapter X Converting Browsers to Buyers: Key Considerations in Designing Business-to-Consumer Web Sites
- Chapter XI User Satisfaction with Web Portals: An Empirical Study
- Chapter XVII Internet Markets and E-Loyalty
