Main Windows of the SAS Windowing Environment
Main Windows of the SAS Windowing Environment
List of SAS Windows and Window Commands
The basic SAS windows are the Explorer, Results, Program Editor, Log, and Output windows, but there are more than thirty other windows to help you with such things as printing and fine-tuning your SAS session.
The following table lists all portable SAS windows and the commands that open them.
| Note | Additional information about how many of these windows work can be found by clicking the help button inside each window. |
| Window Name | Window Command(s) |
|---|---|
| Define a new previewer "Defining a New Previewer" on page 266 | DMPRTCREATE PREVIEWER |
| Define a new printer"Defining a New Printer" on page 256 | DMPRTCREATE PRINTER |
| Distributed Multidimensional Metadata | MDMDDB* |
| Documents | ODSDOCUMENTS |
| Explorer | ACCESS, BUILD, CATALOG, DIR, EXPLORER, FILENAME, LIBNAME, V6CAT, V6DIR, V6FILENAME, V6LIBNAME |
| Explorer Options | DMEXPOPTS |
| EFI (External File Interface) | EFI* |
| File Shortcut Assignment | DMFILEASSIGN |
| Find | EXPFIND |
| Font (host-specific) | DLGFONT* |
| Footnotes | FOOTNOTES |
| FSBrowse | FSBROWSE |
| FSEdit | FSEDIT |
| FSForm | FSFORM formname |
| FSLetter | FSLETTER |
| FSList | FSLIST |
| FSView | FSVIEW |
| Help | HELP |
| Keys | KEYS |
| Log | LOG |
| Metadata Browser | METABROWSE* |
| Metafind | METAFIND |
| Metadata Server Connections | METACON |
| My Favorite Folders | EXPROOT FILES* |
| New Library | DMLIBASSIGN |
| Notepad | NOTEPAD, NOTE, FILEPAD filename |
| Options (SAS system options) | OPTIONS |
| Output | OUTPUT, OUT, LISTING, LIST, LST |
| Page Setup | DMPAGESETUP |
| Password | SETPASSWORD (followed by a two-level data set name) |
| Preferences (host-specific) | DLGPREF* |
| | DMPRINT |
| Print Setup | DMPRTSETUP |
| Printer Properties | DMPRTPROPS |
| Program Editor | PROGRAM, PGM |
| Properties | VAR libref.SAS-data-set , V6VAR libref.SAS-data-set |
| Query | QUERY |
| Registry Editor | REGEDIT |
| Results | ODSRESULTS |
| SAS/AF | AF, AFA |
| SAS/ASSIST | ASSIST |
| SASCOLOR | SASCOLOR |
| SAS/EIS* | EIS |
| System Options | OPTIONS |
| Templates | ODSTEMPLATES |
| Titles | TITLES |
| Tool Editor (host-specific) | TOOLEDIT* |
| Viewtable | VIEWTABLE, VT |
Window commands marked with * are not supported under z/OS.
| Note | Some additional SAS windows that are specific to your operating environment may also be available. Refer to the SAS documentation for your operating environment for more information. |
The Five Main Windows in the Windowing Environment
Overview
The five main windows in SAS are: Explorer, Results, Program Editor, Log, and Output windows.
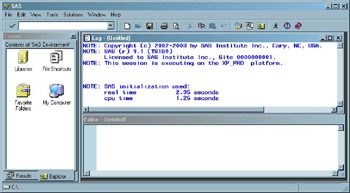
Display 18-7: Default View of SAS Windowing Environment (Microsoft Windows)
Operating Environment Information: The arrangement of your SAS windows depends on your operating environment. For example, in the Microsoft Windows operating environment, the Editor window appears instead of the Program Editor.
SAS Explorer Window
| Use to | View, add or delete files, libraries, shortcuts. |
| Open by | Typing EXPLORER in the command line, or select |
| Description | The Explorer window enables you to manage your files in the windowing environment. You can use the SAS Explorer to do the following tasks :
|
You can display the Explorer window with or without a tree view of its contents.
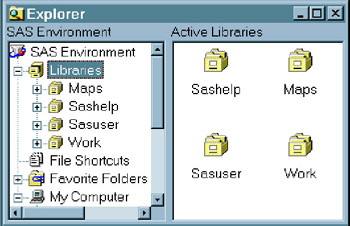
Display 18-8: SAS Explorer, with Tree View, Microsoft Windows Operating Environment
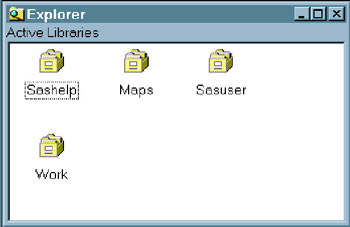
Display 18-9: SAS Explorer, Without Tree View, Microsoft Windows Operating Environment
| Note | You can resize the Explorer window by dragging an edge or a corner of the window. You can resize the left and right panes of the Explorer window by clicking the split bar between the two panes and dragging it to the right or left. |
Exploring Files with the SAS Explorer
You can use the SAS Explorer to explore and manage SAS files and other files. In the Explorer window, you can view and manage your SAS files, which are stored in libraries. A library is a storage location for SAS files and catalogs. By default, SAS defines several libraries for you.
This example uses the SAS Explorer to display the contents of a library:
-
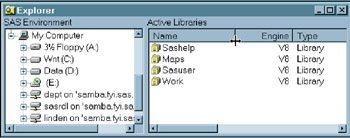
In the Explorer window, double-click Libraries . The active libraries are listed.
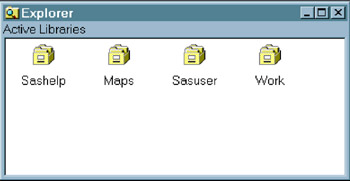
Display 18-10: Typical Explorer Window, Without Tree View, Showing Active Libraries -
Double-click the Sashelp library. All members of the Sashelp library are listed.
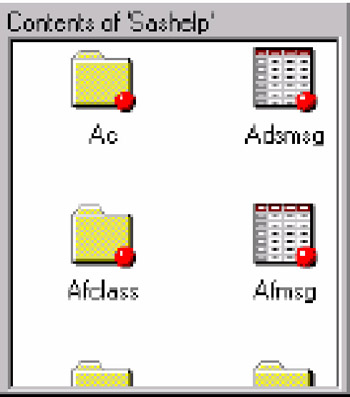
Display 18-11: Explorer Window, Without Tree View, Showing the Contents of a Sashelp Library -
Move back up to the top level of the Explorer window by clicking twice on the Up One Level selection under View on the toolbar.
Using SAS Explorer to Assign File Shortcuts ( filerefs )
A file shortcut is also known as a file reference or fileref. Filerefs save you programming time by enabling you to assign a nickname to a commonly used file. You can use the FILENAME statement to create a fileref or you can use the file shortcut assignment window from SAS Explorer.
The following example shows you how to create a file shortcut with SAS Explorer.
-
In the top level of the Explorer window, select File Shortcuts .
-
Select

The File Shortcut Assignment window appears.
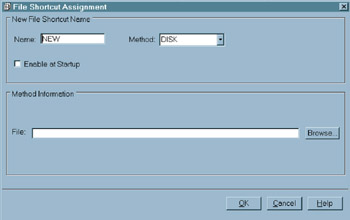
Display 18-12: File Shortcut Assignment Window -
Type a name in the Name field (up to eight alphanumeric characters ). This name is the file shortcut reference (fileref), and you can use it to point to an external file.
-
Select the Method that you want to use for the file shortcut. The devices that are available from the Method drop-down list depend on your operating environment. DISK is the default (if available for your operating environment). See your operating environment documentation for more information.
-
Select Enable at Startup if you want SAS to automatically assign the file shortcut each time that SAS starts. This option is not available for all file shortcut methods . If it is not available, the Enable at Startup check box is disabled. If you want to stop a file shortcut from being enabled at startup, select the file shortcut in the SAS Explorer window, and then select Delete from the pop-up menu.
-
Fill in the fields of the Method Information area. The fields available in this area depend on the method that you selected.
Note Selecting a new method type erases any entries that you may have made in the Method information field.
-
Select
 to create the new file shortcut. The file shortcut appears in the File Shortcut folder of the SAS Explorer window.
to create the new file shortcut. The file shortcut appears in the File Shortcut folder of the SAS Explorer window.
Using SAS Explorer to Copy a SAS Data Set
This example shows you how to copy a data set called Prdsale, which is a sample data file included when you install SAS software.
-
Open the Explorer window by selecting
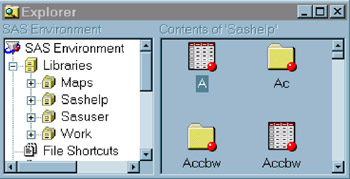
Display 18-13: SAS Explorer in Tree View Mode, Showing Some Members of a Sashelp Library -
In the left pane, single-click the Sashelp library to show the library contents in the right pane. Scroll to the icon for the Prdsale data set.
-
Right-click the Prdsale data set.
-
Select Copy from the menu.
-
Right-click the Work Library.
-
Select Paste from the menu.
-
The Prdsale data set appears in the contents of the Work Library.
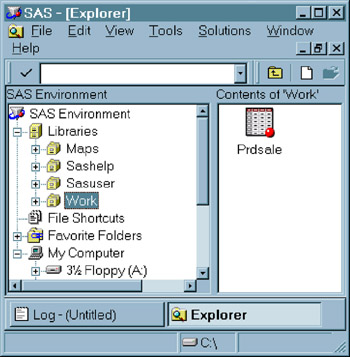
Display 18-14: SAS Explorer In Tree View Mode, Showing a File in a Work Library
Because the contents of the Work library are temporary, this copy of the Prdsale data set will be deleted when you end your SAS session.
Using SAS Explorer to Rename a File
You can use SAS Explorer to rename anything in a SAS library that is not write protected. This set of instructions outlines how to use SAS Explorer to rename a data set:
-
Open SAS Explorer and click on a library. A list of files in the library appears.
-
Select the file you want to rename and right-click it. A pop-up menu appears.
-
Select Rename from the pop-up menu. A Rename window appears, containing the name of the file you selected, and a blank space for typing in the new name.
-
Type in the new name and click
 .
.
| Note | Changing a file name may cause a SAS program that uses the old file name to stop working. |
Using SAS Explorer to View Details about Files
You can use the View menu to view the contents of a library with large icons or small icons, as a list, and with details displayed. This example shows you how use Explorer to view the details for the Sashelp.Prdsale data set.
-
Open the Sashelp library.
-
Select
 from the menu. Information about the files is displayed.
from the menu. Information about the files is displayed. Note The DETAILS system option controls how many details you can see about a data set. If you enable the DETAILS system option, you can see additional row and column information in the Explorer window. & pound ;
-
Resize the Details columns by moving the pointer over the separator bar between the detail fields. When the pointer changes to a resizing tool, click and drag the separator bar to get the desired size .
Display 18-15: Explorer Window with Pointer in Position (between Name and Engine) to Resize Columns. DETAILS Option Set to NODETAILS
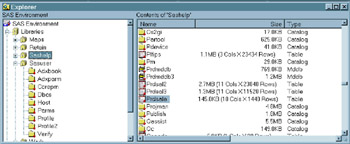
Display 18-16: Explorer Window with DETAILS Option Enabled
For more information about the DETAILS system option, see the SAS Language Reference: Dictionary .
Using SAS Explorer to Sort Files
Files in the Explorer window are sorted alphabetically by file name. You can sort by any column in ascending or descending order:
-
Open the Sashelp library.
-
Click the Type column to sort the files by file type.
-
Click the Type column again to reverse the sort order.
-
To return the files to their original order, select

Using SAS Explorer to Open a File
You can view the contents of SAS files directly from the Explorer window:
-
Double-click the Sashelp library.
-
Find the Prdsale data set in the list and double-click it to open it. The table opens in the VIEWTABLE window in browse mode.
-
When you are finished looking at the data in the data set, select
 from the VIEWTABLE window.
from the VIEWTABLE window. -
Return to the top level of the Explorer window.
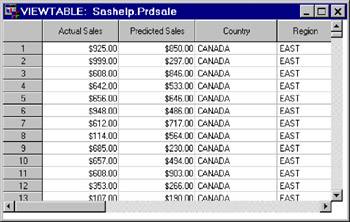
Display 18-17: Viewtable Window Displaying a Data Set
Using SAS Explorer and NOTEPAD to Create and Save a Program
In addition to the NOTEPAD, which is described here, you can also use the Program Editor (or Editor in some operating systems) to create and save programs. You can also use NOTEPAD and the Program Editor to work on two programs in the same session.
The following set of instructions shows you how to create and save a SAS program:
-
In the top level of the Explorer window, select

-
Select Source Program , and click
 . The NOTEPAD window appears.
. The NOTEPAD window appears. -
Type the following program into the NOTEPAD window:
proc options; run;
-
Select

As a result, the Log window lists the settings for your system options.
-
Select
-
With the default directory selected, type sysopt.sas in the File name box.
-
Click
 or
or  .
.
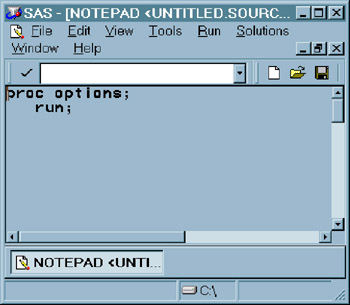
Display 18-18: SAS Notepad, with a Program
To recall and run the program that you just saved, follow this set of instructions:
-
Select

-
From the menu, select the library where you saved your program, if that library is not already available.
-
Select sysopt.sas (the program you just saved) from the menu. The program appears in NOTEPAD.
-
Select

Program Editor Window
| Purpose | Compose, edit, and submit SAS programs. |
| To open | Type PROGRAM in a command line, or select |
| Details | In the Program Editor window, you can enter, edit, and submit SAS programs. To open your SAS programs in the SAS windowing environment, you can drag and drop them onto the Program Editor window. |
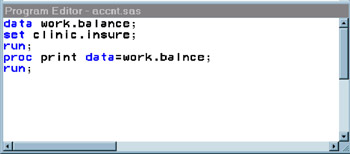
Display 18-19: Program Editor Window, with a Sample Program
This set of instructions shows you how to use the Program Editor to create and save a SAS program, submit the program, and view and save your results.
Create and Save a Program
-
In the top level of the Explorer window, select

-
Select Source Program and click
 .
. -
Type the following program into the Editor or Program Editor window:
proc datasets lib=sasuser; run; quit;
-
This program prints a listing of the contents of the SASUSER library (or to the log on z/OS).
-
Click
 to run the program.
to run the program. -
Click
 to save the program.
to save the program. -
Type a name and select a location for the file in the Save as window.
Operating Environment Information: In the Microsoft Windows operating environment, the Results window is docked along with the Explorer window. When a program produces output, the Results window comes to the front and overlays the Explorer window.
Log Window
| Purpose | View messages about your SAS session and SAS programs. | ||
| To open | Type LOG in a command line, or select | ||
| Details |
| Note | To keep the lines of your log from wrapping when your window is maximized, use the LINESIZE= system option. |
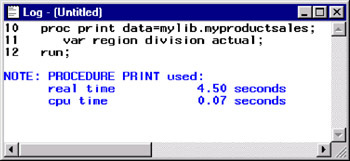
Display 18-20: Log Window
Output Window
| Purpose | View the output of SAS programs | ||
| To open | Type OUTPUT in a command line, or type LISTING in a command line, or select | ||
| Details |
| Note | To keep the lines of your output from wrapping when your window is maximized, use the LINESIZE= system option. |
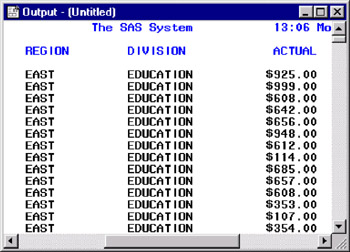
Display 18-21: Output Window
Results Window
| Purpose | View the output from running a SAS program. |
| To open | Type ODSRESULTS in a command line, or select |
| Details | The Results window uses a tree structure to display various types of output that you may have while you are running SAS. You can view, save, and print individual items of output. By default, the Results window is positioned behind the Explorer window and it is empty until you submit a SAS program that creates output. Then the Results window moves to the front of your display. |
To use the Results window, you first run a SAS program that generates output. You can run any SAS program that creates output, such as the following program, which creates a graph with PROC PLOT.
options linesize=80; data generate; do x=0 to 100 by 2; y=2.54+3.83*x; output; end; run; proc plot data=generate; plot y*x; run;
After running a program that produces output, the results window adds a line indicating that the output was successfully generated. You can then select this output from the Results Window and view it.
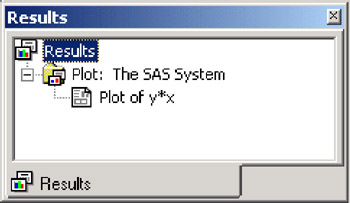
Display 18-22: Results Window, Showing an Output List
New Library Window
| Purpose | Assign a new library. |
| To open | Type DMLIBASSIGN in a command line, or from the Explorer window, select |
| Details | The New Library Window makes it easy to create libraries. After you create a new library, you can use SAS Explorer to associate SAS files, such as data sets, catalogs, and programs, with the library. By default, SAS software defines several libraries for you (including Sashelp, Sasuser, and Work). |
When you define a library, you specify a location for your SAS files. When you undefine a SAS library, SAS no longer has access to the contents of the library. However, the contents of the library still exist in your operating environment. After you create a library, you can manage SAS files within it.
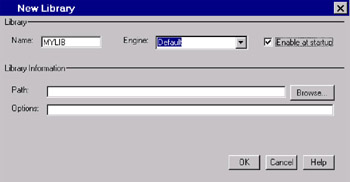
Display 18-23: New Library Window
Operating Environment Information: Depending on your operating environment, you can create libraries using engines that allow you to read different file formats, including file formats from other vendors .
Using the New Library Window to Assign a New Library
-
In the Explorer window, double-click Libraries .
-
From the Explorer menu, select
-
In the New Library window, type Mylib for the name, and leave the Default engine selected.
-
Select Enable at startup so that the library is created each time you start SAS.
-
Click
 and select a directory to use for this library. In the Select dialog you must open the directory you want to use so that the full path into that directory is assigned. Click
and select a directory to use for this library. In the Select dialog you must open the directory you want to use so that the full path into that directory is assigned. Click  .
. -
Click
 to assign the library. Mylib appears in the Active Libraries list.
to assign the library. Mylib appears in the Active Libraries list.
Properties Window
| Purpose | View and change the properties of a data set. |
| To open | Type VAR in the command line, followed by the name of the data set that you want to open, in the form of libref.SAS-data-set ,or right-click on a data set from the SAS Explorer window and select Properties . |
| Details | When you open the Properties window, you can select tabs that give you additional information about the data set. |
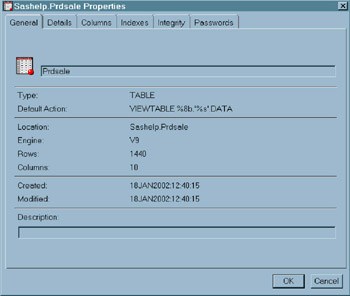
Display 18-24: Properties Window Displaying the Details for Sashelp.Prdsale. Select Other Tabs for More Information.
Keys Window
| Purpose | Change or create new keyboard commands. |
| To open | Type KEYS in a command line, or select |
| Details | The Keys window displays function key definitions for the current window. Default function key settings are provided with the SAS System, but you can easily add, edit, or delete them. |
To add new function key definitions:
-
After opening the Keys window, place your cursor next to the key you want to assign to a command. Make sure your cursor is under the Definition column.
-
Type the name of the command you want to assign.
-
Click
 to save your changes.
to save your changes.
To change existing key functions:
-
Type over the command that is already assigned to a particular key with the name of a new function.
-
Click
 to save your changes.
to save your changes.
To delete key functions:
-
Type over the command that is already assigned to a particular key.
-
Save the Keys window.
Valid Commands in the Keys Window
In the Keys window you can use these commands:
-
SAS windows commands
-
the Color, Search, Scrolling, Text Store, Window Management, and Window Size and Position commands.
In addition, you can use the following commands:
| Command | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CANCEL | Cancels any changes made to the current key settings and closes the Keys window. | ||
| COPY < name > |
| Note | If you change a key definition in the current Keys window and then save the Keys window, you must close and reopen the Keys window before issuing the COPY command. |
END
Saves the definitions and closes the Keys window.
PURGE
Removes key definitions that are not shared among devices.
SAVE < name >
Stores the current function key settings and lets you continue editing the keys definitions. If < name > is omitted, the keys are, by default, stored in the catalog SASUSER.PROFILE.
See SAS Help and Documentation for more information about commands.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 258