Section 5.8. Moving Data Between Documents
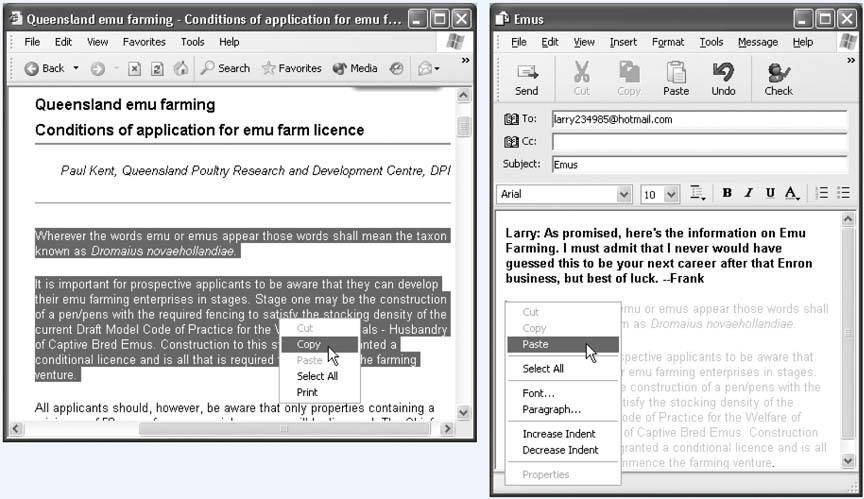
5.8. Moving Data Between DocumentsYou can't paste a picture into your Web browser, and you can't paste MIDI music information into your word processor. But you can put graphics into your word processor, paste movies into your database, insert text into Photoshop, and combine a surprising variety of seemingly dissimilar kinds of data. And you can transfer text from Web pages, email messages, and word processing documents to other email and word processing files; in fact, that's one of the most frequently performed tasks in all of computing. 5.8.1. Cut, Copy, and PasteYou can cut and copy highlighted material in any of three ways. First, you can use the Cut and Copy commands in the Edit menu; second, you can press Ctrl+X (for Cut) or Ctrl+C (for Copy); and third, you can right-click the highlighted material and choose Cut or Copy from the shortcut menu, as shown in Figure 5-4. When you do so, the PC memorizes the highlighted material, socking it away on an invisible storage pad called the Clipboard. If you choose Copy, nothing visible happens; if you choose Cut, the highlighted material disappears from the original document. At this point, you must take it on faith that the Cut or Copy command actually worked. Pasting copied or cut material, once again, is something you can do either from a menu (choose Edit The most recently cut or copied material remains on your Clipboard even after you paste, making it possible to paste the same blob repeatedly. Such a trick can be useful when, for example, you've designed a business card in your drawing program and want to duplicate it enough times to fill a letter- sized printout. On the other hand, whenever you next copy or cut something, whatever was previously on the Clipboard is lost forever. Figure 5-4. Suppose you want to email some text on a Web page to a friend. Start by dragging through it and then choosing Copy from the shortcut menu (or choosing Edit |
| UP TO SPEED Text-Selection Fundamentals |
| Before doing almost anything to text in a word processor, like making it bold, changing its typeface, or moving it to a new spot in your document, you have to highlight the text you want to affect. For millions of people, this entails dragging the cursor extremely carefully, perfectly horizontally, across the desired text. And if they want to capture an entire paragraph or section, they click at the beginning, drag very carefully diagonally, and release the mouse button when they reach the end of the passage. That's all fine, but because selecting text is the cornerstone of every editing operation in a word processor, it's worth learning some of the faster and more precise ways of going about it. For example, double-clicking a word highlights it, instantly and neatly. In fact, by keeping the mouse button pressed on the second click, you can now drag horizontally to highlight text in crisp one-word chunksa great way to highlight text more quickly and precisely. These tricks work anywhere you can type. In most programs, including Microsoft's, additional shortcuts await. For example, triple-clicking anywhere within a paragraph highlights the entire paragraph. (Once again, if you keep the button pressed at the end of this maneuver, you can then drag to highlight your document in one-paragraph increments .) In many programs, including Word and WordPad, you can highlight exactly one sentence by clicking within it while pressing Ctrl. Finally, here's a universal trick that lets you highlight a large blob of text, even one that's too big to fit on the current screen. Start by clicking to position the insertion point cursor at the very beginning of the text you want to capture. Now scroll, if necessary, so that the ending point of the passage is visible. Shift-click there. Windows instantly highlights everything that was in between your click and your Shift-click. |
5.8.2.1. Drag-and-drop to the desktop
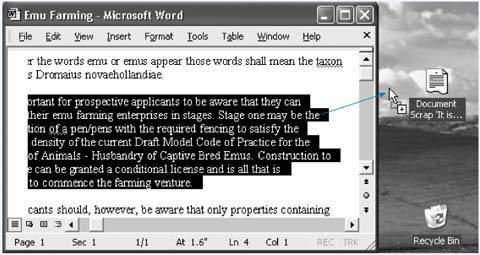
Figure 5-6 demonstrates how to drag text or graphics out of your document windows and directly onto the desktop. There, your dragged material becomes an icona Scrap file .
Figure 5-6. A Scrap file will appear when you drag material out of the document window and onto the desktop. Its icon depends on the kind of material contained within, as shown here at left.
When you drag a clipping from your desktop back into an application window, the material in that clipping reappears. Drag-and-drop, in other words, is a convenient and powerful feature; it lets you treat your desktop itself as a giant, computer-wide pasteboardan area where you can temporarily stash pieces of text or graphics as you work.
You can drag a Scrap file onto a document's taskbar button, too. Don't release the mouse button yet. In a moment, the corresponding document window appears, so that you can continue your dragging operation until the cursor points to where you want the Scrap file to appear. Now release the mouse; the Scrap material appears in the document.
Tip: Like any icon, you can rename a Scrap file to remind yourself what's in it. But if you forget, simply double-click it to open it in its original program.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 162
 Paste), by right-clicking and choosing Paste from the shortcut menu, or from the keyboard (press Ctrl+V).
Paste), by right-clicking and choosing Paste from the shortcut menu, or from the keyboard (press Ctrl+V).