| In most of the examples in this chapter, we have used print statements or some other simplistic method to display data. However, Visual Basic has always allowed some type of automatic data binding, or associating a set of records with controls on a form. The controls in Visual Basic .NET (such as the DataGrid) are designed for use with ADO.NET. Fortunately, you can take advantage of the fact that XML is a shared format between the older ADO Recordset and ADO.NET DataSet. In this section, we will perform a simple exercise used to display an ADO Recordset in a DataGrid control. To begin, you'll need to have the Membership database created in a database and be able to successfully connect to it as described throughout this chapter. Next, start a new Windows Application and begin following the steps. -
Using the procedure described earlier, add a reference to Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.7 to your project. -
Add three Button controls to the form. Set their Name properties to btnLoadRecordset, btnWriteDataSet, and btnLoadDataSet. Set their Text properties to Load Recordset, Write DataSet, and Load DataSet. -
Add a DataGrid control to the form. Set its Name property to grdPersonList. -
Add the code from Listing 21.6 to the form. Listing 21.6 ADOGRID.ZIP Converting a Recordset to a DataSet Private dsPerson As DataSet Private Sub btnLoadRecordset_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnLoadRecordset.Click Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset rs = New ADODB.Recordset() rs.CursorType = ADODB.CursorTypeEnum.adOpenStatic rs.Open("Select * from Person",_ "Server=localhost;UID=sa;pwd=;Database=BrianTest;Provider=SQLOLEDB") If System.IO.File.Exists("c:\temprs.xml") Then System.IO.File.Delete("c:\temprs.xml") End If rs.Save("c:\temprs.xml", ADODB.PersistFormatEnum.adPersistXML) dsPerson = New DataSet() dsPerson.ReadXml("c:\temprs.xml", XmlReadMode.InferSchema) grdPersonList().DataSource = dsPerson grdPersonList().DataMember = "row" messagebox.Show("The grid has been loaded from the database using ADO.") End Sub Private Sub btnWriteDataSet_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object,_ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnWriteDataSet.Click If System.IO.File.Exists("c:\tempds.xml") Then system.IO.File.Delete("c:\tempds.xml") End If dsPerson.WriteXml("C:\tempds.xml") messagebox.Show("The contents of the dataset bound to the_ grid have been written to c:\tempds.xml") End Sub Private Sub btnLoadDataSet_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object,_ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnLoadDataSet.Click If System.IO.File.Exists("c:\tempds.xml") Then dsPerson = New DataSet() dsPerson.ReadXml("c:\tempds.xml", XmlReadMode.InferSchema) grdPersonList().DataSource = dsPerson grdPersonList().DataMember = "row" messagebox.Show("The grid has been loaded from the XML file c:\tempds.xml.") Else messagebox.Show("Click write first.") End If End Sub -
Run the program and click the btnLoadRecordset button. You should see results similar to those in Figure 21.5. Figure 21.5. Visual Basic .NET's DataGrid control allows you to edit and sort a DataSet that is bound to it. 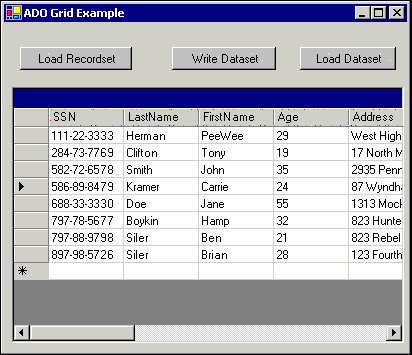 When you click the button, data is retrieved from the database into a recordset and then saved as an XML file. The XML file is then loaded into a DataSet object, which is bound to the DataGrid control. Notice that the DataGrid control allows to you add, edit, and delete rows. -
Alter the data by typing in the grid, that is, change someone's last name. -
Click the btnWriteDataSet button. This will write the dataset object in memory to an XML file. -
Stop the program and restart it. Click the btnLoadDataSet button and you should see the record, including the change that was made using the data grid.
As you can see, by using XML we can easily create a DataSet object from a Recordset object. In the next chapter we'll explore datasets and other ADO.NET concepts in more detail. |