Restricting User Capabilities
Restricting User Capabilities
Beginning in Mac OS X 10.2, Apple has provided a convenient means of controlling logged-in users' capabilities, such as what applications they can run and whether they can modify system preferences. This works beyond the Finder and also guards against invocation of applications from the Terminal. In a lab or community setting, this can work to provide effective guest access without requiring extensive user and group administration.
Editing User Capabilities
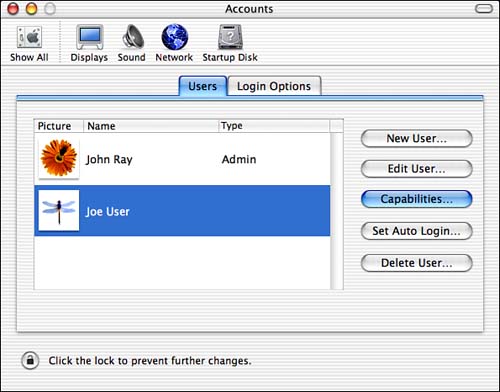
To access the user capability editor, you must first create a standard user account via the Accounts System Preferences panel. Administrative users cannot have capability restrictions. Select the user to modify in the Accounts list of the Users tab, then click the Capabilities button, as shown in Figure 10.7.
Figure 10.7. Edit capabilities of standard user accounts within the Accounts system preferences panel.
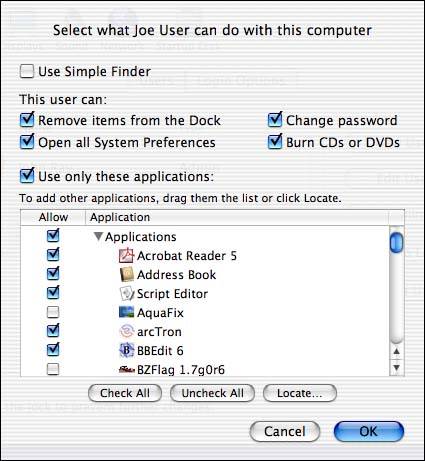
The Capabilities sheet, shown in Figure 10.8, is displayed. Choose from the these limitations on the account:
-
Use Simple Finder . Removes all but basic file launching capabilities from the account. This will be covered in more detail shortly.
-
Remove Items from the Dock . Lab and teaching settings work best if there is consistency across accounts. To keep a static base set for the dock (no applications, files, or folders can be added or removed), click the Remove Items from the Dock check box. Note: The label for this option is misleading. It prevents any changes to the Dock, rather than simply removing items.
-
Open All System Preferences . If unchecked, users can access system preferences related to only their accounts: all Personal category preferences, Universal Access, Keyboard, Mouse, and Sound.
-
Change Password . Allow the user to change the account password. For a guest or kiosk account, this would be disabled.
-
Burn CDs or DVDs . To eliminate the capability to burn optical media on the system, uncheck this option.
-
Use Only These Applications . When checked, the user will be restricted to running only the applications or application categories checked in the list at the bottom of the pane. You can expand a category with the disclosure arrow in front of its name to show the applications it contains. Unchecking an application or category removes access from that item. You can add applications by clicking the Locate button or dragging their icons into the list.
Figure 10.8. Restrict what the user can access.
NOTEUser account restrictions (capabilities) do not modify the permissions of the applications that they control. They also do not enable you to control command-line applications. You must use traditional user/group permissions in combination with Apple user capabilities to administer command-line and GUI tools effectively. |
If a user violates an application restriction, she is warned with an error message, shown in Figure 10.9, and the attempt is logged via syslogd in /var/log/system.log as follows :
Jan 27 16:41:11 John-Rays-Computer ./Navigator: CG/CPS: The application with pid 615 is not in the list of permitted applications and so has been exited.
Figure 10.9. Users are warned if they attempt to launch an application beyond their accounts' capabilities.

Although there isn't a reporting function built in to monitor these sorts of attempted policy restrictions, the logsentry product documented in Chapter 19, "Logs and User Activity Accounting," will easily automate violations tracking on your system.
Simple Finder
The "Simple Finder" is, as the name implies, a simplified version of the Mac OS X Finder. It provides a static dock with access to the applications chosen in the Capabilities setup, the user's Documents folder, the Shared folder, and Trash, as shown in Figure 10.10.
Figure 10.10. The Simple Finder limits access to most navigation and file management functions.

Users navigate through multiple screens of files by using the buttons at the bottom of the window. Documents must be saved to the ~/Documents folder to be easily accessible through the interface.
There is no direct means of navigating to other folders, but this should not be taken as a form of security. Access to the Terminal still enables a user to open files located elsewhere on the system. Alternatively, adding folders to the Login Items pane in System Preferences causes them to be opened in the Simple Finder at login.
Properly configured, the Simple Finder can be an effective means of providing a simple "launcher" for children or kiosk applications. It should not, however, be assumed to be secure without proper configuration of the applications that can be launched, such as restricting access to applications such as the Terminal and System Preferences.
| |
| |
| Top |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 158