8.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
Page 104
updated sequentially layer by layer, from the input to the output layer, in order to generate output in the form of the activations of the output layer neurones. Let xj denote the total input received by neurone j, which is represented by:
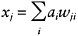 |
(3.1) |
where ai is the activity of neurone i, and wji is the weight of connection from the ith neurone to the jth neurone. Once the value of xj is computed from Equation (3.1), it is converted to an output value (for transmission to the next layer if the neurone lies on an intermediate layer) using a mapping function. The sigmoid function is a common choice of mapping function (Figure 3.1). It is a monotonically increasing non-linear function defined by:
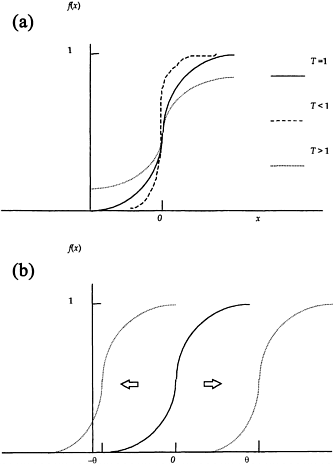
Figure 3.1 (a) The shape of the sigmoidal curve varies with parameter T. (b) The location of the sigmoid function has shifted after bias θ is added or subtracted.
| [Cover] [Contents] [Index] |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 354