CTO CIO - Sample Forms
CTO /CIO - Sample Forms
The following represents some sample reports and forms that are being submitted, reviewed ,and processed by a CTO/CIO (22). Additional reports, forms, proposals, and documents are available with the author.
Bargaining Strategies with Vendors
The following represents some of the best bargaining strategies presented by CIO Magazine (22).
Overview
Some bargaining strategies are more effective than others when looking for value from your IT vendor, according to the survey of 118 IT executives performed by CIO Magazine recently. While cost-cutting efforts may help the bottom line initially, squeezing vendors too tightly may not be as effective longer term. Instead, CIOs report that focusing negotiations on business objectives such as improving service will create more value for the organization. CIOs reported that when negotiating with their technology vendors they most frequently focus on negotiating lower initial fees, negotiating lower ongoing fees, consolidating vendors, negotiating free services like consulting and demanding higher standards for service level agreements (SLAs). The practices that were most effective in reducing per user costs, such as negotiating lower fees and consolidating vendors, were less effective in adding business value. The negotiating strategies that were most effective in adding business value include vendor consolidation, demanding higher standards for SLAs, negotiating comprehensive SLAs focused on business objectives and paying the vendor when value is delivered/project completed. The majority of CIOs said they would continue to rely on these tactics once the economy and the business climate improve. Almost all of the executives relying on the list of strategies below had to request these benefits or arrangements, however, vendors were more likely to offer free services or variable pricing. (22)
Key Findings
Negotiation strategies The most common strategies for negotiating with IT vendors were negotiating lower initial fees (94%), negotiating lower ongoing fees (88%), consolidating vendors (72%), negotiating free services like consulting (70%) and demanding higher standards for SLAs (68%). The least practiced strategies were gaining share agreements (21%), variable pricing or pay for use (36%) and negotiating comprehensive SLAs focused on business objectives (34%).
Reducing per user costs The practices that were most effective in reducing per user costs included negotiating lower ongoing fees (67%), consolidating vendors for greater volume discounts (65%), negotiating lower initial fees (60%), lengthening or shortening term of contracts (49%), negotiating free services (49%) and end-to-end solutions/compatibility with other vendors' products (58%).
Reducing contract values Not surprisingly, the practices that were most effective in reducing contract values were similar to those that reduced per user costs and included consolidating vendors for greater volume discounts (54%), negotiating lower ongoing fees (51%), negotiating lower initial fees (50%), lengthening or shortening contract terms (39%) and a la carte feature/product/module selection (36%).
Adding business value Interestingly, the negotiating strategies that were most effective in adding business value differed from those that lowered costs. While consolidating vendors topped the list (58%), other practices include demanding higher standards for SLAs (57%), negotiating comprehensive SLAs focused on business objectives (54%), paying the vendor when value is delivered/project completed (50%) and negotiating free services like consulting (46%) were also effective in bringing value to the business. (22)
Survey Questions
| Are you currently using this practice in negotiations with your technology vendors? | (% yes.) |
| Negotiate lower (initial) fees | 94% |
| Negotiate lower, ongoing (maintenance, upgrade) fees | 88% |
| Improved/higher standards for SLAs | 68% |
| Variable pricing (on-demand, ASP model, etc.) | 36% |
| A la carte feature/product selection/add on modules (vs. all or nothing) | 61% |
| Consolidating vendors for volume discounts | 72% |
| Lengthening or shortening length of contracts | 61% |
| Customization of products/services | 41% |
| Free services (consulting, etc.) | 70% |
| End-to-end solutions requiring vendor to work with/be compatible with other vendors' products | 58% |
| Penalties for failing to meet performance agreement/SLAs | 66% |
| Pay when value is delivered/project completed | 64% |
| Gain share agreements (vendor paid a portion of business value generated) | 21% |
| Comprehensive SLAs focused on business objectives (such as problem resolution) vs. technical metrics only | 34% |
| Poison pill clause or guarantees of services in case the vendor is acquired | 47% |
% of respondents that said this practice was effective (rated 4 or 5) in reducing per user costs
| Negotiate lower (initial) fees | 60% |
| Negotiate lower, ongoing (maintenance, upgrade) fees | 67% |
| Improved/higher standards for SLAs | 31% |
| Variable pricing (on-demand, ASP model, etc.) | 31% |
| A la carte feature/product selection/add on modules (vs. all or nothing) | 40% |
| Consolidating vendors for volume discounts | 65% |
| Lengthening or shortening length of contracts | 49% |
| Customization of products/services | 20% |
| Free services (consulting, etc.) | 49% |
| End-to-end solutions requiring vendor to work with/be compatible with other vendors' products | 48% |
| Penalties for failing to meet performance agreement/SLAs | 33% |
| Pay when value is delivered/project completed | 35% |
| Gain share agreements (vendor paid a portion of business value generated) | 16% |
| Comprehensive SLAs focused on business objectives (such as problem resolution) vs. technical metrics only | 38% |
| Poison pill clause or guarantees of services in case the vendor is acquired | 18% |
% of respondents that said this practice was effective (rated 4 or 5) in reducing contract values
| Negotiate lower (initial) fees | 50% |
| Negotiate lower, ongoing (maintenance, upgrade) fees | 51% |
| Improved/higher standards for SLAs | 19% |
| Variable pricing (on-demand, ASP model, etc.) | 29% |
| A la carte feature/product selection/add on modules (vs. all or nothing) | 36% |
| Consolidating vendors for volume discounts | 54% |
Sample Technical Report for CIO/CTO
The following is a sample technical report presented to a CTO/CIO. (22)
Guidelines - Outline for Technical Report to CTO / CIO
Executive Summary
Briefly (about one page) describe the technology in non-technical terms - what is it, and how is it different from, and how will it integrate with the current system.
Summarize the key benefits from implementing the technology.
Summarize your recommendation, including the implementation plan (required resources, schedule, costs, etc.).
Evaluate relevant alternatives.
Discussion
Expand upon the exec summary
Problem definition
Planning assumptions
Any modifications to current business practices
Benefits - Impact (tangible, intangible)
Critical success factor risks
Indicate if the system must be implemented in more than one phase, or project. The appendix should provide a proposed schedule with resource requirements. Define the phases, and indicate when the first phase will be implemented, and the initial benefits.
Indicate if the company should implement any short-term and long-term strategies to minimize the impact of the new system and to exploit the opportunity within the company. Your recommendations should address the following.
-
The technical infrastructure (changes to the existing structure)
-
The new data base architecture
-
Development and implementation of new software
Indicate the benefits from implementing the recommendations (financial, qualitative, legal, organizational, competitive). Briefly describe and evaluate any feasible alternatives, and summarize their advantages and disadvantages, and why they are not the preferred recommendation.
Ex.
-
Completely redesign/replace our current system to install the new technology
-
Integrate the new technology with the current system
-
Outsource our system to an ASP, who will be responsible for developing and operating it. Other firms in our industry have done so, at an annual cost of $$.
-
Make the following minimal changes to our system. This will provide the basic benefits at minimal cost. Estimate the first year and subsequent annual cost of the recommended plan. This should include any increased HW and SW license costs, and costs of additional skills and people. There are intangible and qualitative costs. These might include:
-
The cost of lost customer good will
-
Lower employee morale
-
Recommend the preferred vendor. State if it has to be customized/adapted to interface with the existing system, and any bridge software that will have to be developed in-house (or hire a consulting firm).
State the reasons for the recommendation: Ex. because it is compatible with our existing systems...because they are recognized as being one of the leading vendors...and it's the best combination of function and price.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Summarize the recommendation.
Appendix
The appendix contains the supporting data and lists the relevant information sources (technical articles, vendor's supporting literature, any internal department positions, etc.) (22) (52)
Creating CIO Agenda
This would be a typical CIO Agenda. (52)
| The CIO Agenda | |||
| Strategies for handling the new imperatives | |||
| ENTERPRISE ENVIRONMENT | Fighting for Survival | Staying Competitive | Breaking Away |
| IMPERATIVE | |||
| Lead | Build Credibility | Know and engage decision makers | Guide the top exec to new business models |
| Anticipate | Monitor drivers and threats | Understand key trends | Stimulate technology and business demands |
| Strategize | Reduce business costs | Synchronize IT enabled investments | Invest for innovation, growth |
| Organize | Configure for cost effectiveness | Implement a professional services function | Configure a business-IT partnership |
| Deliver | Drive disciplines value delivery | Source services strategically | Build future capabilities |
| Measure | Review total cost of ownership | Implement benefits realization | Evaluate against opportunities framework |
| DATA: GARTNER EXP | |||
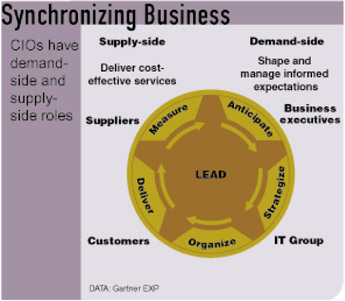
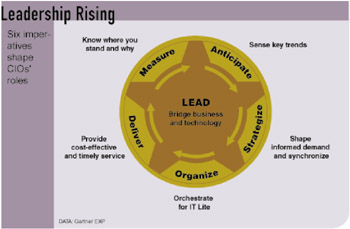
Gartner's CIO Imperatives that Shape Roles
Some CIO imperatives that shape the CIO role are presented. (52)
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 213