Licensing
When you install SQL Server, you'll see a dialog box asking which licensing option you want to use: per-processor or per-seat.
NOTE
The license agreement in the SQL Server box is a legal document that you should read and understand. This section explains the licensing schemes but does not represent the official licensing policy of the product. Packaging and licensing periodically change. Consult the licensing agreement to be sure you're in compliance and have chosen the best options for your needs.
SQL Server Processor License
A Processor License includes access for an unlimited number of users to connect from inside the corporate LAN or WAN or outside the firewall. Under the per-processor licensing model, a Processor License is required for each processor running the SQL Server 2000 software. Processor Licenses can be used in any Internet, extranet, or intranet scenario. No additional Server Licenses, Client Access Licenses, or Internet Connector Licenses will need to be purchased.
Server Licenses and CALs
A Server License (for either Standard or Enterprise Edition) is required for every server on which that edition of SQL Server software is installed. The only exception is a Passive machine in an Active-Passive cluster. Each client needing access to any of the SQL Servers needs a Client Access License (CAL). You can think of a client as any device (for example, a PC, workstation, terminal, or pager) utilizing the services of either SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition or SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition. A client with a per-seat CAL can access any instance of SQL Server in the environment. You can deploy additional installations of SQL Server with minimal expense, and you don't have to buy additional client licenses. You simply acquire as many additional server licenses as you need, and your users are already licensed to use them. Figure 4-1 illustrates a scenario requiring two SQL Server licenses and three CALs deployed in the per-seat mode.
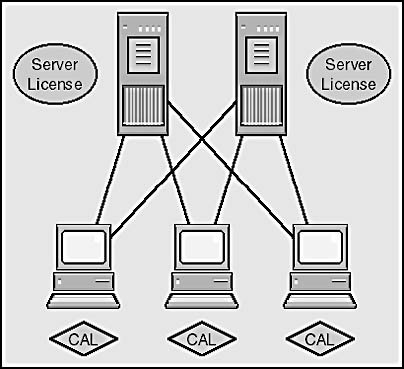
Figure 4-1. A scenario requiring two Server Licenses and three CALs.
You should consider you licensing agreement carefully before installation as the licensing mode cannot be changed without reinstalling SQL Server. In addition to the two licensing modes discussed above, there are some additional considerations.
Multiplexing: Use of Middleware, Transaction Servers, and Multitiered Architectures
Sometimes organizations develop network scenarios that use various forms of hardware and software that reduce the number of devices that directly access or utilize the software on a particular server, often called multiplexing or pooling hardware or software. For example, let's say a client PC is using a server application that calls the Microsoft Transaction Service (MTS) component of Microsoft Windows 2000 Server on one server, which in turn pulls data from a Microsoft SQL Server database on another server. In this case, the only direct connection to Microsoft SQL Server comes from the server running MTS. The client PC has a direct connection to the server running MTS, but also has an indirect connection to SQL Server because it is ultimately retrieving and using the SQL Server data through MTS. Use of such multiplexing or pooling hardware and software does not reduce the number of CALs required to access or utilize SQL Server software. A CAL is required for each distinct input to the multiplexing or pooling software or hardware front end. If, in the preceding example, 50 PCs were connected to the MTS server, 50 SQL Server CALs would be required. This is true no matter how many tiers of hardware or software exist between the SQL Server and the client devices that ultimately use its data, services, or functionality.
Multiple Instances
SQL Server 2000 includes a multi-instancing feature that allows customers to install SQL Server more than once on a server. If you're using SQL Server Standard Edition, you must fully license each instance server (whether in per-seat or per-processor mode). If you're using SQL Server Enterprise Edition, you can install an unlimited number of instances on each machine without requiring any additional licensing.
There are additional issues when determining licensing requirements for SQL Server Personal Edition and for SQL Server Desktop Engine. And if you are running SQL Server on MSCS, there are different licensing issues depending on whether the SQL Servers are configured on the cluster as active-active or as active-passive. The Microsoft Web site has full details on the licensing requirements in these, and all other, situations. Please refer to http://www.microsoft.com/sql for any of the following:
- End User License Agreement
- Upgrade roadmaps to SQL Server 2000
- Additional Questions and Answers
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 179