Understanding Wi-Fi Networks
| You're on the road, and you've found a location with a Wi-Fi broadcast device that your mobile computer can talk to. A Wi-Fi broadcast device is variously referred to as an access point, an AP, or a hotspot. With your access point located, you're ready to sit right down, establish a wireless connection, and start reading your email and surfing the Web, right? Not so fast, partner! It's really important to understand that being able to "talk" with a wireless access point just means that you can "talk" with a wireless access point. It doesn't mean that you can connect to the Internet unless the wireless access point is itself connected to the Internet. So if Starbucks (or whoever) wants to provide you with the chance to surf on their turf while you sip that latte, Starbucks needs to provide an Internet connection. Generally, this connection is wired, and uses a cable or DSL (digital subscriber line) telephone for high speeds. A high-speed wire brings the Internet to the location, and a Wi-Fi access point broadcasts the wireless Internet connectivity to wireless devices. (In technogeek speak, the wireless devices are generically referred to as clients.) Between the Internet connection and the Wi-Fi access point, some hardware also needs to be designed to connect with the Internet and share the connectivity. This can be done a whole lot of different ways, depending on many factors. For example, is a wired network also involved? I'll be getting into these details in Part IV. For now, you need to understand that connecting to the Internet via Wi-Fi involves four things:
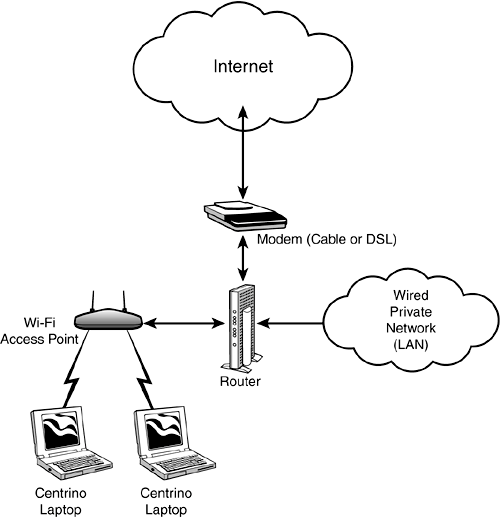
A fairly typical simple Wi-Fi network setup of this sort, that lets Wi-Fi users connect to the Internet, is shown in Figure 8.3. Figure 8.3. To connect to the Internet via Wi-Fi, the wireless Wi-Fi access point must be plugged in to equipment and an Internet connection, usually cable or DSL.
|
EAN: N/A
Pages: 204
- Frame-Mode MPLS
- RIP PE-CE Routing Command Reference
- Constraint-Based Routing and Operation in MPLS TE
- VPLS Topology-Single PE or Direct Attachment
- Case Study 2: Implementing Multi-VRF CE, VRF Selection Using Source IP Address, VRF Selection Using Policy-Based Routing, NAT and HSRP Support in MPLS VPN, and Multicast VPN Support over Multi-VRF CE