Creating Zone Transfers in DNS
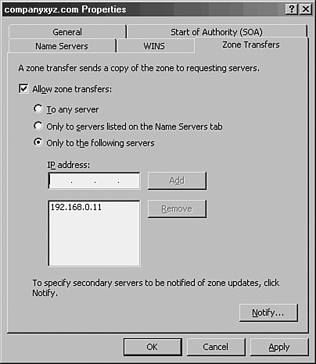
| Copying the DNS database from one server to another is accomplished through a process known as a zone transfer . Zone transfers are required for any zone that has more than one name server responsible for the contents of that zone. The mechanism for zone transfers varies, however, depending on the version of DNS and whether the zone is Active Directoryintegrated. DNS servers can be configured to notify other DNS servers of changes to a zone and begin a zone transfer on a scheduled basis. To set up a server to send zone transfers to another server from a forward lookup zone, follow these steps:
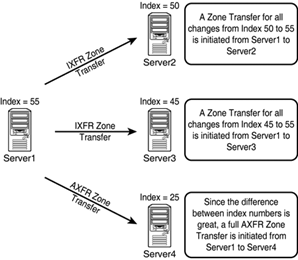
Only to Servers Listed In addition to specifically defining recipients of zone transfers by IP address, you can select the Only to Servers Listed on the Name Servers Tab radio button as well, assuming that the recipient server or servers are listed under the Name Servers tab. Full Zone TransferThe standard method for zone transfers, which transfers the entire contents of a DNS zone to other servers, is known as asynchronous zone transfer (AXFR) or full zone transfer. This type of zone transfer copies every item in the DNS database to a separate server, regardless of whether the server already has some of the items in the database. Older implementations of DNS used AXFR exclusively, and it is still used for specific purposes today. Incremental Zone Transfer (IXFR)An incremental zone transfer (IXFR) is a process by which all incremental changes to a DNS database are replicated to another DNS server. This saves bandwidth over AXFR replication changes because only the delta , or changes made to the database since the last zone transfer, are replicated. IXFR zone transfers are accomplished by referencing an index number that is referenced on the SOA of the DNS server that holds the primary zone. This number is incremented upon each change to a zone. If the server requesting the zone transfer has an index number of 45, for example, and the primary zone server has an index number of 55, only those changes made during the period of time between 45 and 55 will be incrementally sent to the requesting server via an IXFR transfer. However, if the difference in index numbers is too great, the information on the requesting server is assumed to be stale, and a full AXFR transfer will be initiated. For example, if a requesting server has an index of 25, and the primary zone server's index is 55, an AXFR zone transfer will be initiated, as illustrated in Figure 13.15. Figure 13.15. IXFR zone transfers. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 325