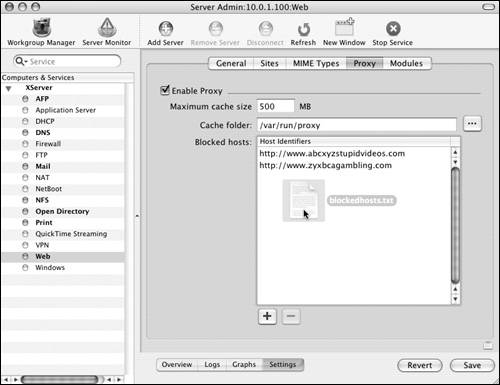
Enabling Web Proxies
|
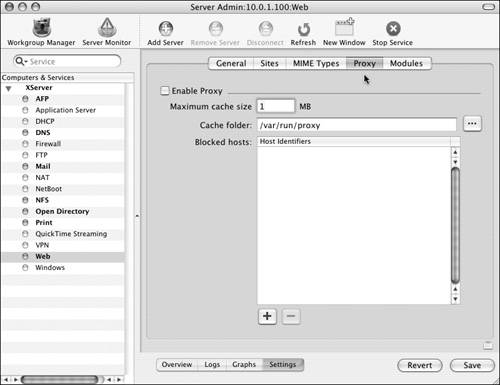
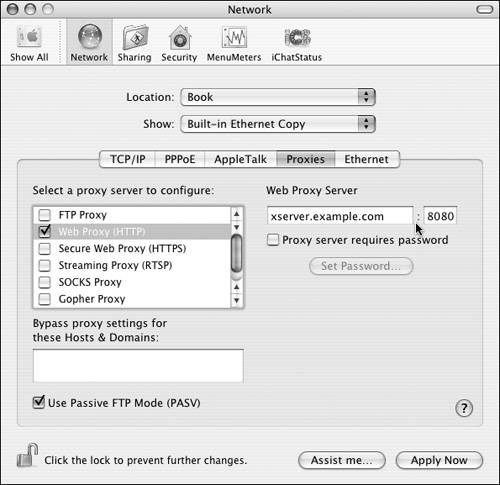
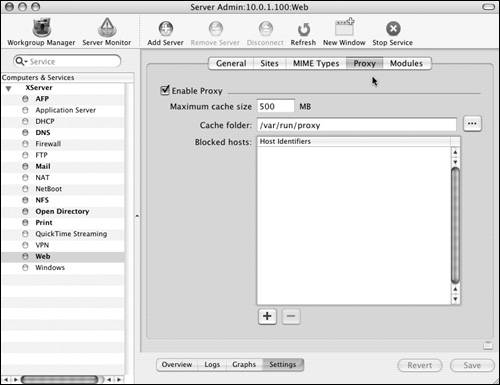
| Primarily, Web proxies are enabled to improve the performance of requests made to external Web sites by Web users on your local network. Many of your users visit the same Web sites throughout the day. A Web proxy caches this external Web site content; Web browsers on your local network then read the cached content rather than use your potentially slower Internet connection. Recently, though, Web proxies have fallen out of favor as high-speed Internet connections have become commonplace. To enable a Web proxy:
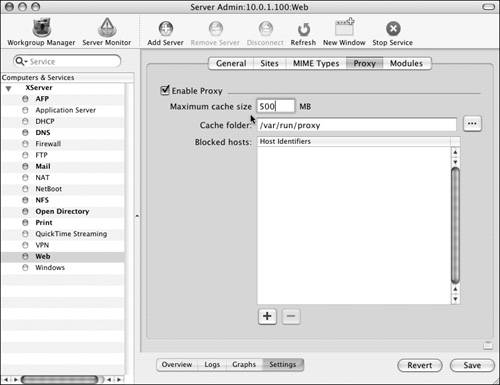
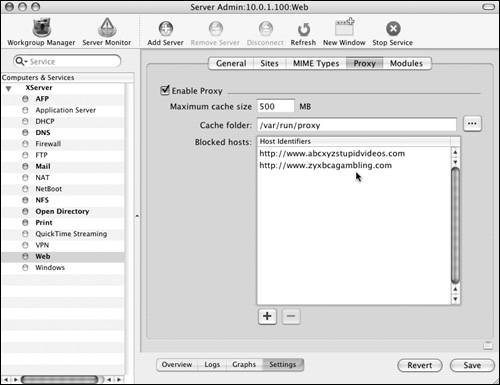
Configuring blocked Web sitesWhen you're using a Web proxy, all the Web traffic from your client computers must pass through the proxy server. You can take further advantage of this situation by creating a list of blocked Web site hosts. Doing so prevents your users from going to any Web site that you've defined in the list. To block Web sites:
|
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 105
- Step 1.1 Install OpenSSH to Replace the Remote Access Protocols with Encrypted Versions
- Step 1.2 Install SSH Windows Clients to Access Remote Machines Securely
- Step 3.2 Use PuTTY / plink as a Command Line Replacement for telnet / rlogin
- Step 4.1 Authentication with Public Keys
- Appendix - Sample sshd_config File