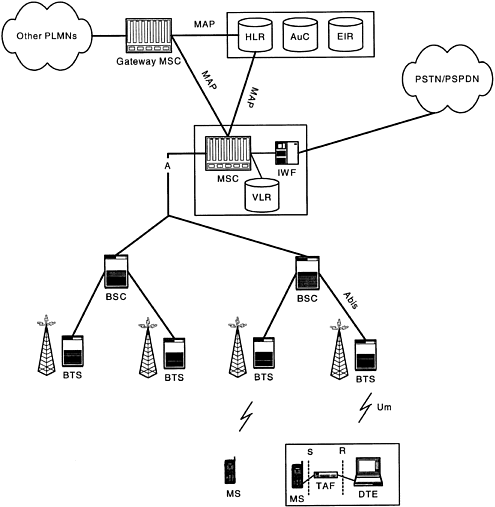
Before discussing the details of GSM data services, let's first consider an overview of a GSM network for providing TCH data service. A GSM network consists of several main network elements (Figure 4-1).
Home location register: The HLR is a central database for a public land mobile network (PLMN) to store subscription information of users. It keeps information about service profile, location, and activity status of a subscriber. HLR is connected to MSCs and VLRs using GSM MAP protocol.
Mobile switching center: The MSC performs the telephony switching function of the system. It does call control to and from other telephony and data network elements. It also captures billing information from a call. The MSC is connected to the BSS using the A interface protocol.
The Gateway MSC is a gateway to a PLMN and provides call routing to/from other PLMNs and PSTNs.
Visitor location register: The VLR contains subscriber information, which is needed in servicing a roaming MS in a visited network. Although specified as a separate entity, VLR is usually integrated into MSC. When an MS roams into a visited network, its information is transferred from the HLR to the VLR using the location update procedure.
Authentication center: The AuC provides authentication parameters to verify the user 's access. It also provides encryption parameters for ciphering over the air interface.
Equipment identification register: The EIR is a database that contains information for preventing calls from stolen, unauthorized mobile stations (MSs). The database maintains this information based on the equipment identifier, IMEI.
Base station controller: The BSC controls a set of BTSs. It provides cellular specific functions, like handover power control.
Base transceiver station: The BTS handles the radio interface. The BTS is connected to the BSC using the Abis interface.
Interworking function: The IWF provides a mechanism for transferring digital data signals from the GSM PLMN to the other type of network (e.g., PSTN, ISDN, or PSPDN). The interworking function also performs any protocol conversion between the two dissimilar networks.
Mobile station: A mobile station has GSM-specified call control, mobility management, and radio interface. It is connected to the network using air interface (Um). As GSM data user equipment, an MS is a logical function complemented by the terminal adaptation function (TAF) and sometimes data terminal equipment (DTE).
Terminal adaptation function: The TAF is used to adapt terminal equipment to connect to an MS. In Figure 4-1, an ISDN DTE is shown that is connected to TAF via an ISDN R interface. The TAF is connected to an MS via an ISDN S interface.
Data terminal equipment: DTE is regular data terminal equipment as used in fixed networks. The DTE, TAF, and MS are all logical functions of user equipment and can be integrated as one device.