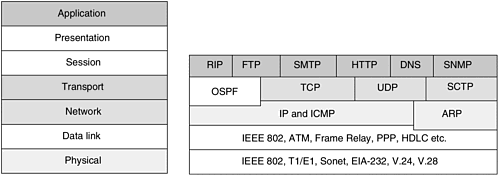
2.2 Internet Model
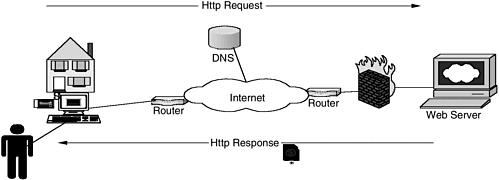
| The Internet model in comparison to OSI is an optimized version. The functionality of the presentation and session layers is incorporated into the application layer when required and eliminated sometimes. The protocol stack in the Internet model is shown in Figure 2-2. Figure 2-2. Internet model. The suite of protocols at the network, transport, and application layers defined by the Internet Protocol (IP) model provides the basis for building internetworks such as the Internet. Consider, for example, a user surfing the Web and the protocols that are utilized. Figure 2-3 shows a user accessing the Web. Figure 2-3. Web page request via HTTP. The user connects to the Internet via his or her ISP. As a result of a successful connection, the user's PC is assigned an IP address dynamically. Address assignment may be done using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). The user starts a Web browser (e.g., Internet Explorer or Netscape) and requests to connect to the uniform resource locator (URL) www.nokia.com. The browser application uses the HTTP protocol to form an HTTP request. The HTTP request is carried over TCP. Address resolution of the URL needs to be done. A DNS query is sent to the DNS server (the address of which was configured via DHCP). DNS queries are sent over UDP. The DNS response contains the "A" record of the requested URL. The HTTP request is sent to the destination, whose IP address is obtained from the A record. The source IP address is the IP address of the network interface on the PC itself. The Web server receives the HTTP request and sends an HTTP response. The HTTP response contains the data in HTML format. The browser displays the content to the user. What we see from this example is that a number of protocols are utilized in a simple transaction such as requesting a Web page. The rest of this chapter looks at the network layer, transport layer, and application layer protocols in more detail. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 164
- MPLS Terminology
- Basic MPLS VPN Overview and Configuration
- Case Study-Hub and Spoke MPLS VPN Network Using BGP PE-CE Routing for Sites Using Unique AS Numbers
- VPLS Topology-Single PE or Direct Attachment
- Case Study 2: Implementing Multi-VRF CE, VRF Selection Using Source IP Address, VRF Selection Using Policy-Based Routing, NAT and HSRP Support in MPLS VPN, and Multicast VPN Support over Multi-VRF CE