Navigating the Start Menu: Whats Changed
Navigating the Start Menu: What’s Changed
Clicking the Start button on the taskbar displays the Start menu. You can also display the Start menu by pressing the Windows logo key. As with Windows XP, the Start menu in Windows Vista has two views:
-
The Start menu (or Simple Start menu, as it is sometimes referred to) is the default view which provides easy access to programs, folders, and search.
-
The Classic Start menu is an alternative view which provides the look and functionality of the Start menu in Windows 2000 and earlier versions of Windows.
The Start menu, shown in Figure 2-5, has three key areas:
-
Programs list Displays recently used programs and programs that have been pinned to the Start menu. By default, Internet Explorer and Windows Mail (previously called Microsoft Outlook Express) are pinned to the Start menu, and up to eight recent programs are displayed as well.
-
Search box Allows you to search your entire computer for files, folders, or programs. To use the Search box, open the Start menu, type your search text, and then press Enter. The Clear button appears when you type your search text. Click the Clear button to clear the search results and return to the normal view.
-
Right pane Provides access to commonly used folders and features. The right pane also provides the Power button (puts the computer in sleep mode or shuts it down, depending on the system configuration), the Lock button (locks the computer), and the Options button (displays the following options: Switch User, Log Off, Lock, Shut Down, and Restart).
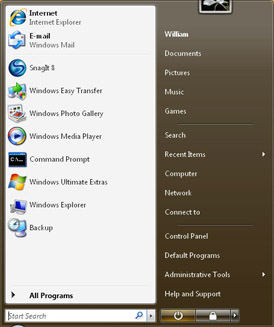
Figure 2-5: The Start menu
Managing Programs List on the Start Menu
The left pane on the Start menu displays recently used programs and programs that have been pinned to the Start menu. By default, Internet Explorer and Windows Mail (previously called Outlook Express) are pinned to the Start menu, and up to eight recent programs are displayed as well.
When you are working with the standard Start menu, you can modify the programs list in several ways. To modify the default settings, right-click the Start button, and then select Properties. In the Taskbar And Start Menu Properties dialog box, the Start Menu tab is selected by default. Click Customize, and then set the Number Of Recent Programs To Display option as appropriate. By configuring the Show On Start Menu options, you can stop displaying links for the Web browser and mail program or configure a different browser and mail program to which you want to link.
| Tip | If you want to provide quick access to programs, you can pin those programs to the Start menu. To do this, click the Start button, navigate to the program you want to be able to quickly access, and then right-click the program name. Select Pin To Start Menu to add the program to the Start Menu. |
Using the Right Pane on the Start Menu
The right pane on the Start menu provides access to commonly used folders and features. The right pane also provides the Power button (puts the computer in sleep mode or shuts it down, depending on the system configuration), the Lock button (locks the computer), and the Options button (displays the following options: Switch User, Log Off, Lock, Restart, Sleep, and Shut Down).
Important but subtle interface changes are reflected in the right pane of the Start menu. By default, Windows XP and Windows Vista store user documents in different ways:
-
In Windows XP, user documents are stored by default in personal folders under %SystemDrive%\Documents and Settings\%UserName%. A user’s personal folder contains a My Documents folder, which in turn contains other folders, such as My Pictures and My Music. Windows XP also has folders named My Computer and My Recent Documents.
-
In Windows Vista, user documents are stored by default in personal folders under %SystemDrive%\Users\%UserName%. A user’s personal folder contains separate Contacts, Desktop, Documents, Pictures, Links, Downloads, and Favorites folders. Windows Vista also has folders named Computer and Recent Documents.
Because of the different way that Windows Vista stores user documents, the My, My, My is gone, gone, gone from the interface, which might be just as well. C:\Users\William\Documents is much easier to use and reference than C:\Documents and Settings\William\My Documents. That said, however, Windows XP and Windows Vista both track the location of the currently logged on user’s profile folder by using the %UserProfile% environment variable.
The Windows Vista changes to where documents, pictures, and user profiles are located also make it easier to navigate the file system from the command line. For example, when you open a command prompt in Windows XP, your current directory is your user profile directory %UserProfile%, which is C:\Documents and Settings\Mitch Tulloch on my computer. If I want to change my current directory to where my pictures are located, I have to type the following:
cd "My Documents\My Pictures"
Note the need to enclose the path in quotes—these are needed because of the spaces present. In Vista however, I need to type only this:
cd Pictures
Less typing means more productivity. In fact, I might need to type only cd p and press TAB a few times until cd Pictures appears, and then press Enter. You can do the same for the Windows XP example, but you’d have to do it in two steps. That is, type cd m (TAB, TAB, TAB… and press Enter) followed by cd m (TAB... and press Enter). The bottom line, though, is that the fewer times you need to enclose paths in quotes, the easier it becomes to navigate from the command line. Now if only they had changed the Program Files directory into just Programs!
Mitch Tulloch
Author and MVP—For more information, see http://www.mtit.com.
Within the newly reorganized structure of personal folders, a user’s document and data folders are stored as top-level folders within a personal folder. Thus rather than the Documents folder containing a number of subfolders for pictures, music, and so on, the Documents folder is meant to contain only documents. Reorganizing the structure of personal folders should make it easier to manage and back up a user’s personal data.
Other important changes are reflected in the right pane as well. To understand these changes, let’s review the option buttons provided in the right pane. From top to bottom, the option buttons are as follows:
-
Current user The name of the currently logged on user. Clicking this option opens the user’s personal folder in Windows Explorer.
-
Documents Opens the %UserProfile%\Documents folder in Windows Explorer.
-
Pictures Opens the %UserProfile%\Pictures folder in Windows Explorer.
-
Music Opens the %UserProfile%\Music folder in Windows Explorer.
-
Games Opens the %ProgramFiles\Microsoft Games folder in Windows Explorer. The Games item is not listed in the Start menu for business editions of Windows Vista.
Tip In Windows Vista Home Premium, games available include Chess Titans, Hearts, Minesweeper, Solitaire, FreeCell, Mahjong Titans, Purble Place, and Spider Solitaire. Windows Vista Home Basic has all the games except Chess Titans and Mahjong Titans. Saved data for games is stored in the %UserProfile%\Saved Games folder. Click the Options menu to configure the Set Up Game Updates And Options dialog box options to keep games up to date automatically, clear history details on the most recently played games, and unhide games. Group Policy can be used to control the availability of the Games option.
-
Search Opens a local computer search in Windows Explorer. Use the Search In list to select or specify an alternative search location.
-
Recent Items A menu view that lists recently opened files.
-
Computer Opens a window where you can access hard disk drives and devices with removable storage.
Tip The Computer window is the fastest way to open Windows Explorer and access a computer’s disks. In the Computer window, double-click a disk to browse its contents. By default, the Search box in Windows Explorer performs localized searches of the currently open folder and its subfolders.
-
Network Opens a window where you can access the computers and devices on your network. Also provides quick access to Network Center and the Connect To A Network wizard.
-
Connect To Displays the Connect To A Network dialog box for connecting to wireless networks.
-
Control Panel Opens Control Panel, which provides access to system configuration and management tools.
-
Default Programs Displays the Default Programs window, which lets you choose the programs that Windows Vista uses by default for documents, pictures, and more. You can also associate file types with programs and configure AutoPlay settings.
-
Help And Support Displays the Windows Help And Support console, which you can use to browse or search help topics.
Several additional options can be added to the right pane, including:
-
Administrative Tools Clicking this option displays a list of system administration tools. To display the Administrative Tools option on the Start menu, right-click the Start button, and then select Properties. In the Taskbar And Start Menu Properties dialog box, click the Customize button on the Start Menu tab. In the Customize Start Menu dialog box, scroll to the end of the available options. For System Administration Tools, select Display On The All Programs Menu And The Start Menu.
-
Printers Opens a Printers window, which lists and provides access to currently configured printers.
-
Run Displays the Run dialog box, which can be used to run commands. To display the Run option, right-click the Start button, and then select Properties. In the Taskbar And Start Menu Properties dialog box, click the Customize button on the Start Menu tab. In the Customize Start Menu dialog box, scroll down and then select the Run Command check box.
Note Because the Search box can be used to open and run commands, you might not need to use the Run option. For example, to open a Microsoft Management Console, you can click the Start button, type MMC, and then press Enter. You don’t need to click in the Search box before you begin typing. Pressing Enter opens the first item in the results list. If for some reason MMC isn’t the first item, you would need to click MMC in the results list rather than pressing Enter.
Using the Search Box on the Start Menu
The Search box on the Start menu allows you to search your entire computer for files, folders, or programs. To use the Search box, open the Start menu, type your search text. Search results are displayed in the left pane of the Start menu. Clicking an item in the results list opens that item. To clear the search results and return to normal view, click the Clear button to the right of the Search box or press the Esc key.
| Note | Because the Search box is the only text entry field on the Start menu, you don’t need to click in the Search box before you begin typing. Just type your search text. |
Computer searches are performed by Windows Search Service. Windows Search Service searches the entire computer using the search text you’ve specified. The search proceeds on several levels. Windows Search Service:
-
Matches the search text to words that appear in the title of any program, file, or folder and then returns any matches found.
-
Matches the properties of programs, files, and folders as well as the contents of textbased documents.
-
Looks in the Favorites and History folders for matches.
Because Windows Search Service indexes content and caches properties as part of its normal processes, results typically are returned quickly. You can configure the types of items searched in the Start Menu Properties dialog box.
| Tip | Windows Search Service is the next generation of the Indexing Service included in earlier versions of Windows. By default, the service indexes the documents contained in the %SystemDrive%\Users folders. The Indexing And Search Options utility in Control Panel can be used to view indexing status and to configure indexing options. By default, index data is stored in the %SystemRoot%\ProgramData\Microsoft\USearch folder. |
Windows Vista can perform several other types of searches as well:
-
Local Folder Search When you open a folder, you’ll find a Search text box in the upperright corner of the Windows Explorer window. By default, typing search text in this text box and pressing Enter performs localized searches of the currently open folder and its subfolders. Unlike the Search box on the Start menu, you must click in this Search text box prior to entering your search text. You can use the Search In list to specify alternative search locations.
-
Internet Search Click the Options button to the right of the Search text box, and then select the Search The Internet option. Search The Internet uses the computer’s default search provider to search the Internet using the search text you’ve provided. The default search provider is MSN Search. You can set the default search provider using the Internet Options utility in Control Panel.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 101