Lesson 3: Designing RIS Security
To simplify the deployment of Windows 2000 clients, many organizations use RIS to help deploy Windows 2000 Professional images to desktop computers. The risk in using RIS to deploy clients is that if RIS isn't configured securely, an unauthorized user might be able to install an unauthorized computer on the network.
After this lesson, you will be able to
- Design secure deployment of Windows 2000 Professional by using RIS
Estimated lesson time: 30 minutes
Designing RIS Security
RIS is a collection of services that work together to allow remote installations of preconfigured Windows 2000 Professional desktop computers. The services that comprise RIS include the following, illustrated in Figure 9.7.
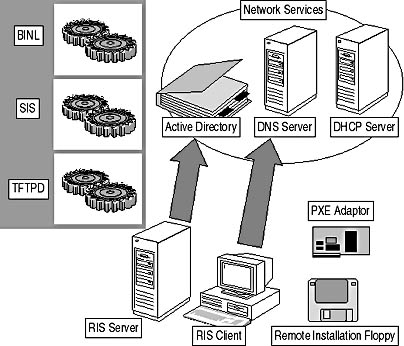
Figure 9.7 Components of remote installation services
- Boot Information Negotiation Layer (BINL). The BINL service answers DHCP requests from Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) network adapters or clients using a remote installation floppy. If the network has multiple RIS images, the BINL service will direct the client computer to the correct installation files based on the credentials provided by the user when requesting the image. The BINL service determines whether the installation is a reinstallation that will use an existing computer account or a new installation that requires creation of a new computer account by inspecting the target computer and Active Directory.
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol Daemon (TFTPD). The files that initiate the RIS installation are transferred from the RIS server to the client by using Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
NOTE
TFTP is used instead of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) because a TFTP file transfer involves less overhead. TFTP provides a connectionless transfer by using User Datagram Protocol (UDP). - Single Instance Store (SIS). The SIS allows multiple RIS images to be stored at a RIS server but reduces the duplication of files stored at the RIS server. If a file is duplicated between multiple images, the SIS keeps only a single instance of the file.
You configure and start these services with the Remote Installation Setup Wizard, RISetup.
Assessing Security Risks for Remote Installation
Consider the following practices whenever you implement RIS on your network:
- Prevent unauthorized RIS servers from being deployed on the network
- Determine whether the RIS server should respond only to specific client computers
- Restrict which users can create RIS image computers
- Limit user access to specific RIS images
- Ensure that proper security configuration is restored with a RIS image
- Address data transmission security during the initial RIS processing
Authorizing RIS Servers
The remote installation process requires the RIS server to be authorized in Active Directory. As with DHCP servers, only authorized RIS servers will respond to RIS clients requesting a RIS installation.
RIS servers are authorized in the DHCP console by members of the Enterprise Admins group. The RIS server will require authorization only if it doesn't have the DHCP Service installed. If the RIS server has already been authorized in Active Directory for the DHCP Service, there's no need to reauthorize the computer for RIS.
NOTE
When a PXE client is started on the network, the DHCP discover packet sent by the PXE client will request both an IP address for the client and the location of a PXE boot server, also known as the RIS server. The RIS installation can't proceed unless both the client IP address and the RIS server are provided.
Defining Which RIS Servers Will Respond to Client Requests
By default, RIS servers won't respond to client installation requests until you enable the ability to respond at the RIS server. For higher-security networks, you should not only enable the RIS server to respond to installation requests, but you should also restrict the responses to prestaged clients, as shown in Figure 9.8.
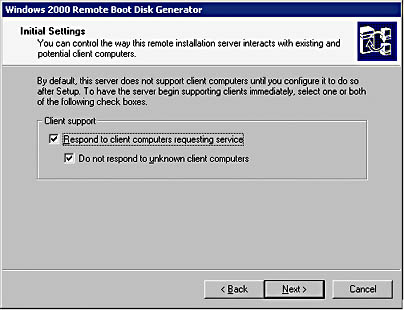
Figure 9.8 Configuring RIS to respond only to known client computers
Prestaged client computers are computers that have a computer account existing in Active Directory before RIS is installed. A common method of prestaging clients is to configure the globally unique identifier (GUID) attribute for the computer account in Active Directory, as shown in Figure 9.9.
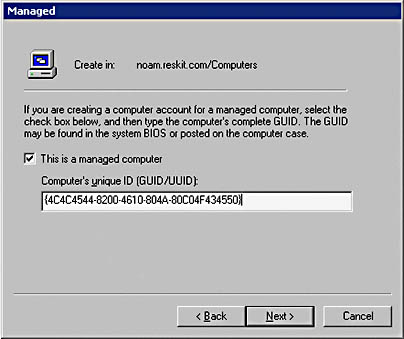
Figure 9.9 Configuring the GUID for a computer account
TIP
If the client is a PC98 or NetPC-compliant computer, you can find the GUID either in the system BIOS or on the computer case.
In addition, the user account performing the installation must have read and write permissions for all properties of the prestaged computer object and rights to reset and change passwords for the computer account.
Restricting the Creation of Computer Accounts
In some cases you may want to grant network users the necessary permissions to create the computer account during the client installation. To do this, complete the following steps:
- Determine the location in Active Directory where computer accounts will be created. You can determine that computer accounts will be created in one of three locations, illustrated in Figure 9.10.
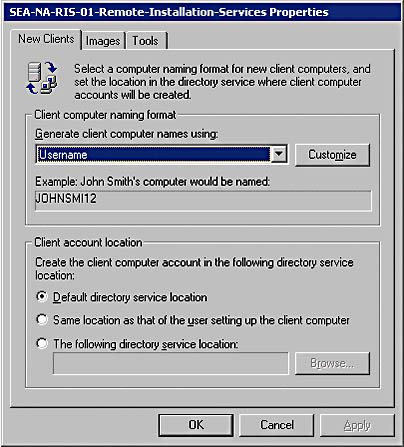
Figure 9.10 Configuring the directory service location for computer accounts
- The default location (the Computers container) in the same domain as the RIS server responding to the client request
- The same OU as the user account that's performing the client installation
- To a specific OU provided by an administrator
- Grant the user accounts the necessary permissions to create the computer account. Grant Read permissions and Create Computer Object permissions for the OU where the computer account will be created. Grant these permissions with the Delegation Of Control Wizard by granting the Join A Computer To The Domain privilege in the Delegation Of Administration Wizard.
Once you complete these two steps, the users with the delegated permission can perform remote installation of the operating system.
Restricting Which RIS Images a User Can Load
If you plan for users to select from multiple RIS images, you can restrict which images are available to users by configuring DACLs to change the default permissions.
The default permissions for a RIS image allow all users to install the image. You can modify which groups can install a RIS image by defining the security on an image's Templates subfolder, as shown in Figure 9.11.
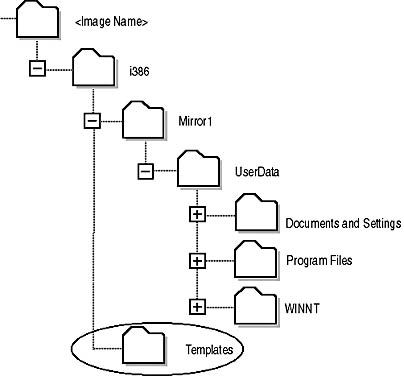
Figure 9.11 Changing NTFS permissions on the templates subfolder to restrict who can load a RIS image
By creating a custom domain local group that contains the user accounts that can install a specific RIS image, you can restrict who can install each image and show users only images they are allowed to see when they perform a remote installation.
Ensuring Proper Security Settings on the RIS Image Computer
Before using the RIPrep utility to prepare a RIS image, make sure that you've installed all necessary applications and have configured all required security settings. This includes registry, NTFS settings, and all other security template-related settings. When the RIPrep image is downloaded to destination RIS clients, your security settings will be maintained.
You can't include EFS encrypted files in the RIS image. Files encrypted with EFS will be unusable at any destination RIS client computers because the clients won't have the EFS private key required to decrypt the file encryption key.
Protecting Data Transmissions Between RIS Clients and RIS Servers
RIS uses TFTP for the initial transfer of data from the RIS server to the RIS client. TFTP doesn't encrypt data transmitted between the client and the server. Make sure that you're not using an account with Administrator rights on the network for the RIS process. A network sniffer could capture the credentials and use them to launch attacks against the network. Instead, configure an account that has only the permissions to install the RIS image to the client computer.
NOTE
Because you use RIS to install a client operating system, you can't implement IPSec to protect the TFTP data stream between the RIS server and the RIS client computers. Only the Windows 2000 operating system supports the use of IPSec.
Making the Decision
When you use RIS to deploy client computers, use the decision matrix shown in Table 9.5 to ensure that security is maintained on your network.
Table 9.5 Securing RIS Deployments
| To | Do the Following |
|---|---|
| Prevent deployment of unauthorized RIS servers | Restrict membership in the Enterprise Admins group because only members of this group can authorize RIS servers. Authorize only approved RIS servers. Restrict installation of RIS services on existing DHCP servers since they are already authorized in Active Directory. |
| Restrict RIS-installed computer accounts to a specific OU | Allow only prestaged computer accounts to install RIS images. Create the prestaged computer accounts in the desired OU. Alternatively, configure a specific location in Active Directory where computer accounts will be created for remote installations. |
| Restrict who can perform remote installations | Assign only approved users the permission to create computer accounts in the OU where remote installation computer accounts will be created. If using prestaged computer accounts, assign only approved users the permissions to modify the attributes of the prestaged computer accounts. |
| Restrict which images a user can load using remote installation | Change the DACLs on the RIS image's Templates subfolder to only allow authorized security groups READ permissions. |
| Maintain default security for RIS images | Preconfigure all security settings at the source computer before running the RIPrep utility to create the remote installation image. |
| Protect administrative permissions during RIS installations | Delegate the permissions to create computer accounts in Active Directory and never use an Administrator account for the remote installation because the TFTP protocol doesn't encrypt network data transmissions. |
Applying the Decision
To meet their RIS security requirements, Lucerne Publishing can either prestage computer accounts for remote installation or change permissions to allow users to create the computer accounts. If Lucerne Publishing chooses to prestage the computer accounts, you must add the following tasks to the security plan:
- Ensure that a member of the Enterprise Admins group authorizes all RIS servers in Active Directory.
- Determine the GUIDs for each new computer and create the computer account in an OU named RIS Computers in the domain that will contain the new computer account. This action ensures that each computer is installed in the correct domain, because only RIS servers from that domain process the RIS request.
- For the prestaged computer objects, create a domain local group that has the permissions to modify the attributes of the computer object. This action ensures that the users can perform the remote installation and make the necessary modifications to the computer account.
- Configure the RIS server so that it doesn't respond to requests from unknown clients. This configuration restricts remote installation to prestaged computer accounts.
If Lucerne Publishing decides to allow users to create the computer accounts in Active Directory, add the following tasks to the security plan:
- Ensure that a member of the Enterprise Admins group authorizes all RIS servers in Active Directory.
- Configure the RIS server to create the computer accounts in the RIS Computers OU.
- Delegate all authorized users with the ability to Join A Computer To The Domain at the RIS Computers OU.
- Modify the DACL for the Templates folder of the remote installation package to allow only users from the domain to download the image.
The decision to use prestaged computers or grant users the ability to create computer accounts will depend largely on how many computers will be installed. The more computers, the less likely it will be that an administrator will want to precreate the computer accounts and manually enter GUID attribute information. Even using scripts will require the manual installation of each GUID.
Lesson Summary
RIS is a key component of change and configuration management within Windows 2000. You must design the ability to create and install RIS images carefully so that only authorized users can use this service.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 172