Lesson 4: Designing SNMP Security
Many network administrators use Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to provide a preemptive method of detecting network faults. This protocol allows SNMP agents to inform SNMP management stations when abnormal events take place on the network that the network administrator should address.
After this lesson, you will be able to
- Design security for deploying SNMP
Estimated lesson time: 30 minutes
Designing SNMP Security
SNMP allows a network administrator to proactively manage a network by providing early detection of network faults or incorrect network configuration. Network administrators use SNMP to do the following:
- Monitor network performance. SNMP can determine network throughput and determine if data is being transmitted successfully on the network. You can use the monitoring of network performance to detect network faults.
- Detect network faults or unauthorized access. You can configure SNMP alerts to inform the SNMP management station when specified events take place. These events can include a failed router, attempted management of an SNMP agent by an unauthorized management station, or the restart of a device.
- Configure network devices. Use SNMP to configure SNMP agents remotely.
- Audit network usage. Use SNMP to determine network usage. You can use this information to determine overused areas of the network.
An SNMP environment has several participants, including
- SNMP management stations. SNMP management stations run software capable of querying and managing SNMP agents on the network.
NOTE
Windows 2000 doesn't ship with an SNMP management station component. The Windows 2000 support tools includes a simple graphical SNMP manager called SNMPUtilg.exe. For an extended feature set, consider implementing third-party solutions such as HP OpenView from Hewlett-Packard or Unicenter TNG from Computer Associates. - SNMP agents. SNMP agents run a service that's able to respond to SNMP management requests and to alert SNMP management stations when unauthorized management is attempted or when predefined events take place.
SNMP agents send status messages to the SNMP management station. The status messages include regular updates sent to an SNMP management station or responses to SNMP queries. In specific instances the SNMP agent will send an SNMP trap message to indicate that a defined event has taken place.
NOTE
Another difference between SNMP status messages and SNMP trap messages is that they're directed to different ports on the SNMP management station. SNMP status messages are sent to User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 161 on the SNMP management station, and SNMP trap messages are sent to UDP port 162.
Assessing the Security Risks of SNMP
SNMP allows you to query network devices and clients for configuration information. In the wrong hands, this configuration information may reduce your network's security by exposing sensitive information, such as Active Directory account information or router configuration.
To provide security for your organization's SNMP deployment, you must consider the following design points:
- Configuration of SNMP communities
- Configuration of approved SNMP management stations
- Interception of SNMP status messages and SNMP trap messages
Restricting Management to Specific SNMP Communities
The SNMP protocol provides limited security through the configuration of SNMP communities. SNMP communities define a collection of SNMP agents that can be managed as a collection on the network. The SNMP community doesn't have to map to domains within your Active Directory, but it should map to areas of management within your network.
An SNMP agent can belong to multiple communities, and you can configure rights for each community. You can assign rights to be
- None or Notify. The SNMP agent won't discard any requests from management stations in the community where the right is assigned.
- Read Only. The SNMP agent processes GET, GET-NEXT, and GET-BULK requests from the community but discards all SET requests.
- Read Create or Read Write. The SNMP agent processes all requests from the SNMP community including GET, GET-NEXT, GET-BULK, and SET requests. SET requests are limited to the addition of new objects in a Management Information Base (MIB) table.
Figure 9.12 shows an SNMP agent configured to belong to two communities, Corporate and Redmond. SNMP management stations have been assigned different rights for each community.
Within this dialog box, you can enable the option to send authentication traps. An authentication trap will inform a configured SNMP management station if an SNMP management station from a community that's not included in the approved communities list attempts to manage the SNMP agent.
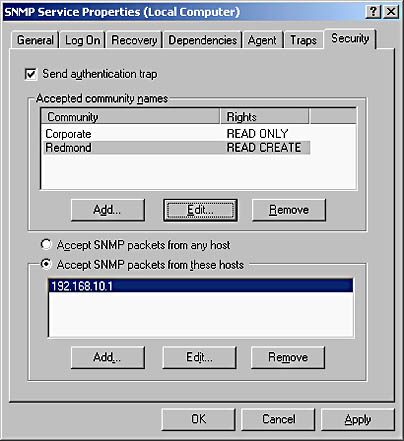
Figure 9.12 SNMP agent configured to respond to two communities
Restricting Management to Specific SNMP Management Stations
Figure 9.12 shows additional security configuration for the SNMP Service. You can configure each SNMP agent to respond only to specific SNMP management stations. If an SNMP message is received from an unapproved management station, the SNMP agent will send an SNMP trap message to a configured management station. In addition, you can configure SNMP agents to send messages only to a preconfigured management station. This configuration prevents unauthorized management stations from requesting data from SNMP agents. If an unauthorized management station attempts to manage the SNMP agent, you can configure an authorized management station as the host that SNMP trap messages are sent to indicating the unauthorized access, as shown in Figure 9.13.
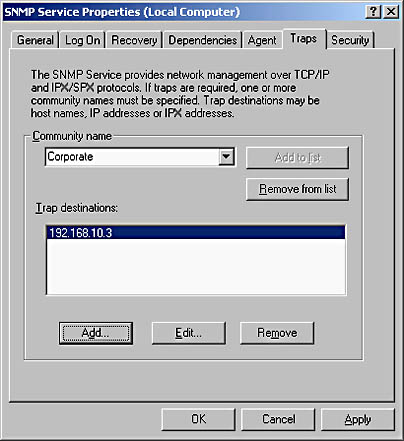
Figure 9.13 Configuring the destination for SNMP trap messages for the Corporate community
Protecting SNMP Messages from Interception
Because SNMP status messages and SNMP trap messages are sent in clear text across the network, a network sniffer can intercept the SNMP messages and read the information in them. You can configure IPSec to require that SNMP status messages and SNMP trap messages be encrypted.
Be careful when implementing IPSec. All SNMP agents must support the use of IPSec. If a single SNMP agent doesn't support IPSec, you'll have to configure IPSec to only request and not require IPSec encryption. Otherwise you'll have to remove the SNMP agent that doesn't support IPSec from your management scheme.
Making the Decision
Table 9.6 outlines the design decisions that you face when designing a secure SNMP deployment for your Windows 2000 network.
Table 9.6 Securing the SNMP Service
| To | Do the Following |
|---|---|
| Prevent SNMP management stations from modifying configuration by using SNMP SET commands | Configure the communities in which the SNMP agent participates to be Read-Only communities. This configuration prevents the SNMP agent from processing SNMP SET messages. |
| Prevent unauthorized SNMP management stations from managing SNMP agents | Change the community name from the default name of "Public." Be sure to choose a community name that's difficult to guess. |
| Track unauthorized management attempts | Configure the SNMP agent to send trap messages for authentication traps and to have the SNMP traps sent to a spe cific SNMP management station. |
| Protect SNMP messages from interception | Encrypt SNMP messages by using IPSec. This requires that all SNMP management stations and SNMP agents support IPSec encryption. |
Applying the Decision
Lucerne Publishing wants to use SNMP to manage network devices, clients, and servers. As mentioned earlier, each domain will manage its own SNMP environments and SNMP will be used to query information, not to configure SNMP-enabled devices. To ensure security for its SNMP environment, Lucerne Publishing will include the following items in its security design:
- Deploy separate community names that map to the domains within the lucernepublishing.tld forest. The community names shouldn't be the actual domain names because this would be too easy to guess. Likewise, the names shouldn't include the default name Public, because this is a common target for SNMP attacks.
- Configure all SNMP communities as Read-Only. Lucerne Publishing plans to use SNMP to query SNMP agents and to respond to SNMP traps. These processes don't require write abilities to the SNMP agents. Configuring communities as Read-Only prevents the use of SNMP SET commands.
- Restrict management to occur only within the domain. Add the other community names to the list of community names for each SNMP agent and configure them with the NONE right to prevent management from other areas of the network.
- Detect unauthorized SNMP management attempts. Lucerne Publishing should configure each SNMP agent to send authentication trap messages to track unauthorized management attempts. Configure each SNMP agent with a listing of authorized management stations and an SNMP management station to which the SNMP trap messages will be sent.
Lucerne Publishing has to review its situation carefully to determine whether it should implement IPSec for SNMP messages. The company must find out if all network devices deployed on its network support IPSec. If they don't, it would be unwise to deploy IPSec because Lucerne Publishing would lose the ability to monitor the network devices.
Lesson Summary
SNMP is an excellent tool for proactively managing your network. If you configure it properly for security, you can prevent attackers from taking advantage of security weaknesses in the SNMP protocol. When you deploy SNMP in your environment, always make sure that you configure approved communities and SNMP management stations. Don't leave the default configuration because the default uses the Public community name and allows any SNMP management stations to manage SNMP agents on the network.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 172