Tool 82: Forced Choice
| AKA | Forced Comparison |
| Classification | Decision Making (DM) |
Tool description
The forced choice technique is a team decision making process in which previously identified options are compared against team-established criteria. Criteria may include implementation time, cost of change, feasibility, effectiveness, and so on. Options are systematically compared with all other options, and a tally mark is assigned to the option considered best. Total marks for each option determine ranking.
Typical application
-
To identify a preferred alternative or choice on the basis of rating and ranking criteria.
-
To search for quick results and choices.
-
To arrive at a team decision from a list of options.
Problem-solving phase
| Select and define problem or opportunity | |
| → | Identify and analyze causes or potential change |
| → | Develop and plan possible solutions or change |
| Implement and evaluate solution or change | |
| Measure and report solution or change results | |
| Recognize and reward team efforts |
Typically used by
| Research/statistics | |
| Creativity/innovation | |
| Engineering | |
| 3 | Project management |
| Manufacturing | |
| Marketing/sales | |
| 2 | Administration/documentation |
| Servicing/support | |
| Customer/quality metrics | |
| 1 | Change management |
before
-
Brainstorming
-
Consensus decision
-
Starbursting
-
Problem selection matrix
-
Solution matrix
after
-
Numerical prioritization
-
Cost-benefit analysis
-
Resource Requirement Matrix
-
Factor analysis
-
What-if analysis
Notes and key points
-
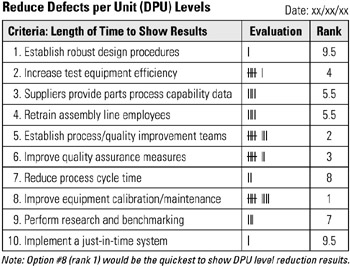
If two options receive the same number of evaluation marks (see this example, options number 3-4), then rank this tie as 5.5 for both to account for rank positions 5-6.
-
Lowest rank is considered best option.
Step-by-step procedure
-
STEP 1 The facilitator displays a list of previously recorded options for solutions or improvements. See example Reduce Defects per Unit (DPU) Levels.
-
STEP 2 Next, the facilitator asks participants if any of the options shown need clarification.
-
STEP 3 The criteria or standard for evaluation of options against each other is discussed and finalized.
-
STEP 4 The team starts to compare each option against all other options in descending order, for example, option 1 and option 2 as compared to stated criteria. Best option receives a tally mark. Continue with options 1 and 3, etc.
-
STEP 5 When all options have been compared with option 1, then option 2 is compared with all subsequent options and best options receive a mark. This process continues until all comparisons have been made.
-
STEP 6 The number of marks are totaled and the highest total is assigned rank 1. Rank 1 is the best option for lowering the DPU level quickly, as shown in this example.
Example of tool application
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 326
- Structures, Processes and Relational Mechanisms for IT Governance
- Integration Strategies and Tactics for Information Technology Governance
- An Emerging Strategy for E-Business IT Governance
- A View on Knowledge Management: Utilizing a Balanced Scorecard Methodology for Analyzing Knowledge Metrics
- Governance in IT Outsourcing Partnerships