How Validation Works
Validation in InfoPath is used to check values entered against some criteria that the form designer has established. This criteria could be used to enforce something very simple, like making the user fill out all the blank fields in a form, or it could be used to check values against certain company policies using a complex, compound set of criteria. When the criteria is true, an error message is generated, allowing the user to correct the problem before submitting or saving the form.
This criteria is called a validation rule, which is created within InfoPath using a standard set of validation operators (explained later in the chapter, in the section “Using Validation Operators”). You can use these operators to create complex sets of validation criteria—when the criteria is true, a validation error will occur.
Validation errors within an InfoPath form can manifest themselves in two ways. The first is with an inline error message, like the one shown in the illustration. If a control is marked as “Can’t be blank,” an inline error message appears as a red underline “in line” with the field where the error has occurred.
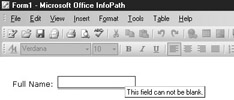
Otherwise, the inline error appears as a red-dashed border around the control. As a user moves their mouse over the field, ScreenTips text appears with an error message that the form designer has specified. The user can also right-click the field in question and obtain the full error description (which has also been specified by the form designer).
The other method used to display validation errors is a standard Windows dialog box that displays some text that the form designer has specified, as shown in Figure 9-1.
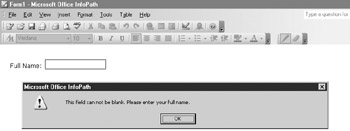
Figure 9-1: An example of a dialog box alert
For larger or complex forms with a number of different data entry controls, the dialog box method can quickly draw attention to validation errors, but the inline method also has the advantage of being unobtrusive. Regardless of which method you decide to use, validation rules are created in the same way, which is what you will be looking at in the following sections.
| Note | You may also notice that you can perform validation by using scripting within InfoPath. If you are interested in using this method of validation, check out Chapter 10, which covers this and other scripting applications. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 142