WORKERS AND ARTIFACTS
WORKERS AND ARTIFACTS
In the Rational Unified Process, how is all this translated concretely into terms of workers, artifacts, activities, and workflow? Figure 13-5 shows workers and artifacts in the configuration and change management workflow. The main workers involved in configuration and change management are as follows :
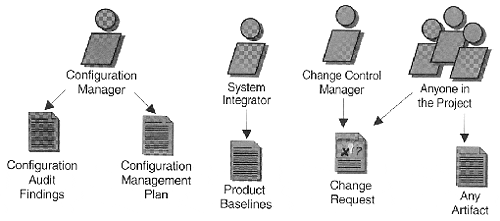
Figure 13-5. Workers and artifacts in the configuration and change management workflow
-
The Configuration Manager is responsible for setting up theproduct structure in the CM system, for defining and allocating workspaces for developers, and for integration. The Configuration Manager also extracts the appropriate status and metrics reports for the Project Manager.
-
The Change Control Manager oversees the change control process. This role is usually played by a Configuration, or Change, Control Board (CCB), which should consist of representatives from all interested parties, including customers, developers, and users. In a small project, a single person, such as the project manager or software architect, may play this role. The Change Control Manager is also responsible for defining the Change Request Management process, which should be documented in the CM plan.
The following workers are also involved in this workflow:
-
Implementers access adequate workspace and the artifacts they need to implement the changes for which they are responsible.
-
Integrators accept changes in the integration workspace and build the product.
-
Any worker can submit a change request.
-
The architect provides input to the product structure by means of the implementation view.
The Change Control Board is a group of various technical and managerial stakeholders, such as the Project Manager, the Architect, the Configuration Manager, and any stakeholder (customer representative, marketing personnel, and so on). The role of the CCB is to assess the impact of changes, determine priorities, and approve changes.
The key artifacts of configuration and change management are as follows:
-
The configuration management plan
The CM plan describes the policies and practices to be used on the project for CM: versions, variants, workspaces, and procedures for change management, builds, and releases. The CM plan defines the rules and responsibilities for the CCB. It is a part of the software development plan.
-
Change requests
Change requests may be of a wide variety: they may document defects, changes to requirements, or the delta from one iteration to the next . Each change request is associated with an originator and a root cause. Later, impact analysis attaches the impact of the change in terms of affected artifacts, cost, and schedule. As the change request evolves, its state changes; history items, in particular the CCB decisions, are attached to it.
In addition, this workflow includes the following:
-
The implementation model drives the product used by the configuration manager to set up the CM environment.
-
Metrics and status reports
are extracted from the CM and CRM support environment to be included in status assessment reports.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 176
- Step 2.1 Use the OpenSSH Tool Suite to Replace Clear-Text Programs
- Step 3.2 Use PuTTY / plink as a Command Line Replacement for telnet / rlogin
- Step 3.4 Use PuTTYs Tools to Transfer Files from the Windows Command Line
- Step 4.3 How to Generate a Key Pair Using OpenSSH
- Step 4.6 How to use PuTTY Passphrase Agents