| There are many means by which you can modify framesets and frame elements in the frameset. Modifying the Frameset Element To make any modifications to your frameset, open the frameset file and select the frameset in the Document window (click a frame border), or use the Frames panel (easier) by clicking on the frame and then clicking the <frameset> tag selector button for the appropriate parent frameset. Use the Property inspector to make any desired changes (see Figure 9.7). Figure 9.7. When a frameset document is open and the frameset is selected, the Property inspector makes frameset- related options available. 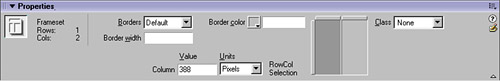 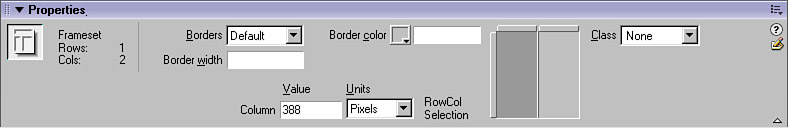
Modifying Frame Elements in the Frameset How you set up your frames is important because the information in the frame element relates to the way in which these elements will behave. Dreamweaver MX 2004 Frame Options in the Property Inspector The following list discusses several frame properties of interest. -
FrameName ” The name a link's target attribute or a script uses to refer to the frame. A frame name has to be a single word. When naming a frame, do not use periods (.), hyphens (-), or spaces. A frame name must start with a letter and not a numeral. Be aware that frame names are case sensitive. Don't use terms that are set aside for use in JavaScript (such as top or navigator ). -
Src ” Denotes the source document to display in the frame. Clicking the folder icon opens the Select HTML File dialog box, allowing you to browse and select a file. -
Scroll ” Indicates whether scroll bars appear in the frame. Attribute values available are Yes (scroll is always available when needed), No (scroll is never available), Auto (scroll available only when needed), and Default. When the Default setting is selected, it doesn't set a value for the corresponding attribute, which allows each browser to use its default value. Because most browsers default to Auto, the scroll bars appear only when there is not enough room in a browser window to display all the contents of the current frame. -
Borders ” Displays or hides the borders of the current frame when viewed in a browser. Attribute values available are Yes (provides a frame border), No (disallows a frame border), and Default. Most browsers default to showing borders, unless the parent frameset has Borders set to No. A border is hidden only when all frames that share the border have a Borders setting of No, or when the parent frameset's Borders property is set to No and the frames sharing the border have a Borders setting of Default. Selecting a Borders option for a frame from the Properties dialog box takes priority over the frameset's border settings. -
NoResize ” Stops visitors from resizing the frames in the browser. Turn on or off by checking. -
Border Color ” Adds a colored border to the frames. Clicking on the Color Box takes you to the Color Cubes color palette and the Continuous Tone palette, where you can use the eyedropper to choose a Web-safe color. All colors on the Color Cubes and Continuous Tone palettes are Web-safe. Clicking on the System Color Picker button takes you to the System Color Picker. This enables you to choose a custom color. Note that colors chosen from this palette are not Web-safe. The selected color applies to all borders that touch the frame, and overrides the frameset's specified border color. -
Margin Width ” Defines the width in pixels for the left and right margins and directly affects the space between the frame borders and the content. -
Margin Height ” Defines the width in pixels for the top and bottom margins and directly affects the space between the frame borders and the content. |