Working with the Group Policy Management Console
| Microsoft significantly improved the tools used to manage Group Policy with the 2003 server series. With the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), navigating and evaluating policy objects in Active Directory is a much simpler process. In an SBS environment, the GPMC can be used as a standalone console, or you can access it through the Server Management Console. Navigating the Group Policy Management ConsoleFigure 20.2 shows the GPMC snap-in in the Server Management Console. The GPMC has been expanded to the domain level so that you can see all the policy objects present at the domain level. Figure 20.2. The Group Policy Management Console snap-in is listed with other snap-ins under the Advanced Management section of the Server Management Console.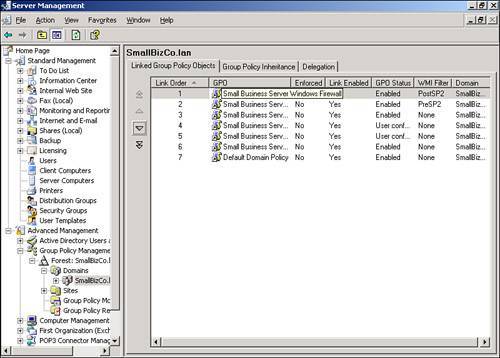 From this view, many of the properties of the policy objects can be seen, including the name of the GPO, whether the GPO is enabled or enforced, any WMI filters applied to the GPO, and the order in which the policy objects are applied. As shown in Figure 20.2, the first policy object processed, the Small Business Server Windows Firewall GPO, has the PostSP2 WMI filter set, meaning that only workstations running Windows XP SP2 or later will process the settings in that GPO. The fourth and fifth policies listed only contain computer configuration settings so the User Configuration settings have been disabled so that those objects will be skipped when the rest of the user settings are applied. Note The Group Policy Management Console can also be run outside the Server Management Console. Simply run gpmc.msc at a command prompt or in Start, Run to launch the GPMC. Figure 20.3 shows that you can browse the Active Directory OU structure to locate additional policies. In this case, Figure 20.3 shows two additional GPOs attached to the Domain Controllers OU. Figure 20.3. The browse tree in the left pane allows you to navigate the Active Directory structure to view GPO items.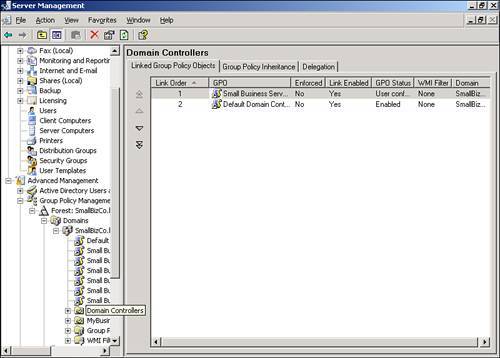 In addition, navigating the browse tree to the Group Policy Objects folder, shown in Figure 20.4, displays all the GPOs present in the Active Directory structure. Unfortunately, in this view, you cannot immediately tell where in the AD structure the GPOs are tied. Figure 20.4. The Group Policy Objects folder displays all the GPOs that exist in Active Directory.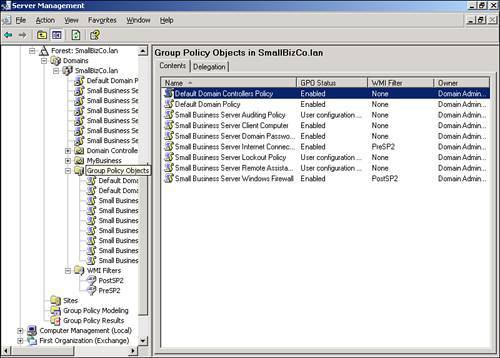 Viewing Group Policy SettingsThe Group Policy Management Console provides easy access to view all the settings for each GPO. Those who worked with Group Policy prior to the Windows Server 2003 series remember having to browse to an OU or domain (or suite) in Active Directory Users and Computers and selecting the correct options in the Group Policy tab under the object properties. The GPMC puts all the relevant settings of the GPO in one location for simple review. If you double-click on a GPO object listed in the GPO view shown previously in Figure 20.2, the GPMC displays the settings of the GPO, the details of which are described in the next section. Group Policy ScopeThe initial view of the GPO in the GPMC is shown in Figure 20.5. The Scope tab is initially displayed, which describes the details of how and where the GPO is applied. Figure 20.5. The Scope tab for each GPO indicates where the GPO is linked, what security filtering is applied, and what WMI filtering is applied, if any.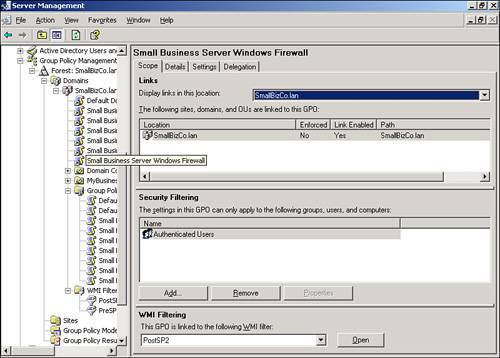 In Figure 20.5, the Small Business Server Windows Firewall GPO links to the domain, so its settings are applied to every user and computer in the domain. You can also quickly see that the GPO link is enabled but not enforced. Group Policy DetailsWhen you click on the Details tab, you see the view detailed in Figure 20.6. Figure 20.6. The Details tab gives technical information about the GPO.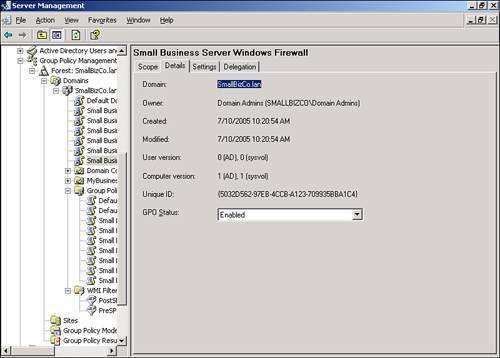 In the Details tab, you can see where the GPO is linked (SmallBizCo.lan), who owns the GPO (SMALLBIZCO\Domain Admins), when it was created and modified, the GUID for the object, and its enabled status. The versions for the user configuration and computer configuration are listed as well. In this example, the User Version shows 0 for AD and 0 for sysvol. This indicates that the user configuration for this GPO has not been modified from the original installation. The Computer Version shows 1 for AD and sysvol, indicating that one set of modifications has been saved to this GPO since it was originally created. Note If you see different version numbers between AD and sysvol, the GPO files stored on the sysvol share are out of sync with the GPO settings stored in Active Directory. You will not generally see this happen, however, unless an administrator has attempted to edit the GPO files in sysvol by hand. Group Policy SettingsClicking on the Settings tab displays the view shown in Figure 20.7. This is the view most administrators use when reviewing group policy settings. Figure 20.7. The Settings tab displays all the active settings in the selected GPO.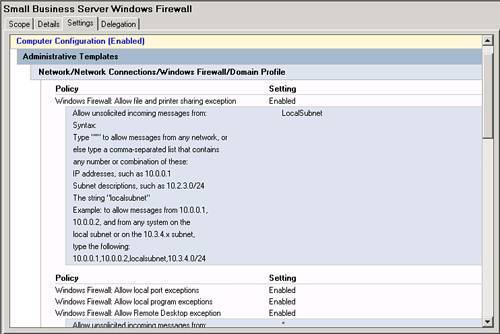 When you first select the Settings tab, the GPMC runs a report on the GPO settings to display them in the format shown in Figure 20.7. The settings are broken down into the group elements described in the "Group Policy Elements" section earlier in the chapter. In Figure 20.7, you can see the computer configuration settings start with settings in the Administrative Templates element. This means that no settings are defined in this GPO for the Software or Windows settings elements. The path to the setting in the GPO is also listed so that the first element listed, Windows Firewall: Allow File and Printer Sharing Exception, can be found by navigating the path Computer Configuration, Administrative Templates, Network, Network Connections, Windows Firewall, Domain Profile to find the specific policy. Figure 20.8 shows a better view of the settings included in the Small Business Server Windows Firewall GPO, specifically the Extra Registry Settings and that no user configuration settings are defined in this GPO. Figure 20.8. All the details for each policy setting defined are listed in this view.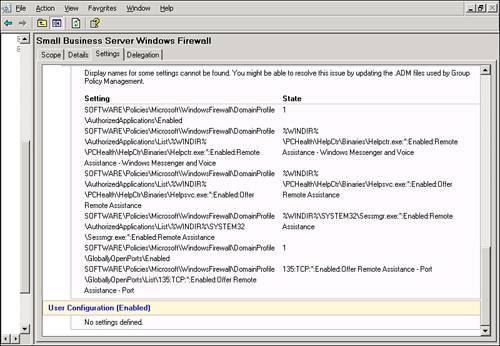 Group Policy DelegationThe last tab in this view, the Delegation tab shown in Figure 20.9, lists the permissions on the GPO enabled for the listed security groups. Figure 20.9. All the details for each policy setting defined are listed in this view.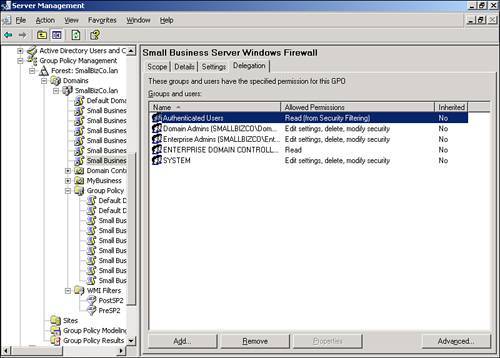 In Figure 20.9, the Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins, and SYSTEM objects have what amounts to full control over the selected GPO. The Authenticated Users and ENTERPRISE DOMAIN CONTROLLERS objects only have Read permissions on the GPO. Three levels of access can be assigned to a GPO. Read allows an object to see the contents of the GPO and determine, based on the settings on the GPO, whether the contents should be applied. Edit Settings allows an object to modify the policy settings within the GPO but not to modify the permissions on the GPO or remove it from the domain. Edit Settings, Delete, Modify Security allows the object to perform all actions on the GPO, including removing the object from the domain. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 253