Configuring Networking Settings
While Windows 2000 Setup prompts you for the necessary network settings, you might need to change these settings at some point after completing setup—possibly immediately, if the settings you specified were wrong or incomplete. This section explains how to get your server running properly on your network.
Changing Your Network Identity
Change is sometimes necessary—although with a server, it's better to spend your time planning first than to have to make changes later. However, as Robbie Burns often said while reconfiguring his server, "The best laid schemes o' mice and men gang aft a-gley." So even with careful planning, you can discover that a machine needs to have a different name or needs to be joined to a different domain.
Changing a Stand-Alone Server
To change the identity of a server that isn't a domain controller, log on using an administrator's account and follow these steps.
- Open the System tool in Control Panel, and then click the Network Identification tab.
- To change your computer name and domain or workgroup membership, select Properties. Then enter the new name for your computer in the New computer name text box in the Identification Changes dialog box, as shown in Figure 6-5.
- To change the domain or workgroup you belong to, choose either the Domain option or the Workgroup option, and then type the domain or workgroup name in the text box.
- Click More to manually specify the domain name for your computer and to preview the NetBIOS name for your system. Click OK when you're finished.
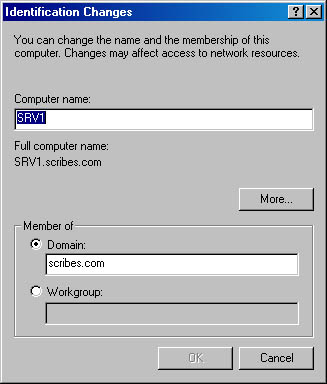
Figure 6-5. The Identification Changes dialog box.
![]()
REAL WORLD Naming Computers
It's a good idea to use a computer name that is both DNS-compatible and NetBIOS-compatible so that all types of clients see the same name for your computer. To do this, keep the name shorter than 15 characters long, and don't use asterisks or periods. To obtain the best application compatibility, also try to avoid using spaces, underscores, and hyphens.
![]()
NOTE
Changing the identity of a domain controller is a multistep process. First you must demote the domain controller. Then you can change the identity, and finally, you can promote the domain controller again. The steps for this process are detailed in Chapter 11.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 366