36.3 HOMERF
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
36.3 HOMERF
In many homes, there will be multiple PCs and a number of peripherals such as printers, modems, variety of telephones such as fixed telephones, cordless telephones and mobile telephones. In such homes, a low-cost solution to network PCs and peripherals is required. With such a network, we can develop applications such as:
-
Operating home appliances (air conditioner, music player, etc.) through a cordless phone.
-
Sharing the same modem and telephone line to access the Internet from two or more computers.
-
Exchanging data between two PCs or a PC and a laptop.
-
Forwarding calls to different cordless handsets.
-
Backing up of data of a PC without wiring up two PCs.
Home networks are now gaining popularity to support such applications. Though wired networks based on standards such as IEEE 1394 are available, wireless home networks are more attractive because of ease of use, fast installation, and easier maintenance. The two standards that have been proposed for wireless home networks are IEEE 802.11b and HomeRF.
Shared wireless access protocol (SWAP) sponsored by the HomeRF working group (http://www.homerf.org), provides a low-cost solution to home networking requirements. The broad specifications of this standard are:
-
Range: Up to 150 feet (covering a home, backyard and garage).
-
No. of devices: Up to 127 per network.
-
Frequency band: 2.4GHz (ISM band).
-
Transmit power: 100 mW.
-
Speed: 10Mbps peak data rate with fallback mode to 5Mbps, 1.6Mbps, 0.8Mbps. For 10Mbps data rate, 15 5MHz channels are used and for 1.6Mbps data rate, 75 1MHz channels are used.
-
Access: Frequency hopping spread spectrum with 50 hops per second.
The protocol stack for the HomeRF system is shown in Figure 36.6. It uses the TCP layer above the IP for regular data services, UDP for audio and video streaming applications and, above the MAC layer, DECT (digital enhanced cordless telecommunications) standards for toll quality voice applications.
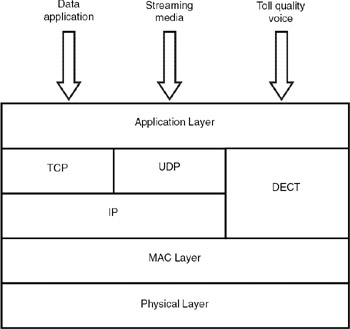
Figure 36.6: HomeRF protocol layers.
Physical layer: The physical layer specifications are: 10Mbps peak data rate with fallback modes to 5Mbps, 1.6Mbps, 0.8Mbps. Data is modulated using constant envelope FSK modulation technique and transmitted over the 2.4GHz channel using frequency hopping.
HomeRF is a radio technology to interconnect various home appliances. It operates in the 2.4GHz ISM band with speeds up to 10Mbps. A HomeRF network can support up to 127 devices.
MAC layer: For data and streaming audio/video applications, CSMA/CA protocol is used. For voice applications, reservation TDMA is used. The bulk of the MAC frame is used for data communication, but the streaming media services get priority. Based on the number of voice calls, time is reserved for voice slots. If voice packets fail, they can be resent at the start of the next frame.
As shown in Figure 36.7, the HomeRF network consists of a connection point (CP) and different home devices. The CP is connected to the Internet or the fixed network on one side and communicates with the home devices (such as laptop, PC, audio headset, and cordless handset through the radio medium. A network can support a maximum of 127 nodes. The nodes of the network can be of four types:
-
Connection point that supports both voice and data services.
-
Voice terminals, which use TDMA to communicate with the base station.
-
Data nodes, which use CSMA/CA to communicate with the base station or other devices.
-
Voice and data nodes, which can support both types of services.
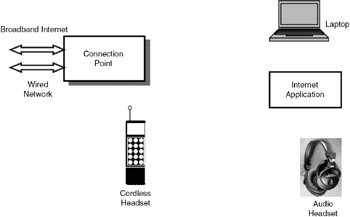
Figure 36.7: HomeRF network.
Up to eight simultaneous streaming media sessions and up to eight simultaneous toll-quality two-way cordless device connections are supported.
Each network is given a 48-bit ID, so the concurrent operation of multiple collocated networks is possible. The network ID, frequency hopping, and 128-bit data encryption provide the necessary security for the network and the data.
HomeRF technology holds lot of promise but, perhaps because of the competition from other technologies, the standardization committee was disbanded in January 2003.
HomeRF supports data and voice services. For voice services, the TDMA access mechanism is used, and for data services, CSMA/CA access mechanism is used.
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 313