Chapter 26: Tripwire
|
Tripwire is a program that monitors the reliability of critical system files and directories by identifying changes made to them. Tripwire configuration options include the ability to receive alerts via e-mail if particular files are altered and automated integrity checking via a cron job. Using Tripwire for intrusion detection and damage assessment helps you keep track of system changes. Because Tripwire can positively identify files that have been added, modified, or deleted, it can speed recovery from a break-in by keeping the number of files that must be restored to a minimum.
Tripwire compares files and directories against a database of file locations, dates modified, and other data. The database contains baselines, which are snapshots of specified files and directories at a specific point in time. The contents of the baseline database should be generated before the system is at risk of intrusion. After creating the baseline database, Tripwire then compares the current system with the baseline and reports any modifications, additions, or deletions.
While Tripwire is a valuable tool for auditing the security state of Red Hat Linux systems, Tripwire is not supported by Red Hat, Inc. Refer to the Tripwire project’s website (http://www.tripwire.org) for more information about Tripwire.
How to Use Tripwire
Figure 26-1 illustrates how Tripwire works.
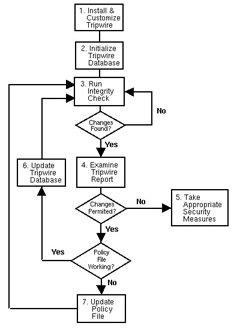
Figure 26-1: Using Tripwire
The following describes in more detail the numbered blocks shown in Figure 26-1.
-
Install Tripwire and customize the policy file. Install the tripwire RPM (see the section “Installing the Tripwire RPM”). Then, customize the sample configuration and policy files (/etc/tripwire/twcfg.txt and /etc/tripwire/twpol.txt, respectively) and run the configuration script, /etc/tripwire/twinstall.sh. For more information, see the section “Customizing Tripwire.”
-
Initialize the Tripwire database. Build a database of critical system files to monitor based on the contents of the new, signed Tripwire policy file, /etc/tripwire/tw.pol. For more information, see the section “Initializing the Tripwire Database.”
-
Run a Tripwire integrity check. Compare the newly created Tripwire database with the actual system files, looking for missing or altered files. For more information, see the section “Running an Integrity Check.”
-
Examine the Tripwire report file. View the Tripwire report file using /usr/sbin/twprint to note integrity violations. For more information, see the section “Viewing Tripwire Reports.”
-
If unauthorized integrity violations occur, take appropriate security measures. If monitored files have been altered inappropriately, you can either replace the original files from backup copies, reinstall the program, or completely reinstall the operating system.
-
If the file alterations were valid, verify and update the Tripwire database file. If the changes made to monitored files are intentional, edit Tripwire’s database file to ignore those changes in subsequent reports. For more information, see the section “Updating the Tripwire Database.”
-
If the policy file fails verification, update the Tripwire policy file.
To change the list of files Tripwire monitors or how it treats integrity violations, update the supplied policy file (/etc/tripwire/twpol.txt), regenerate a signed copy (/etc/tripwire/tw.pol), and update the Tripwire database. For more information, see the section “Updating the Tripwire Policy File.” Refer to the appropriate sections within this chapter for detailed instructions on each step.
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 278