Slow Networking Services
| |
When services on a network start to slow down, trouble is surely just around the corner. When this happens, it's possible that disk space on the server is running low, memory needs to be reconfigured, or a token ring board has gone bad and broken the ring. If the NICs in the server aren't capable of handling a lot of traffic, think about upgrading to higher performance NICs. Don't use old 8-bit NICs for your server; use 32-bit NICs at the very minimum.
Hark! I hear a board beaconing
Token ring is a funny creature because it forms a ring, and the data travels around the ring in a circular fashion. When a break in the ring occurs, data travels in a U shape instead. People located at the bottom of the U don't notice the slowdown as much, but those located at the tops see a tremendous slowdown . A token ring break typically happens when wiring gets out of whack or when one NIC starts beaconing. (This means the NIC is sending a signal that something is wrong with it.) If you use hubs that aren't intelligent , or Multistation Access Units (MAUs), you have to isolate the bad token ring board or port on the MAU by a process of elimination . We've had to take an entire ring and unplug one MAU at a time, and then unplug one port at a time. The older MAUs are actually relays, and you have to use a MAU tool to reset the relay. Other times, you need to replace the faulty NIC.
Oh where, oh where has the bandwidth gone?
You should check to see whether an application running on the network is consuming a lot of bandwidth. Applications consuming a lot of bandwidth occur frequently in 10-Mbps (10MB per second) Ethernet environments in which you have a lot of network activity and database applications. In some poorly designed database applications, when a user makes a database query, the entire contents of the database are downloaded to the user's workstation for processing. This creates a lot of extraneous traffic. To help alleviate this problem, you can upgrade to database software that has a database engine to do the record crunching ; the user gets only the results. Another solution to this problem is to upgrade to a faster network-wiring scheme, such as 100-Mbps Ethernet.
High-volume printing can also cause this problem. If certain users or groups of users are printing volumes of data during the day, think about switching them to print at night (if possible) to alleviate network congestion. You can set up a print definition for those users that allows their information to be printed only during certain hours.
Some organizations elect to upgrade their existing network backbone to help relieve bandwidth congestion problems, but the associated cost is high. Organizations that have remote offices sometimes place an extra Windows 2003 Server in the remote office and install it as a domain controller. This allows user authentication to be performed locally at the remote office, which conserves WAN bandwidths. Other organizations elect to upgrade their current network backbone to 100 Mbps while leaving the users connected to the hubs at 10 Mbps. This involves upgrading the devices connected to the backbone to include 100-Mbps NICs and cables, plus adding a switch capable of changing between the workstation speed of 10 Mbps to the backbone speed of 100 Mbps. With this arrangement, even if users are going full throttle , the server still has 90-percent bandwidth available for other clients .
Congestion on the network
If you have an Ethernet network that's experiencing lots of collisions and errors, there could be a problem with the Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) media access method. If you have intelligent hubs on the network, you can view information about the network either through a graphical interface or by looking at the LEDs on the hubs. A high collision rate is usually an indication of faulty wiring or bad boards . It can also mean that the bandwidth utilization is high. Ethernet has a lower utilization than token ring. Sometimes you need to segment off high-volume users.
Where did all the disk space go?
If your server's disk space is low, you're in for a fair amount of trouble because servers can contain print queues, as well as user's data and applications. When disk space begins to run low, all sorts of strange problems appear. You should buy a lot of RAM up front, because Windows 2003 uses much more than its predecessor, Windows NT. If you have the minimum RAM required by Microsoft, you'll run into problems trying to do more than one task, so add lots more on top of the minimum.
Windows 2003 uses disk space to swap recently used information back and forth from RAM. Therefore, if you have more RAM, you'll be able to access files faster. You can look at your memory information and how it's being used by choosing Start All Programs Accessories System Tools System Information System Summary.
Low disk space causes Windows 2003 to encounter difficulties when trying to write to the Pagefile.sys file. To view and change the minimum and maximum size of this file, choose Start Control Panel System, click the Advanced tab, and then click the Settings button under the Performance heading. In the Performance Options dialog box that appears, click the Advanced tab, then click the Change button under the Virtual Memory heading. You see a screen similar to the one shown in Figure 20-4.
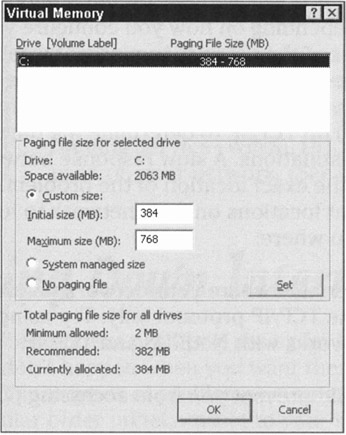
Figure 20-4: The Virtual Memory dialog box.
You should have at least the same minimum and maximum numbers that Windows 2003 recommends.
Do it after hours
Is someone performing a network task that's transferring a large amount of data, such as restoring a lot of files? Or is someone performing a function such as remirroring drives? If a network has large storage drives that are mirrored and the mirroring breaks, you can remirror the drives , but doing it during working hours isn't a good idea. Check to see whether anyone is performing some sort of maintenance - either on the network or the server. If a large restoration of files is required across the network, try to do it during nonpeak hours.
If you check in System Monitor and see a heavy resource load, you can get a better handle on who's placing that load by choosing Start Administrative Tools Computer Management, expanding System Tools Shared Folders, and checking the resource usage per share, per person.
| |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 195