6.7 CORE SHDSL Framer (PMS-TC)
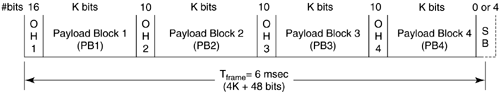
6.7 CORE SHDSL Framer (PMS-TC)The structure of the SHDSL core frame is based on the superframe structure of HDSL2 as described in Chapter 4. This section briefly describes the SHDSL core frame per Recommendation G.991.2. Figure 6.19 shows the core SHDSL physical layer superframe. The nominal frame period ( T frame ) is 6 msec. There are four blocks for payload data bits identified as PB1 “PB4. Because the line bit rate is variable, the number of bits in an SHDSL superframe will depend on the payload bit rate. Figure 6.19. SHDSL core frame structure. There are also five subblocks allocated for overhead bits labeled as OH1 “OH4 and block SB (stuff bits). OH1 has 16 bits, OH2 “OH4 each has 10 bits, and the SB block has nominally 2 bits, but the size may vary between 0 and 4 bits. Note, however, that for the nominal superframe there are nominally 48 bits in the overhead channel. The following is a summary of the overhead bit definitions.
The six CRC bits are used for performance monitoring of the subscriber line. The six CRC check bits, crc-1 “crc-6, are those associated with the contents of the previous SHDSL superframe. The CRC is computed over all of the bits in the superframe except for the 14 sync word bits, the 6 CRC bits, and the nominally 2 SBs; hence, the data message contains 4K + 26 bits. The message polynomial is constructed such that first CRC computable bit is the coefficient of the term x 4K+25 , and the last bit is the coefficient of the term x . The polynomial is then multiplied by a factor of x 6 , and the result is divided (modulo-2) by the generator polynomial x 6 + x + 1. The coefficients of the remainder polynomial are used in the order of occurrence as the ordered set of check bits crc-1 “crc-6. In the remainder polynomial, the coefficient of the term x 5 is crc-1 and that for the term x is crc-6. The embedded operations channel has 24 bits allocated in a 6 msec frame. This corresponds to a 4 kb/s clear data communications channel. This channel is used to pass operations and maintenance information between the CO and CP HDSL2 transceiver units. |
| Top |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 154
- Measuring ROI in E-Commerce Applications: Analysis to Action
- Technical Issues Related to IT Governance Tactics: Product Metrics, Measurements and Process Control
- Governing Information Technology Through COBIT
- The Evolution of IT Governance at NB Power
- Governance Structures for IT in the Health Care Industry