U
U
u- prefix A letter sometimes substituted for the Greek letter m (mu), meaning micro, used as a prefix in measurements denoting one millionth, or 10-6. See also micro- (definition 2).
UA n. See user agent.
UART n. Acronym for universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter. A module, usually composed of a single integrated circuit, that contains both the receiving and transmitting circuits required for asynchronous serial communication. A UART is the most common type of circuit used in personal computer modems. Compare USRT.
ubiquitous computing n. A term coined by Mark Wieser (1988) at the Xerox PARC Computer Science Lab to describe a computing environment so pervasive in daily life that it s invisible to the user. Household appliances such as VCRs and microwave ovens are contemporary low-level examples of ubiquitous computing. In the future, prognosticators say, computers will be so embedded in all facets of life so ubiquitous that their presence will fade into the background. Ubiquitous computing is considered to be the third stage in the evolution of computing technology, after the mainframe and the personal computer. Acronym: UC.
UC n. See ubiquitous computing.
UCAID n. Acronym for University Corporation for Advanced Internet Development. An organization created to provide guidance in advanced networking development within the university community. UCAID is responsible for the development of the Abilene fiber-optic backbone network that will interconnect over 150 universities into the Internet2 project.
UCE n. Acronym for unsolicited commercial e-mail. See spam.
UCITA n. Acronym for Uniform Computer Information Transactions Act. Legislation proposed or enacted in several states that will set legal standards and control systems for dealing with computer information. UCITA is a model law intended as an amendment to the Uniform Commercial Code to cover new technology-related issues. One of UCITA s main provisions is a standard for mass market software shrinkwrap and clickwrap agreements. See also clickwrap agreement, shrinkwrap agreement.
UCSD p-system n. A portable operating system and development environment that was developed by Kenneth Bowles at the University of California at San Diego. The system was based on a simulated, 16-bit, stack-oriented pseudomachine. The development environment included a text editor and compilers for several languages, such as FORTRAN and Pascal. Programs written for a p-system were more portable than programs compiled to machine language. See also bytecode, pseudomachine, p-system, virtual machine.
UDDI n. Acronym for Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration. A platform-independent framework functioning like a directory (similar to a telephone book) that provides a way to locate and register Web services on the Internet. The UDDI specification calls for three elements: white pages, which provide business contact information; yellow pages, which organize Web services into categories (for example, credit card authorization services); and green pages, which provide detailed technical information about individual services. The UDDI also contains an operational registry, which is available today.
UDP n. Acronym for User Datagram Protocol. The connectionless protocol within TCP/IP that corresponds to the transport layer in the ISO/OSI reference model. UDP converts data messages generated by an application into packets to be sent via IP, but it is unreliable because it does not establish a path between sender and receiver before transmitting and does not verify that messages have been delivered correctly. UDP is more efficient than TCP, so it is used for various purposes, including SNMP; the reliability depends on the application that generates the message. See also communications protocol, ISO/OSI reference model, packet, SNMP, TCP/IP. Compare IP, TCP.
UDT n. Acronym for uniform data transfer. The service used in the OLE extensions to Windows that allows two applications to exchange data without either program knowing the internal structure of the other.
UI n. See user interface.
UKnet n. 1. The University of Kentucky s campus network. 2. In the United Kingdom, an Internet service provider (ISP) based at the University of Kent. See also ISP.
ULSI n. See ultra-large-scale integration.
UltimateTV n. A television digital recording technology developed by Microsoft. UltimateTV can record up to 35 hours of DIRECTV broadcasts. Because the television signal is recording on UltimateTV s hard drive, viewers can pause a live show, rewind scenes, and watch previously shown parts of the show in slow or fast motion while UltimateTV records the remainder of the show live.
Ultra DMA/33 n. A data transfer protocol, based on direct memory access, for transferring data between a hard drive and a computer s RAM. Ultra DMA/33 improves ATA/IDE performance, doubles burst transfer rates to 33 megabytes per second, and increases data transfer integrity. See also ATA, direct memory access, IDE (definition 1).
ultrafiche n. Microfiche with very high density. The image in ultrafiche is reduced at least 90 times from its original size. See also microfiche.
ultra-large-scale integration n. The highest currently possible density at which components (transistors and other elements) are packed onto an integrated circuit. Ultra-large-scale is generally applied to component densities of 1,000,000 or greater. Acronym: ULSI. See also integrated circuit. Compare large-scale integration, medium-scale integration, small-scale integration, super-large-scale integration, very-large-scale integration.
ultralight computer n. See portable computer.
UltraSCSI n. An extension of the SCSI-2 standard that doubles the transfer speed of Fast-SCSI to allow a transfer rate of 20 megabytes per second (MBps) on an 8-bit connection and 40 MBps on a 16-bit connection. See also SCSI, SCSI-2.
Ultra Wide SCSI n. See UltraSCSI.
UMA n. 1. Acronym for upper memory area. The portion of DOS memory between the first 640K and 1 MB. Compare high memory area. 2. Acronym for Uniform Memory Architecture. See SMP.
UMB n. Acronym for upper memory block. A block of memory in the UMA (upper memory area) that can be used for device drivers or TSRs. A UMB is allocated and managed by special memory manager programs such as EMM386.EXE. See also device driver, TSR, UMA (definition 1).
UML n. Acronym for Unified Modeling Language. A language developed by Grady Booch, Ivar Jacobson, and Jim Rumbaugh of Rational Software that can be used for specifying, building, and documenting software and non-software systems, such as business models. UML notation provides a common foundation for object-oriented design by providing descriptions of modeling concepts including object class, associations, interface, and responsibility. The UML standard is supported by software developers and vendors and overseen by the Object Management Group (OMG).
UMTS n. Acronym for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System. Third-generation wireless communications standard developed to provide a consistent set of packet-based voice, text, video, and multimedia capabilities to users in any communications environment worldwide. When UMTS reaches full implementation, users will be able maintain computer and phone Internet connections from anywhere in the world.
unary adj. Of, pertaining to, or characteristic of a mathematical operation with a single operand (object); monadic. Compare dyadic.
unary operator n. An operator that takes only one operand for example, unary minus (as in 2.5). See also operator. Compare binary operator.
unbuffered adj. Of, pertaining to, or characteristic of something that does not store data characters in memory but instead processes them as they are received. See also buffer.
unbundle vb. To separate the items of a composite sales package; for example, to sell components of a software package separately rather than as a package. Compare bundle.
unbundled adj. Not included as part of a complete hardware/software package; the term particularly applies to a product that was previously bundled, as opposed to one that has always been sold separately.
UNC n. Acronym for Universal Naming Convention or, sometimes, Uniform Naming Convention. The system of naming files among computers on a network so that a file on a given computer will have the same pathname when accessed from any of the other computers on the network. For example, if the directory c:\path1\path2\...pathn on computer servern is shared under the name pathdirs, a user on another computer would open \\servern\pathdirs\filename.ext to access the file c:\path1\path2\...pathn\ filename.ext on servern. See also URL, virtual path.
uncompress vb. To restore the contents of a compressed file to its original form. Also called: decompress. Compare compress.
unconditional branch n. A transfer of execution to another line of code in a program without a check for some condition being true or false. The transfer always takes place whenever such an instruction is encountered. See also branch (definition 2). Compare conditional branch.
undelete1 n. The act of restoring deleted information. An undelete is comparable to (and usually included as part of) an undo command; it is more restricted, however, in that undo reverses any previous act, but undelete reverses only a deletion. Undelete generally refers only to excised text or deleted files. See also undo.
undelete2 vb. 1. To restore deleted information, usually the last item deleted. 2. In file storage, to restore a file s storage information so that a deleted file becomes available for access again. Also called: unerase. See also file recovery.
undeliverable adj. Not able to be delivered to an intended recipient. If an e-mail message is undeliverable, it is returned to the sender with information added by the mail server explaining the problem; for example, the e-mail address may be incorrect, or the recipient s mailbox may be full.
undercolor separation n. In the CMYK color model, the process of converting equal quantities of cyan, magenta, and yellow to equivalent gray levels, which are then printed in black ink. This produces grays that are clearer and sharper than those produced by mixing colored inks. See also CMY, CMYK, color model.
underflow n. A condition in which a mathematical calculation produces a result too near to zero to be represented by the range of binary digits available to the computer for holding that value in the specified precision. See also precision (definition 2), single-precision.
underline vb. To format a selection of text so that the text is printed with a line slightly below it.
Undernet n. An international network of Internet Relay Chat (IRC) servers created in 1992 as an alternative to the larger and more chaotic main IRC network. For information about connecting to Undernet, see http://www.undernet.org. See also IRC.
underscore n. An underline character often used to emphasize a letter or a word; on nongraphics displays, generally used to indicate italic characters.
undo vb. To reverse the last action for example, to undo a deletion, thus restoring deleted text to a document. Many application programs enable the user both to undo and to redo an action. See also undelete (definition 1).
undock vb. 1. To detach a laptop or other portable computer from a docking station. See also docking station, laptop. 2. To move a toolbar from the edge of a window so that the toolbar becomes its own free-floating window. See also toolbar.
unerase n. See undelete1.
unfold adj. See inline (definition 1).
unhandled exception n. An error condition that an application does not internally resolve. When an unhandled exception occurs, the operating system terminates the application that caused the error.
Unibus n. A bus architecture introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation in 1970.
unicast vb. To transmit between a single sender and a single receiver over a network. A two-way, point-to-point transmission, unicast is typical of network communications. Compare anycasting, narrowcast.
Unicode n. A 16-bit character encoding standard developed by the Unicode Consortium between 1988 and 1991. By using 2 bytes to represent each character, Unicode enables almost all the written languages of the world to be represented using a single character set. (By contrast, 8-bit ASCII is not capable of representing all the combinations of letters and diacritical marks that are used just with the Roman alphabet.) Approximately 39,000 of the 65,536 possible Unicode character codes have been assigned to date, 21,000 of them being used for Chinese ideographs. The remaining combinations are open for expansion. Compare ASCII.
unified messaging n. The integration of various communications technologies such as voicemail, fax, and e-mail into a single service. Unified messaging is designed to be a time-saving tool to provide users with a single package with which they can receive, organize, and respond to messages in a variety of media.
Unified Modeling Language n. See UML.
Uniform Computer Information Transactions Act n. See UCITA.
Uniform Data Transfer n. See UDT.
Uniform Memory Access n. See SMP.
Uniform Naming Convention n. See UNC.
Uniform Resource Citation n. A description of an object on the World Wide Web, consisting of pairs of attributes and their values, such as the Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) of associated resources, author names, publisher names, dates, and prices. Acronym: URC.
Uniform Resource Identifier n. A character string used to identify a resource (such as a file) from anywhere on the Internet by type and location. The set of Uniform Resource Identifiers includes Uniform Resource Names (URNs) and Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). Acronym: URI. See also relative URL, Uniform Resource Name, URL.
Uniform Resource Locator n. See URL.
Uniform Resource Name n. A scheme for uniquely identifying resources that might be available on the Internet by name, without regard to where they are located. The specifications for the format of Uniform Resource Names are still under development by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). They include all Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) having the schemes urn:, fpi:, and path:; that is, those that are not Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). Acronym: URN. See also IETF, Uniform Resource Identifier, URL.
UniForum n. 1. The International Association of Open System Professionals, an organization of UNIX users and administrators. 2. A series of UNIX trade shows sponsored by UniForum and managed by Softbank COMDEX, Inc. See also COMDEX.
Unimodem n. 1. The universal modem driver, provided with Windows CE, that translates Telephony Service Provider Interface (TSPI) calls into AT commands and sends the commands to a virtual device driver that talks to the modem. 2. A universal modem that supports standard modem AT commands. Windows CE currently supports only PCMCIA modems.
uninstall vb. To remove software completely from a system, including the elimination of files and components residing in system locations such as the registry in Windows 9x, Windows NT, or Windows 2000. Some applications have built-in uninstall utilities, and in other cases a separate uninstall program can be used. Also called: deinstall.
uninterruptible power supply n. See UPS.
union n. 1. In set theory, the smallest combination of two sets that contains all elements of both sets. 2. In logic, an inclusive OR operation that is, the result, C, of any union of A and B is true (1) except when A and B are both false (0). See the table. 3. In programming, a structure that can be used to store different types of variables (such as integer, character, or Boolean). 4. In database management, a relational operator. Given two relations (tables), A and B, that are union-compatible (contain the same number of fields, with corresponding fields containing the same types of values), A UNION B builds a new relation containing those tuples (records) that appear either in A or in B or in both. Compare difference, intersect.
A OR B = C 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0
union-compatible adj. In database management, of, pertaining to, or characteristic of two relations (tables) that are of the same order (have the same number of attributes) and whose corresponding attributes are based on the same domain (the set of acceptable values).
unipolar adj. Having one state. In electronics, a unipolar device or signal is one in which the same voltage polarity (positive or negative) is used to represent binary states on/off or true/false. Compare bipolar.
unique user n. An individual visitor to a Web site. Tracking unique users is important in ascertaining the success of a given Web site because it indicates how many different visitors access the site, as opposed to the number of hits visits by the same or different individuals the site receives. Also called: unique visitor.
unique visitor n. See unique user.
United States of America Standards Institute n. The former name of the American National Standards Institute. See also ANSI.
unit position n. The one s place in a multiple-digit number for example, the 3 in the number 473.
UNIVAC I n. Short for Universal Automatic Calculator I. The first commercially available electronic computer, designed by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, also the inventors of ENIAC (generally considered the first fully electronic computer). UNIVAC I was the first computer to handle both numeric and textual information.
universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter n. See UART.
Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration n. See UDDI.
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System n. See UMTS.
Universal Naming Convention n. See UNC.
Universal Plug and Play n. See UPnP.
Universal Plug and Play Forum n. See UPnP Forum.
Universal Plug and Play networking n. See UPnP networking.
Universal Product Code n. See UPC.
Universal Resource Locator n. See URL.
universal serial bus n. See USB.
Universal Server n. 1. Software from Oracle Corporation that supplies information from its database in a variety of forms, such as text, sound, and video, in response to HTTP requests. 2. Database software from Informix that works with snap-in software modules to handle user needs for specific data types and ways of processing.
universal synchronous receiver-transmitter n. See USRT.
Universal Time Coordinate n. For all practical purposes, the same as Greenwich Mean Time, which is used for the synchronization of computers on the Internet. Acronym: UTC. Also called: coordinated universal time format.
University Corporation for Advanced Internet Development n. See UCAID.
UNIX n. A multiuser, multitasking operating system. Originally developed by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie at AT&T Bell Laboratories from 1969 through 1973 for use on minicomputers, UNIX has evolved into a complex, powerful operating system that, because it is written in the C language, is more portable that is, less machine-specific than many other operating systems. UNIX has been released in a wide variety of versions, or flavors, including System V (developed by AT&T for commercial release; many current flavors on based on it), BSD UNIX (freeware developed at the University of California Berkeley, which has spun off many related flavors), AIX (a version of System V adapted by IBM to run on RISC-based workstations), A/UX (a graphical version for the Macintosh), Linux (a newer version that runs on the Intel chip), and SunOS (based on BSD UNIX and available on Sun workstations). Many flavors of UNIX are available free. With some flavors, the source code is also free, making it an instrumental part of the open source movement. UNIX is widely used as a network operating system, especially in conjunction with the Internet. See also BSD UNIX, Linux, open source, System V.
UNIX shell account n. A shell account providing command-line access to a UNIX system. See also shell account.
UNIX shell scripts n. Sequences of UNIX commands stored as files that can be run as programs. In MS-DOS, batch (.bat) files provide similar capabilities. See also batch file, shell, shell script.
UNIX-to-UNIX Copy n. See UUCP.
UNIX wizard n. A particularly expert and helpful UNIX programmer. Some companies actually use this phrase as a job title. The newsgroup comp.unix.wizards provides answers to many user questions.
unknown host n. A response to a request for a connection to a server that indicates that the network is unable to find the specified address. See also server (definition 1).
unknown recipients n. A response to an e-mail message that indicates that the mail server is unable to identify one or more of the destination addresses.
unload vb. 1. To remove a storage medium, such as a tape or disk, from its drive. 2. To remove software from system memory. See also memory.
unmanaged code n. Code that is executed directly by the operating system, outside of the common language run time environment. Unmanaged code must provide its own garbage collection, type checking, security support, and so on, unlike managed code, which receives these services from the common language runtime. See also managed code.
unmoderated adj. Of, pertaining to, or characteristic of a newsgroup or mailing list in which all articles or messages received by the server are automatically available or distributed to all subscribers. Compare moderated.
unmount vb. To remove a disk or tape from active use. Compare mount.
unpack vb. To restore packed data to its original format. Compare pack.
unpopulated board n. A circuit board whose sockets are empty. Compare fully populated board.
unread adj. 1. Of, pertaining to, or being an article in a newsgroup that a user has not yet received. Newsreader client programs distinguish between read and unread articles for each user and download only unread articles from the server. 2. Of, pertaining to, or being an e-mail message that a user has received but has not yet opened in an e-mail program.
unrecoverable error n. A fatal error one that a program is unable to recover from without the use of external recovery techniques. Compare recoverable error.
unreliable protocol n. A communications protocol that makes a best effort attempt to deliver a transmission but does not provide for verifying that the transmission arrives without error.
unroll adj. See inline (definition 1).
unset vb. To make the value of a bit position equal to 0. Compare set (definition 1).
unshielded cable n. Cable that is not surrounded with a metal shield. If the wires in an unshielded cable are not at least twisted around each other in pairs, the signals they carry have no protection from interference by external electromagnetic fields. Consequently, unshielded cable should be used only over very short distances. Compare coaxial cable, ribbon cable, twisted-pair cable, UTP.
unshielded twisted pair n. See UTP.
unshielded twisted-pair wiring n. See UTP.
unsolicited commercial e-mail n. See spam.
unsubscribe vb. 1. In a newsreader client program, to remove a newsgroup from the list of newsgroups to which one subscribes. See also newsgroup. 2. To remove oneself as a recipient on a mailing list. See also mailing list.
untar1 n. A utility, available for systems in addition to UNIX, for separating the individual files out of an archive assembled using the UNIX tar program. Compare tar1.
untar2 vb. To separate the individual files out of an archive assembled with the UNIX tar program. Compare tar2.
unzip vb. To uncompress an archive file that has been compressed by a program such as compress, gzip, or PKZIP.
up adj. Functioning and available for use; used in describing computers, printers, communications lines on networks, and other such hardware.
UPC n. Acronym for Universal Product Code. A system of numbering commercial products using bar codes. A UPC consists of 12 digits: a number system character, a five-digit number assigned to the manufacturer, a five-digit product code assigned by the manufacturer, and a modulo 10 check digit. See also bar code.
update1 n. A new release of an existing software product. A software update usually adds relatively minor new features to a product or corrects errors (bugs) found after the program was released. Updates are generally indicated by small changes in software version numbers, such as 4.0b from 4.0. See also version number. Compare release1.
update2 vb. To change a system or a data file to make it more current.
update query n. A database query that changes a set of records according to search conditions or criteria.
upflow n. In the data warehousing process, the stage during which stored information is checked for completeness, summarized, and readied for distribution. See also data warehouse. Compare downflow, inflow, metaflow.
upgrade1 n. The new or enhanced version of a product.
upgrade2 vb. To change to a newer, usually more powerful or sophisticated version.
uplink n. The transmission link from an earth station to a communications satellite.
upload1 n. 1. In communications, the process of transferring a copy of a file from a local computer to a remote computer by means of a modem or network. 2. The copy of the file that is being or has been transferred.
upload2 vb. To transfer a copy of a file from a local computer to a remote computer. Compare download.
UPnP n. Acronym for Universal Plug and Play. A Microsoft initiative which prompted the creation of the UPnP Forum for interconnecting computers, appliances, networks, and services. UPnP extends conventional Plug and Play to include devices connected to networks. It allows peripheral devices to discover and connect to other devices and to enumerate the characteristics of those devices. UPnP is intended to be an element of home networking, in which PCs, appliances, and the services they provide are linked together.
UPnP Device Architecture n. A specification developed by the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Forum that defines the structure of UPnP networking. The UPnP Device Architecture, formerly known as the DCP Framework, provides information about discovery, description, control, eventing, and presentation in a UPnP network. See also UPnP networking.
UPnP Forum n. A consortium of companies and individuals that oversees Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) specifications, protocols, logos, sample implementations, test suites, white papers, and other UPnP-related efforts. See also UPnP, UPnP Device Architecture, UPnP networking.
UPnP networking n. The peer-to-peer networking of intelligent machines, appliances, wireless devices, computers, and other devices according to the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Device Architecture. UPnP networking uses control points, devices, services, and protocols including GENA, SOAP, SSDP, standard TCP/IP, and other Internet protocols. See also UPnP Device Architecture.
uppercase adj. Of, pertaining to, or characterized by capital letters. Compare lowercase.
upper memory area n. See UMA (definition 1).
upper memory block n. See UMB.
UPS n. Acronym for uninterruptible power supply. A device, connected between a computer (or other electronic equipment) and a power source (usually an outlet receptacle), that ensures that electrical flow to the computer is not interrupted because of a blackout and, in most cases, protects the computer against potentially damaging events, such as power surges and brownouts. All UPS units are equipped with a battery and a loss-of-power sensor; if the sensor detects a loss of power, it switches over to the battery so that the user has time to save his or her work and shut off the computer. See also blackout, brownout.
upstream1 n. The direction in which information is delivered from a client to a (Web) server. Compare downstream1.
upstream2 adj. 1. The location of a server in relation to another server. Compare downstream (definition 1). 2. The direction in which data moves from an individual computer to the remote network. With certain communications technologies, such as ADSL, cable modems, and high-speed 56-Kbps modems, data flows upstream more slowly than downstream. For example, a 56-Kbps modem can deliver data at a 56-Kbps maximum only downstream; upstream, it delivers data at either 28.8 or 33.6 Kbps. Compare downstream2 (definition 2).
uptime n. The amount or percentage of time a computer system or associated hardware is functioning and available for use. Compare downtime.
upward-compatible adj. Of, pertaining to, or characteristic of a computer product, especially software, designed to perform adequately with other products that are expected to become widely used in the foreseeable future. The use of standards and conventions makes upward compatibility easier to achieve.
urban legend n. A widely distributed story that remains in circulation in spite of the fact that it is not true. Many urban legends have been floating around the Internet and other online services for years, including the request for cards for the sick boy in England (he s long since recovered and grown up), the cookie or cake recipe that cost $250 (it s a myth), and the Good Times or Penpal Greetings virus, which will infect your computer when you read an e-mail message (it does not exist). See also Good Times virus.
URC n. See Uniform Resource Citation.
URI n. See Uniform Resource Identifier.
URL n. Acronym for Uniform Resource Locator. An address for a resource on the Internet. URLs are used by Web browsers to locate Internet resources. A URL specifies the protocol to be used in accessing the resource (such as http: for a World Wide Web page or ftp: for an FTP site), the name of the server on which the resource resides (such as //www.whitehouse.gov), and, optionally, the path to a resource (such as an HTML document or a file on that server). See also FTP(definition 1), HTML, HTTP, path (definition 1), server (definition 2), virtual path (definition 1), Web browser.
URN n. See Uniform Resource Name.
usable adj. Of, pertaining to, or characteristic of the ease and adaptability with which a product can be applied to the performance of the work for which it is designed. A high degree of usability implies ease of learning, flexibility, freedom from bugs, and good design that does not involve unnecessarily complicated procedures.
usage analysis n. Data collected to evaluate how a Web site is being used, such as visitor user names, how often each page was visited, and the types of Web browsers used.
USB n. Acronym for universal serial bus. A serial bus with a data transfer rate of 12 megabits per second (Mbps) for connecting peripherals to a microcomputer. USB can connect up to 127 peripherals, such as external CD-ROM drives, printers, modems, mice, and keyboards, to the system through a single, general-purpose port. This is accomplished by daisy chaining peripherals together. USB is designed to support the ability to automatically add and configure new devices and the ability to add such devices without having to shut down and restart the system (hot plugging). USB was developed by Intel, Compaq, DEC, IBM, Microsoft, NEC, and Northern Telecom. It competes with DEC s ACCESS.bus for lower-speed applications. See also bus, daisy chain, hot plugging, input/output port, peripheral. Compare ACCESS.bus.
U.S. Department of Defense n. The military branch of the United States government. The Department of Defense developed ARPANET, the origin of today s Internet and MILNET, through its Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). See also ARPANET, Internet, MILNET.
Usenet or UseNet or USENET n. A worldwide network of UNIX systems that has a decentralized administration and is used as a bulletin board system by special-interest discussion groups. Usenet, which is considered part of the Internet (although Usenet predates it), is comprised of thousands of newsgroups, each devoted to a particular topic. Users can post messages and read messages from others in these newsgroups in a manner similar to users on dial-in BBSs. Usenet was originally implemented using UUCP (UNIX-to-UNIX Copy) software and telephone connections; that method remains important, although more modern methods, such as NNTP and network connections, are more commonly used. See also BBS (definition 1), newsgroup, newsreader, NNTP, UUCP.
Usenet User List n. A list maintained by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology that contains the name and e-mail address of everyone who has posted to the Usenet. See also Usenet.
user account n. On a secure or multiuser computer system, an established means for an individual to gain access to the system and its resources. Usually created by the system s administrator, a user account consists of information about the user, such as password, rights, and permissions. See also group1, logon, user profile.
user agent n. In the terminology established by the ISO/OSI reference model for LANs (local area networks), a program that helps a client connect with a server. Acronym: UA. See also agent (definition 3), ISO/OSI reference model, LAN.
user control n. In ASP.NET: A server control that is authored declaratively using the same syntax as an ASP.NET page and is saved as a text file with an .ascx extension. User controls allow page functionality to be partitioned and reused. Upon first request, the page framework parses a user control into a class that derives from System.Web.UI.UserControl and compiles that class into an assembly, which it reuses on subsequent requests. User controls are easy to develop due to their page-style authoring and deployment without prior compilation. In Windows Forms: A composite control that provides consistent behavior and user interface within or across applications. The user control can be local to one application or added to a library and compiled into a DLL for use by multiple applications.
User Datagram Protocol n. See UDP.
user-defined data type n. A data type defined in a program. User-defined data types are usually combinations of data types defined by the programming language being used and are often used to create data structures. See also data structure, data type.
user-defined function key n. See keyboard enhancer, programmable function key.
user-friendly adj. Easy to learn and easy to use.
user group n. A group of people drawn together by interest in the same computer system or software. User groups, some of which are large and influential organizations, provide support for newcomers and a forum where members can exchange ideas and information.
user-initiated update n. An operating system update mechanism, provided by the dial-up boot loader, which is designed to be used by remote users and field technicians. The operating system image is downloaded using a modem connection. See also automatic update, factory update.
user interface n. The portion of a program with which a user interacts. Types of user interfaces, or UIs, include command-line interfaces, menu-driven interfaces, and graphical user interfaces. Acronym: UI.
User Interface Toolbox n. See Toolbox.
username n. The name by which a user is identified to a computer system or network. During the logon process, the user must enter the username and the correct password. If the system or network is connected to the Internet, the username generally corresponds to the leftmost part of the user s e-mail address (the portion preceding the @ sign, as in username@company.com). See also e-mail address, logon.
user name n. The name by which a person is known and addressed on a communications network. See also alias (definition 2).
user profile n. A computer-based record maintained about an authorized user of a multiuser computer system. A user profile is needed for security and other reasons; it can contain such information as the person s access restrictions, mailbox location, type of terminal, and so on. See also user account.
user state n. The least privileged of the modes in which a Motorola 680x0 microprocessor can operate. This is the mode in which application programs are run. See also 68000. Compare supervisor state.
USnail n. 1. Slang for the United States Postal Service. USnail, a term used on the Internet, is a reference to how slow the postal service is in comparison to e-mail. 2. Mail delivered by the United States Postal Service. See also snail mail.
/usr n. A directory in a computer system that contains subdirectories owned or maintained by individual users of the computer system. These subdirectories can contain files and additional subdirectories. Typically, /usr directories are used in UNIX systems and can be found on many FTP sites. See also FTP site.
USRT n. Acronym for universal synchronous receiver- transmitter. A module, usually composed of a single integrated circuit, that contains both the receiving and transmitting circuits required for synchronous serial communication. Compare UART.
UTC n. See Universal Time Coordinate.
UTF-8 n. Acronym for UCS Transformation Format 8. A character set for protocols evolving beyond the use of ASCII. The UTF-8 protocol provides for support of extended ASCII characters and translation of UCS-2, an international 16-bit Unicode character set. UTF-8 enables a far greater range of names than can be achieved using ASCII or extended ASCII encoding for character data. See also ASCII, Unicode.
utility n. A program designed to perform a particular function; the term usually refers to software that solves narrowly focused problems or those related to computer system management. See also application.
utility program n. A program designed to perform maintenance work on the system or on system components (for example, a storage backup program, disk and file recovery program, or resource editor).
UTP n. Acronym for unshielded twisted pair. A cable containing one or more twisted pairs of wires without additional shielding. UTP is more flexible and takes up less space than shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable but has less bandwidth. See the illustration. See also twisted-pair cable. Compare STP. UTP.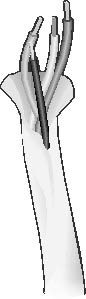
.uu n. The file extension for a binary file that has been translated into ASCII format using uuencode. Also called: . uud. See also ASCII, binary file, uuencode. Compare .uue.
UUCP n. Acronym for UNIX-to-UNIX Copy. A set of software programs that facilitates transmission of information between UNIX systems using serial data connections, primarily the public switched telephone network. See also uupc.
.uud n. See .uu.
uudecode1 n. A UNIX program that converts a uuencoded file back into its original binary format. This program (along with uuencode) allows binary data, such as images or executable code, to be disseminated through e-mail or newsgroups. Compare uuencode2.
uudecode2 vb. To transform a uuencoded file back into its binary original using the uudecode program. Compare uuencode2.
.uue n. The file extension for a file that has been decoded from ASCII format back into binary format using uudecode. See also ASCII, binary file, uudecode.
uuencode1 n. A UNIX program that converts a binary file, in which all 8 bits of every byte are significant, into printable 7-bit ASCII characters without loss of information. This program (along with uudecode) allows binary data, such as images or executable code, to be disseminated through e-mail or newsgroups. A file thus encoded is one-third again as long as the original. Compare uudecode.
uuencode2 vb. To transform a binary file into printable 7-bit ASCII text using the uuencode program. Compare uudecode2.
UUID n. Acronym for universally unique identifier. A 128-bit value that uniquely identifies objects such as OLE servers, interfaces, manager entry-point vectors, and client objects. Universally unique identifiers are used in cross-process communication, such as remote procedure calling (RPC) and OLE. Also called: GUID.
uupc n. The version of UUCP for IBM PCs and PC-compatibles running DOS, Windows, or OS/2. This version is a collection of programs for copying files to, logging in to, and running programs on remote networked computers. See also UUCP.
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 36