Section 13.3. SAP NetWeaver Business intelligence
|
|
13.3. SAP NetWeaver Business intelligenceSAP NetWeaver BI comprises a vast area of functionality that serves many different business needs. A large part of SAP NetWeaver BI is devoted to extracting data from many different sources, cleaning it, and normalizing it so that it can be used to model and analyze a business. This sounds similar to the role of SAP NetWeaver MDM, but SAP NetWeaver BI focuses primarily on transactional datathat is, the data that keeps track of every transaction, every purchase order, every invoice, and so on. Every instance of any activity that goes into a business may find its way into the data warehouse that is at the center of SAP NetWeaver BI, which can make for huge data volumes. Searching through such vast databases can require massive computing power. Explaining all of what SAP NetWeaver BI can do could fill several books. Our purpose in this chapter is to look at the way that SAP NetWeaver BI is being used to help make composite applications work better. 13.3.1. What are the core functions of SAP NetWeaver BI?The core functions of SAP NetWeaver BI include solutions and technologies that cover all of the following IT scenarios. 13.3.1.1. Enterprise data warehousingEnterprise data warehousing (EDW) enables customers to create and operate a data warehouse that works enterprisewide. This methodology encompasses integration of heterogeneous systems, supports various system topologies and their development, and describes a layering methodology for highly flexible information access. An EDW approach also facilitates both strategic analyses and operational reporting. Data integration is achieved via physical as well as virtual means (the latter with real-time access to underlying systems and databases). The IT scenario of EDW comprises two scenario variants, which cover the design time (modeling/implementation) and runtime aspects of a highly flexible, reliable, robust, and scalable SAP NetWeaver BI solution. The scenario variant for modeling the EDW mainly addresses implementation and modeling issues. It includes everything from data modeling (creating InfoProviders) to source definition and transformation to data distribution, and it facilitates metadata management. The scenario variant for running the EDW mainly addresses administration and monitoring issues. It includes data flow control, administration and monitoring, performance optimization (using the highly innovative concept of high-performance analytics), and information life cycle management, and it also facilitates user management. 13.3.1.2. Enterprise reporting, querying, and analysisEnterprise reporting, querying, and analysis provide processes and services to serve all business users' needs with regard to information consumption. This comprises reporting, ad hoc querying, interactive analysis, dashboards, analytic applications, and list views, from design-time and runtime perspectives. The design-time processes are increasingly integrated into an overall strategy for the SAP NetWeaver design time. The runtime environment will utilize the Java platform and open standard technologies to provide a flexible and extensible infrastructure. It can be closely embedded into the operational context. All information that a user gets through reporting, querying, or analysis is actionablei.e., you can print it, attach it to a workflow, distribute it through broadcasting, give feedback on it, and so on. A host of scenario variants will cover the different possibilities of how to define, design, deploy, embed, and interact with SAP NetWeaver BI data by using the different tools and capabilities of the Business Explorer (BEx) Suite. 13.3.1.3. Business planning and analytical servicesPlanning in SAP NetWeaver BI provides the features needed to build planning applications that are tailored to the needs of strategic or operational planning. The focus of the scenario is to integrate planning functionality deeply into the analytical environment of SAP NetWeaver BI in order to leverage an optimal combination of planning and analysis capabilities. The capabilities span from simple manual data entry to SAP Business Information Warehouse (SAP BW) to the design of integrated business planning scenarios that support the integration of planning for all application areas (financial, CRM, SRM, and PLM, for example). The scenario addresses different types of users: administrators, business analysts, and planning contributors. They are involved in different scenario variants. 13.3.1.4. Data qualitySAP NetWeaver BI also plays a key role in ensuring data quality, which is a prerequisite to any effective analysis. If the data is incorrect, any analysis will be as well. Starting with Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL) capabilitiesthrough which data is transferred from enterprise applications to an operational data store and then is followed by advanced functionality for matching records and normalizing dataSAP NetWeaver BI can locate many errors and inconsistencies in both master data and transactional information. Data can then be corrected in the data warehouse so that analysis can proceed, and then the corrections can be propagated to the enterprise applications. The data warehousing capabilities at the heart of these scenarios represent one of the oldest and most mature areas of enterprise computing. Data warehousing is often exciting because in this area, results from academic and computer science research frequently find practical application. In its early days, data warehousing was primarily a batch-oriented function. Data would be loaded from enterprise applications into the data warehouse in overnight extractions. Reports were often run in batches and were distributed in the morning. As technology advanced, special database structures such as star schemas and InfoCubes were developed that allowed rapid computation of complicated queries that fell under the OLAP domain. The current challenges facing SAP NetWeaver BI involve figuring out how to cope with an explosion of data as increasing quantities of information are stored and new data sources such as radio frequency identification (RFID) arrive, with an increasing demand for access to information from an expanding population of users, and with the continuing challenge of increasing speed and reliability. In the midst of all of these challenges, SAP NetWeaver BI is being asked to play an additional role: that of supporting the development of composite applications in the context of ESA. In a fundamental way, every one of SAP NetWeaver BI's core functions helps support composite applications and ESA in one way or another through consolidating information, modeling business activity, and making it easy to access and analyze information and create actionable insights. But there are three specific areas in which SAP NetWeaver BI is being transformed that are particularly helpful in empowering composite applications:
13.3.2. How is business intelligence becoming service enabled?By opening up the functionality of SAP NetWeaver BI through enterprise services, composite applications are able to take advantage of a huge trove of functionality for manipulating and analyzing large volumes of data. One of the most important ways that SAP NetWeaver BI is becoming service enabled is through the XML for Analysis (XMLA) standard. This standard allows programmers to specify and execute OLAP queries through a web services interface. While this allows composite applications to gain access to all that OLAP has to offer, it is just the beginning of what SAP is doing to open up SAP NetWeaver BI through services. Although it is a crucial part of SAP NetWeaver BI, OLAP is only one of many different capabilities. In fact, SAP has created a set of services called SAP NetWeaver BI Consumer Services that provide access to many additional capabilities that will be of use to composite applications. For example, one of the services offered allows the top 10 results of queries to be retrieved, so instead of getting the entire volume of data, the service gets just the first 10 items. Another lets a user specify alerts to be triggered if certain thresholds for indicators are exceeded. For example, if actual sales dropped more than 20 percent below projections, an email alert could be generated. The thresholds and alerting mechanism could be controlled through services. At design time, when applications are being created, SAP NetWeaver BI Consumer Services will be used in the Web Application Designer to provide validation of item attributes or command parameters. In the Report Designer, services will also be used for data validation and for accessing metadata. The BEx Analyzer will use services in its design mode. At runtime, SAP NetWeaver BI Consumer Services will be used in composite applications written in Java, in the BEx Analyzer, for information broadcasting, in Web Dynpro, for custom portal applications, and for interactive planning. While SAP NetWeaver BI Consumer Services were initially created as an internal mechanism for SAP developers, they are likely to become part of the Enterprise Services Inventory at some point in the future once more experience has been gained in using them. 13.3.3. What is the SAP NetWeaver BI Accelerator?The SAP NetWeaver BI Accelerator is a technology that speeds up the SAP NetWeaver BI query runtime through use of compression, indexing, and parallel processing that combine the use of search engine technology with a scalable hardware architecture based on blade servers. The BI Accelerator makes queries 10 to 100 times faster on average, which means that analysis becomes far more interactive even when huge volumes of data are being analyzed. The SAP NetWeaver BI Accelerator works by compressing and indexing InfoCubes and bringing them in through a large in-memory cache spread across a gang of blade servers. As the data enters the BI Accelerator, a process of dictionary-based compression takes place, which reduces the size of the data so that more of it can be stored in memory. The BI Accelerator then indexes the data by column rather than by row using Text Retrieval and information EXtraction (TREX) search engine technology, which dramatically speeds up processing. Then the index is stored in memory and is spread across the gang of blade servers so that processing can take place in parallel. Figure 13-1 shows the BI Accelerator architecture. Figure 13-1. The SAP NetWeaver BI Accelerator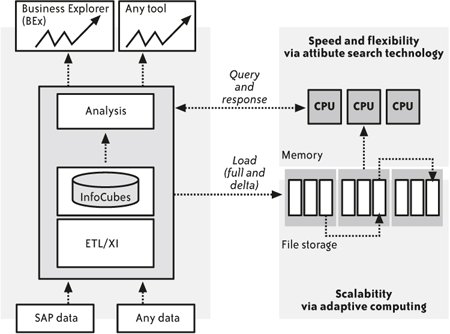 One of the most convenient aspects of the BI Accelerator is that it works invisibly alongside existing SAP NetWeaver BI functionality. No changes are needed in the queries, in the construction of the InfoCubes, or in the applications that use them. The BI Accelerator helps improve performance and user satisfaction in scenarios that involve queries across many millions or billions of records. Data volumes of this magnitude are common in the retail, utility, and telecommunications industries. The need for speed is crucial to scenarios such as call centers, where operators must have quick response times for good closure rates. The BI Accelerator also may avoid the need to improve performance by adjusting the structure of the InfoCubes, which can be a time-consuming and difficult process. For composite application developers, the BI Accelerator functionality of SAP NetWeaver means faster response times so that users can have a more pleasing experience and can work through more queries in a shorter amount of time. 13.3.4. How will SAP NetWeaver BI help embed analytics into composites?While adding services and making queries faster are a tremendous help to composite application developers, perhaps the most profound impact that SAP NetWeaver BI will have is through embedded analytics. Composite applications known as SAP xApp Analytics will be the first wave of embedded analytic applications released to the market. The idea of embedded analytics is to bring all of the power that SAP NetWeaver BI offers to consolidate, analyze, and understand information, to combine it with the ability to take action that enterprise services offer, and then to insert that analytic capability directly into applications in the context of a process in an enterprise application. Too often in the past, using analytic functionality has involved a context switch. A user would be in an enterprise application managing a process for evaluating the credit of a supplier or attempting to choose which order should be fulfilled in a time of scarce resources, and then to perform some analysis, the user would have to leave the enterprise application and enter another application to perform analytics. Once he understood the situation, the user would have to go back to the enterprise application to do something about it. The idea of embedded analytics is that the analytic functionality is prepared to meet the needs of a specific process and then is inserted inside the enterprise application so that no context switching is needed and action can be taken right away. Data from SAP NetWeaver BI can be combined with data extracted from ERP and other enterprise applications to provide a complete picture. Embedded analytics also offer flexibility in another dimension. While many enterprise applications establish a rich context for supporting a process, in the modern business environment it may be difficult to anticipate all the needs of an information worker. Because SAP xApps composite applications for analytics have a large collection of services from which to choose, it is possible to empower users to assemble the information they need at runtime instead of having to limit the choices at design time. ESA makes embedded analytics possible through composite applications based on enterprise services, as shown in Figure 13-2. SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer allows SAP xApps composite applications for analytics to be created quickly and modified easily. SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer is a modeling environment that simplifies development. This allows business analysts who have a hands-on understanding of the sort of analytics needed at various steps in a business process, to create and adapt analytic applications. Modeling is combined with the use of application patterns that capture common structures of analytic applications to further accelerate development. As Figure 13-2 shows, the UI created by SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer uses a layer of analytic services to access SAP NetWeaver BI, potentially with the help of BI Accelerator functionality. The layer of analytic services includes XMLA and BI Consumer Services as well as other services created to provide access to SAP NetWeaver BI functionality or to enterprise applications as needed. Through embedded analytics, the trip from information to action becomes as short as possible. |
|
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 265