Lesson 9: Windows 2000 Remote Access Administration Tools
Windows 2000 has tools and technologies to simplify administration of computers in your network. Terminal Services provides access to Windows 2000 and the latest Windows-based applications for client computers. It also allows system administrators to remotely administer network resources. In addition, Windows 2000 provides the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which allows you to monitor and communicate status information from SNMP agents to network management software. In this lesson, you learn how to use Terminal Services and SNMP to better manage and monitor your network.
After this lesson, you will be able to
- Configure Terminal Server for remote administration
- Install and configure the SNMP service
- Describe how the Windows 2000 SNMP service works
Estimated lesson time: 25 minutes
Windows 2000 Administration Capabilities
With Windows 2000, you can administer computers and services on your network either locally or remotely. Remote administration means using one computer to connect to another computer on a network for management purposes. Windows 2000 allows you to perform administration tasks for all computers on a network centrally, rather than at each computer's physical location. You can either use third-party management systems or use some of the tools and methods that Windows 2000 provides for remote administration.
Terminal Services
When you enable Terminal Services on a Windows 2000 Server, you either select Remote Administration or Application Server mode, as illustrated in Figure 12.22.
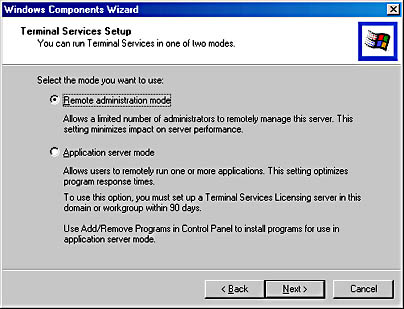
Figure 12.22 Selecting a mode for Terminal Services
Application Server mode allows you to deploy and manage applications from a central location. You can deploy a Windows 2000 interface as well as applications to computers that cannot run Windows 2000. Because Terminal Services is integrated into the Windows 2000 server products, you can run your applications on the server, and provide the user interface to clients that cannot run Windows 2000, such as Windows 3.11 or Windows CE computers connected to a terminal server.
Terminal Services also offers a Remote Administration mode that allows you to access, manage, and troubleshoot clients. Remote Administration mode allows you to remotely administer Windows 2000 servers over any TCP/IP connection, including remote access, Ethernet, the Internet, wireless, WAN, or a VPN. You can install Terminal Services from the Windows Components dialog box of the Add/Remove Programs applet in Control Panel, as illustrated in Figure 12.23.
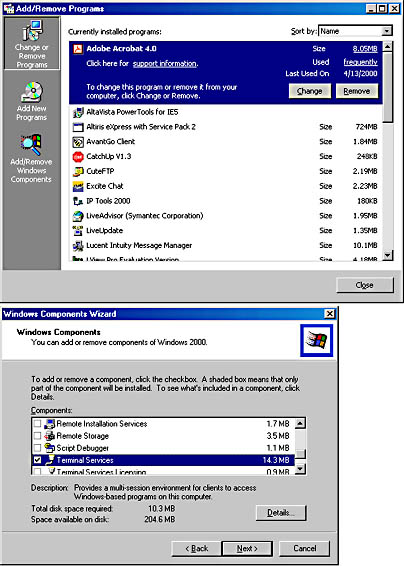
Figure 12.23 Terminal Services option
Using Terminal Server
Although a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connection is configured automatically when Terminal Services is installed, you can use another procedure to make a new connection. Only one RDP connection can be configured for each network adapter in a Terminal server; however, you can configure additional connections using RDP if you install a network adapter for each connection on your computer.
Follow these steps to install a network adapter:
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Terminal Services Configuration.
- Right-click the Connections tab, and then click Create New Connection.
The Terminal Services Connection wizard appears.
- In the first dialog of the wizard, you select a connection type, such as Microsoft RDP 5.0.
- In the second dialog of the wizard, you set the encryption level to either Low, Medium, or High. You can also select standard Windows authentication.
- In the third dialog of the wizard, you can set remote control options and set the level of control.
- In the fourth dialog of the wizard, you select the connection name, transport type, and an optional comment.
- In the fifth dialog of the wizard, you can select one or all network adapters for the transport type, and set the number of connections.
- Click Finish to close the wizard.
Terminal Services allows a maximum of two concurrent Remote Administration connections that do not require licenses. A negligible amount of disk space, memory, and configuration for Terminal Services clients is required.
Follow these steps to allow a Terminal Server client computer to log on to a Windows 2000 Terminal Server:
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- To expand the branches, click the plus symbol (+) next to System Tools, click the plus symbol (+) next to Local Users And Groups, and then click the plus symbol (+) next to Users.
- Double-click the user that you would like to enable to log on as a Windows NT Terminal Server client.
- On the Terminal Services Profile tab, click the Allow Logon To Terminal Server check box, as illustrated in Figure 12.24, and then click OK.
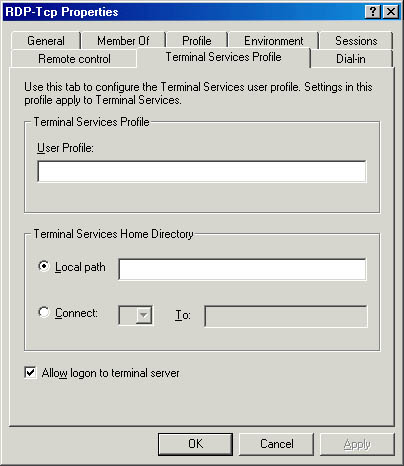
Figure 12.24 Allowing logon to the terminal server
- Close Computer Management.
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Terminal Services Configuration.
- Open the Connections folder, and then click Rdp-Tcp.
- On the Actions menu, click Properties.
- On the Permissions tab, add the users or groups that you want to have permissions to this Windows NT Terminal Server.
- Click OK to close the connection's Properties dialog box.
- Close Terminal Services Configuration.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a network-management protocol frequently used in TCP/IP networks to monitor and manage computers and other devices (such as printers) connected to the network. SNMP can be installed and used on any computer running Windows 2000 and TCP/IP or IPX/SPX.
Follow these steps to install the SNMP service:
- Click Start, point to Settings, click Control Panel, double-click Add/Remove Programs, and then click Add/Remove Windows Components.
The Windows Component wizard appears.
- In Components, click Management And Monitoring Tools, and then click Details.
The Management And Monitoring Tools dialog box appears.
- Select the Simple Network Management Protocol check box, and click OK.
- In the Windows Component wizard, click Next.
The Windows Component wizard installs SNMP.
- Click Finish to close the Windows Component wizard.
Management Systems and Agents
SNMP is comprised of management systems and agents. A management system is any computer running SNMP management software. Although Windows 2000 does not include a management system, many third-party products such as Sun Net Manager or HP Open View are available. A management system requests information from an agent.
As illustrated in Figure 12.25, an agent is any computer running SNMP agent software, such as a Windows 2000-based computer, router, or hub. The Microsoft SNMP service is SNMP agent software. The primary function of an agent is to perform operations that a management system calls for.

Figure 12.25 SNMP agents
The SNMP agent component also allows a Windows 2000 computer to be administered remotely. The only operation initiated by an agent is called a trap. A trap is a message sent by an agent to a management system indicating that an event has occurred on the host running the agent. As illustrated in Figure 12.26, the SNMP management software application does not have to run on the same computer as the SNMP agents.
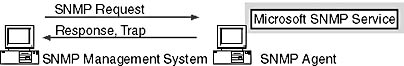
Figure 12.26 SNMP management system and agent
Benefits of SNMP
If you have installed a DHCP server, Internet Information Server, or WINS server software on a Windows 2000-based computer on the network, you can monitor these services by using an SNMP manager program. In addition, you can use Performance Monitor to examine TCP/IP-related performance counters. When you install the SNMP service, TCP/IP performance counters become available in System Monitor. The TCP/IP objects that are added include ICMP, TCP, IP, UDP, DHCP, WINS, FTP, Network Interface, and Internet Information Server. As illustrated in Figure 12.27, Performance Monitor counts
- Active TCP connections
- UDP datagrams received per second
- ICMP messages per second
- Total network interface bytes per second
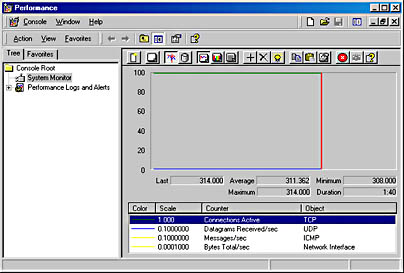
Figure 12.27 Monitoring TCP/IP objects with System Monitor
Lesson Summary
Windows 2000 provides two tools that can be used to remotely administer your system. These tools are Terminal Services and SNMP.
Terminal Services offers a Remote Administration mode that allows you to access, manage, and troubleshoot clients. Remote Administration mode allows you to remotely administer Windows 2000 servers over any TCP/IP connection.
SNMP is a network-management protocol widely used in TCP/IP networks. It can be used to communicate between a management program run by an administrator and the network-management agent running on a host or gateway. You can also use SNMP to monitor and control remote hosts and gateways on an internetwork. The Windows 2000 SNMP service allows a Windows 2000 computer to be monitored remotely. The SNMP service can handle requests from one or more hosts, and it can also report network-management information to one or more hosts, in discrete blocks of data called traps. When you install the SNMP service, TCP/IP performance counters become available in System Monitor.
EAN: N/A
Pages: 244
- Challenging the Unpredictable: Changeable Order Management Systems
- The Second Wave ERP Market: An Australian Viewpoint
- Healthcare Information: From Administrative to Practice Databases
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality
- Development of Interactive Web Sites to Enhance Police/Community Relations