Organizing Disks
You can organize disk drives in several ways. One way is to use multiple hard drives. Each hard drive has an assigned drive identifier such as C, D, etc. Usually, for this type of configuration, each physical hard drive represents just one storage location identified with a letter.
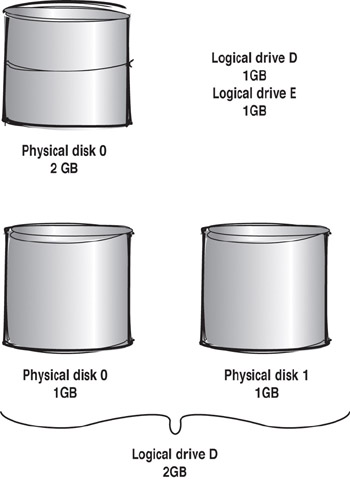
Another alternative is to organize the disk into volumes on the same physical disk. This method requires the creation of partitions. Each partition that is created makes a physical change to the format of the disk. The usable space defined through partitions is considered the logical drive. You can define disk space however you want, regardless of the physical size of the disk. Consider these examples:
logical drive
Based on how you partition your physical drive, the area of the extended partition can be organized into multiple drives. Each drive is assigned a DOS identifier from D to Z.
In the first example, you have a single 2GB physical disk that is partitioned into two logical drives. Each logical drive is 1GB.
In the second example, you have two physical disks that are each 1GB. In this case, the two drives are configured as a single 2GB logical drive by using software.
| Note | To create partitions or logical drives, you can use the DOS FDISK program, or third-party utilities such as Partition Magic, Disk Administrator (if you are using Windows NT), or Disk Management (if you are using Windows 2000, Windows XP, or Windows Server 2003). |
|
|