Remember that the whole point of using these commands is to try to figure out why a particular computer can't connect to the local network or is having problems connecting to the Internet. Take a close look at the results of each command when you run it to glean information that will allow you to rectify a particular connection issue.
 Open Command Window
Open Command Window
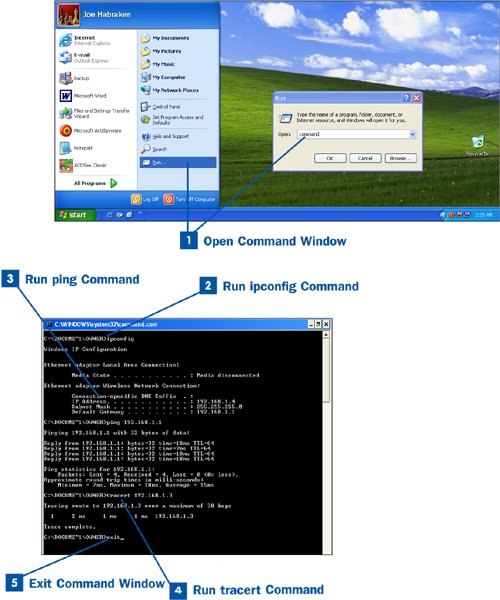
Click the Start button and then choose Run. In the Run dialog box, type command and click OK. The command window opens.
 Run ipconfig Command
Run ipconfig Command
At the command prompt, type ipconfig (or ipconfig with a switch such as ipconfig/all) and press Enter. The results of the command appear in the command window. If you do not see a default gateway, there might be a problem with the IP configuration on the computer or a problem with the router's DHCP server (because the router serves as the default gateway).
Note
The default gateway for the computer should be the IP address of the WiFi router's LAN interface. You can check this using the router's configuration page.
 Run ping Command
Run ping Command
To ping a computer or another device such as the router's LAN interface, you will need to know that device's IP address. You can find the router's LAN IP address using the router's configuration page. Type ping followed by the IP address of the computer or device you want to connect to. Then press Enter.
The results of the ping command show the milliseconds that it takes for the destination device to respond to your ping packet. When you use ping on a WiFi network (a local network), the response to your ping command from the destination computer should be almost instantaneous. However, the response time will vary depending on the amount of network traffic. If everyone on the network is downloading huge files from the Internet, all that activity will slow the response to the ping "challenge." The actual speed of the ping (in milliseconds) isn't as important as a consistent speed. If a ping goes from 18ms for a response to 60ms the next time you do it, traffic is either through the roof on the network or there may be a problem with the computer's WiFi adapter or the router (which is responsible for routing the traffic on the network).
If you don't get a response at all (the ping times out), there is probably a connection problem. Either the target device is not on the network or the router is having trouble routing your request. Check the router's status screen to see what computers are connected to the network. If you don't see the computer you tried to ping, that computer is having a problem connecting to the network. See  Check Router Status for more about viewing a list of computers connected to the WiFi router.
Check Router Status for more about viewing a list of computers connected to the WiFi router.
 Run tracert Command
Run tracert Command
The tracert command will show you the number of hops (routers) it takes for your packet to move from your computer to the destination address. Type tracert and then the IP address of the destination computer or device.
The results of the tracert command show the number of hops to the destination and the number of milliseconds the packet took to go to the destination; then the command shows the number of milliseconds it took for a response from the destination device (meaning computer).
 Exit Command Window
Exit Command Window
To exit the command window, type exit at the command prompt and press Enter. The command window will close and return you to the Windows Desktop.