Configuring System Folders
|
|
If you've had previous experience with Windows (including both Windows 9x/ME and Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP), you know there will be times when you want to move your system folders to different locations (for example, to other drives where you have more free space). However, if you simply move these folders, what you end up with will be a new copy for each of these folders in the previous locations. Why is this the case?
This is because all operating systems of the Windows family store the system folders paths in the registry. So, if you want to move the system folders properly, you need to modify the appropriate registry values that specify the location of the system folders. Microsoft Office applications behave the same way - all of the paths to the standard folders are also stored in the registry. That's why you cannot get rid of the My Documents folder. Registry values that specify the locations of the system folders are stored under HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders.
Notice that, even in Windows 2000, the user interface provider you with the ability to move the My Documents folder to the location you wished.
In Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 this function was further enhanced. Right-click the My Documents folder to open the My Documents Properties window (Fig. 4.18) and click on the Move button. In the next window, you will be prompted to select a new location for the My Documents folder, either by selecting an existing folder or by creating a new folder. There is now, therefore, no need to edit the registry directly.
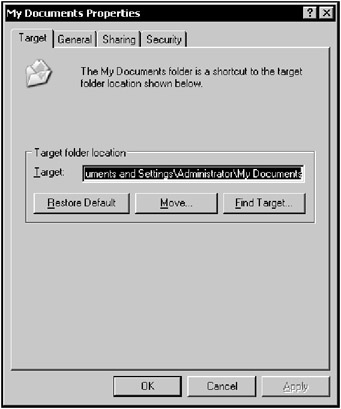
Figure 4.18: Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 provide you with the capability of moving the My Documents folder
|
|