ISDN Overview
| ISDN refers to the call-processing system that enables voice, data, and video to be transmitted over our existing telephone system. ISDN offers several advantages over existing analog modem lines. For example, ISDN connection speeds begin at 64Kbps, whereas typical modem speeds hover between 28.8Kbps and 56Kbps. The call setup time for an ISDN call is also much quicker. ISDN can transmit data packets, voice, or video. ISDN is a viable solution for remote connectivity ( telecommuting ) and access to the Internet. ISDN also supports any of the Network layer protocols supported by the Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) and encapsulates other WAN services, such as PPP. Configuring ISDNYou must perform both global and interface configuration tasks when configuring a router for ISDN. Global configuration tasks include specifying the type of ISDN switch your router connects to at the provider's central office (CO) and defining what type of traffic is interesting. Table 10.4 lists the ISDN global configuration commands. Table 10.4. ISDN Global Configuration Commands
Table 10.5 shows the ISDN commands that must be configured on an interface. Table 10.5. ISDN Interface Configuration Commands
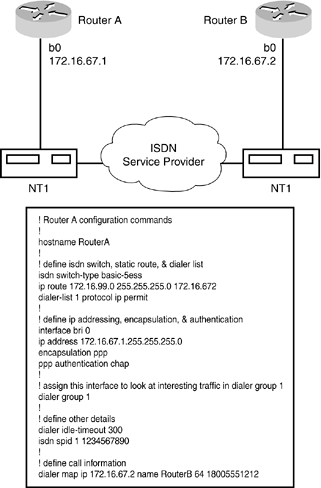
Figure 10.5 presents a simple ISDN DDR configuration for router A and router B. Figure 10.5. DDR configuration example. Monitoring ISDNThe commands listed in this section enable you to monitor the activity and operation of ISDN and DDR configurations. You can monitor ISDN and DDR configurations with the following commands:
Use the show controller bri command to display detailed information about the B and D channels. The following output displays an example of the show controller command: RouterA# show controller bri 0 BRI unit 0 D Chan Info : Layer 1 is ACTIVATED idb 0x32089C, ds 0x3267D8, reset_mask 0x2 buffer size 1524 RX ring with 2 entries at 0x2101600 : Rxhead 0 00 pak=0x4102E8 ds=0x410444 status=D000 pak_size=0 01 pak=0x410C20 ds=0x410D7C status=F000 pak_size=0 TX ring with 1 entries at 0x2101640: tx_count = 0, tx_head = 0, tx_tail = 0 00 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=7C00 pak_size=0 0 missed datagrams, 0 overruns, 0 bad frame addresses 0 bad datagram encapsulations, 0 memory errors 0 transmitter underruns B1 Chan Info: Layer 1 is ACTIVATED idb 0x3224E8, ds 0x3268C8, reset_mask 0x0 buffer size 1524 RX ring with 8 entries at 0x2101400 : Rxhead 0 00 pak=0x421FC0 ds=0x42211C status=D000 pak_size=0 01 pak=0x4085E8 ds=0x408744 status=D000 pak_size=0 02 pak=0x422EF0 ds=0x42304C status=D000 pak_size=0 03 pak=0x4148E0 ds=0x414A3C status=D000 pak_size=0 04 pak=0x424D50 ds=0x424EAC status=D000 pak_size=0 05 pak=0x423688 ds=0x4237E4 status=D000 pak_size=0 06 pak=0x41AB98 ds=0x41ACF4 status=D000 pak_size=0 07 pak=0x41A400 ds=0x41A55C status=F000 pak_size=0 TX ring with 4 entries at 0x2101440: tx_count = 0, tx_head = 0, tx_tail = 0 00 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=5C00 pak_size=0 01 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=5C00 pak_size=0 02 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=5C00 pak_size=0 03 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=7C00 pak_size=0 0 missed datagrams, 0 overruns, 0 bad frame addresses 0 bad datagram encapsulations, 0 memory errors 0 transmitter underruns B2 Chan Info: Layer 1 is ACTIVATED idb 0x324520, ds 0x3269B8, reset_mask 0x2 buffer size 1524 RX ring with 8 entries at 0x2101500 : Rxhead 0 00 pak=0x40FCF0 ds=0x40FE4C status=D000 pak_size=0 01 pak=0x40E628 ds=0x40E784 status=D000 pak_size=0 02 pak=0x40F558 ds=0x40F6B4 status=D000 pak_size=0 03 pak=0x413218 ds=0x413374 status=D000 pak_size=0 04 pak=0x40EDC0 ds=0x40EF1C status=D000 pak_size=0 05 pak=0x4113B8 ds=0x411514 status=D000 pak_size=0 06 pak=0x416ED8 ds=0x417034 status=D000 pak_size=0 07 pak=0x416740 ds=0x41689C status=F000 pak_size=0 TX ring with 4 entries at 0x2101540: tx_count = 0, tx_head = 0, tx_tail = 0 00 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=5C00 pak_size=0 01 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=5C00 pak_size=0 02 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=5C00 pak_size=0 03 pak=0x000000 ds=0x000000 status=7C00 pak_size=0 0 missed datagrams, 0 overruns, 0 bad frame addresses 0 bad datagram encapsulations, 0 memory errors 0 transmitter underruns Both B channels and the D channel are active. Use the show interface bri command to display BRI status, encapsulation, and counter information. The following output displays an example of the show interface command: RouterA# show interface bri 0 BRI0 is up, line protocol is up (spoofing) Hardware is BRI Internet address is 172.16.67.1, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 64 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec) Last input 0:00:07, output 0:00:00, output hang never Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops Five minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec Five minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 16263 packets input, 1347238 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 13983 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants 2 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 2 abort 22146 packets output, 2383680 bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets, 0 restarts 1 carrier transitions The encapsulation type is PPP, and two errors were received on the BRI. Use the show dialer bri command to display general diagnostic information for serial interfaces configured to support DDR. The following output displays an example of the show dialer command: RouterA# show dialer interface bri 0 BRI0 - dialer type = IN-BAND NO-PARITY Idle timer (900 secs), Fast idle timer (20 secs) Wait for carrier (30 secs), Re-enable (15 secs) Time until disconnect 838 secs Current call connected 0:02:16 Connected to 8986 Dial String Successes Failures Last called Last status 8986 0 0 never Default 8986 8 3 0:02:16 Success Default
|
EAN: N/A
Pages: 155