3.5 Roaming Networks
| A WDS extends your wireless network, but you can get similar functionality with multiple base stations that are all connected to an Ethernet network. This creates a single wireless network, called a roaming network . Roaming networks use the same Network Name (SSID) and password for all of the base stations on the network, allowing clients to move freely between the coverage areas of each base station. One benefit of a roaming network is that you can use more than five base stations (you're limited to five in a WDS) to create your wireless network and extend your wireless network's coverage. A roaming network has one DHCP server and cannot use NAT, so you'll need to assign a range of IP addresses for the DHCP server to hand out to the wireless clients. To set up a roaming network, follow these steps:
Figure 3-32. Setting an IP address range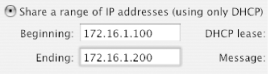
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 100