Enterprise VPNs Overview
| Provider-independent or enterprise VPNs provide connectivity that is deployed on a shared (public) infrastructure with the same policies as a private network, where users expect the same or similar performance, applications, and connectivity. Cisco classifies existing solutions into three major VPN types (see Figure 19-2):
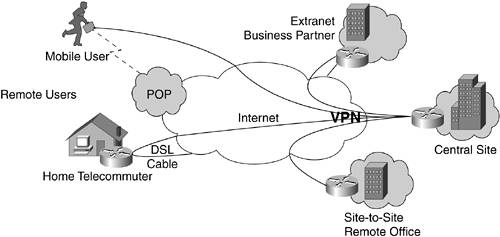
Figure 19-2. Major Cisco VPN Types
Remote access and site-to-site VPN solutions provide an alternative to building a carrier-based private network for enterprise communication. Companies can cost-effectively extend the corporate network to locations that might not have been justified before because they operate across a shared infrastructure rather than a private network. For example, in many domestic applications and most international applications, VPNs provide significant cost savings over private wide-area network (WAN) connections. Also, rather than having multiple independent circuits terminating at the corporate headend, VPNs allow all traffic to be aggregated into a single connection. This scenario usually results in increased bandwidth and cost savings at the headend, and further savings is achieved from not having to maintain a private network. VPNs provide the opportunity for additional cost reduction both within and external to the company. The Internet, as a super-medium, allows the enterprise to change the way its networks operate in the following key directions:
Mobile users can also take advantage of higher-speed Ethernet connections found in many hotels, airports, and convention centers for access to the enterprise network through the Internet and VPN. The cost savings alone, from not having to pay long-distance telephone charges, might justify the use of VPNs in such cases. Another benefit of VPN is that companies can take advantage of the technology to enable new applications and business processes, such as e-commerce, supply chain management, and virtual office concepts. The Internet, as a supermedia, is not an all-purpose remedy or alternative. Some key components, such as security, QoS, reliability, and manageability are some of the factors currently limiting it from becoming a super-alternative. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 235