About Display Options and Smoothness
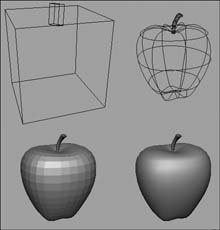
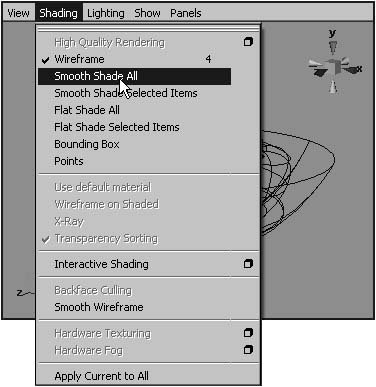
| By using a panel's display options, you can change the way objects are viewedor whether they're viewed at all. You can find these options in the Shading, Lighting, and Show menus at the top of each panel, and the most commonly used options have associated keyboard shortcuts. You can view your scene in wireframe, smooth-shaded, flat-shaded, bounding-box, or points mode, depending on your current task (Figure 2.52). Bounding-box mode can be used to speed interaction in complex scenes. Wireframe mode is handy for selecting components, because you can see the components through the object. Smooth shading gives you the most accurate picture of your objects, whereas flat shading is a compromise between accuracy and speed. Figure 2.52. An apple viewed in bounding box, wireframe, flat-shaded, and smooth-shaded modes. The hardware texturing and lighting options also increase the accuracy of your scene, allowing you to view an approximation of your objects' textures and the effects of the lights in your scene. Although it isn't a panel-specific view option, you can also select NURBS and Subdiv objects to change their display to one of three smoothness levels: rough, medium, or fine. Choosing a setting of rough can ease component selection, because fewer surface lines are shown. A fine setting comes closest to matching the final surface. To change the display options from the Shading menu:
Shading and smoothness shortcuts
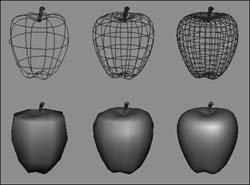
Figure 2.54. From left to right, rough, medium, and fine smoothness.
Figure 2.55. Wireframe mode lets you see through objects and view their entire geometry.
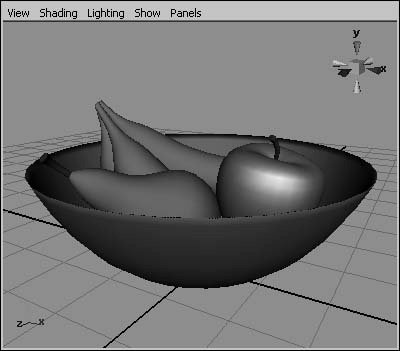
Figure 2.56. Shaded mode presents the surfaces of objects in gray by default, showing their shape but not their texturing or lighting.
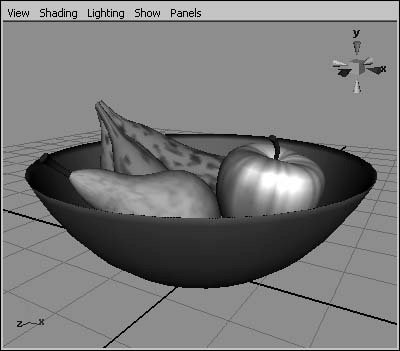
Figure 2.57. Hardware Texturing shows an approximation of the textures that have been applied to objects.
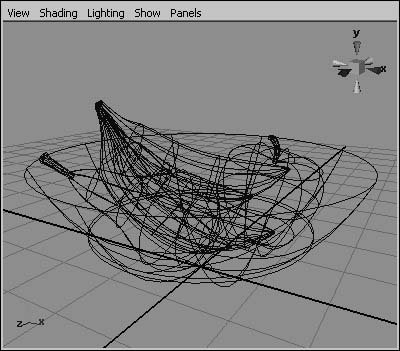
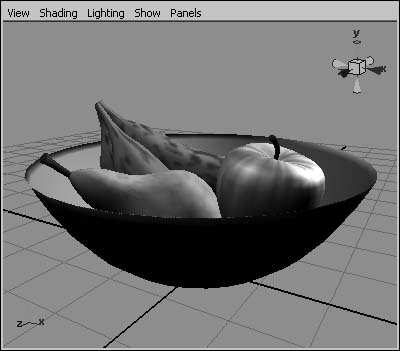
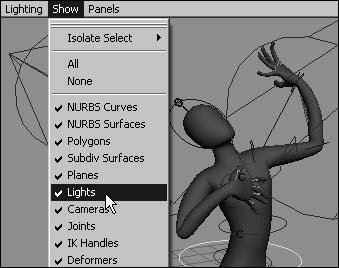
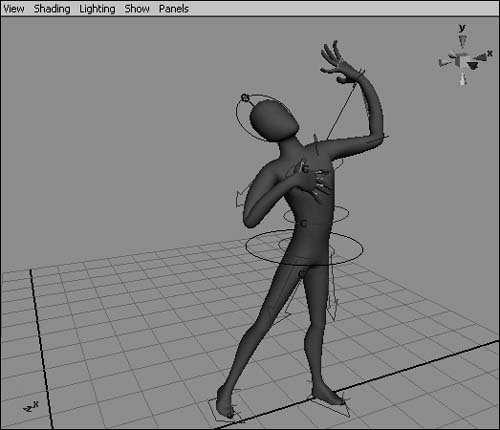
Figure 2.58. Hardware Lighting shows an approximation of the scene's lighting. Using the Show menuThe Show menu comes in handy when you want to work with a particular type of object, such as curves or lights. With it, you can quickly hide the object types you don't need to view, allowing you to see the particular objects that you're working with more clearly. This can be very helpful in complex scenes (Figure 2.59). Figure 2.59. Even a simple single-character animation involves various object types, not all of which you need to work with at once.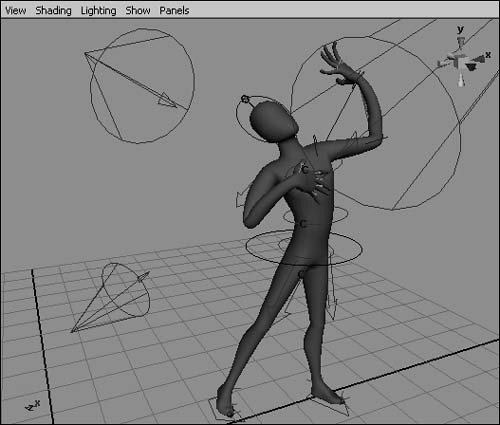 The Show menu lets you turn all types on and off simultaneously, and you can also turn objects on and off individually. You may want to turn off all objects first and then turn on only the object type you want to isolate. The Show menu only visually hides or shows object types; it doesn't delete the objects. Object types turned off in the Show menu still appear in the final render. To hide object types with the Show menu:
To show hidden object types with the Show menu:
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 185