Extending Segmentation over the WAN
| Two main types of connectivity can be provided over a WAN:
Subtle differences exist between supporting the interconnection of segmented MANs/campus networks and the aggregation of segmented branches. However, you can apply the available techniques to either scenario. The techniques for extending VNs over the WAN include the following:
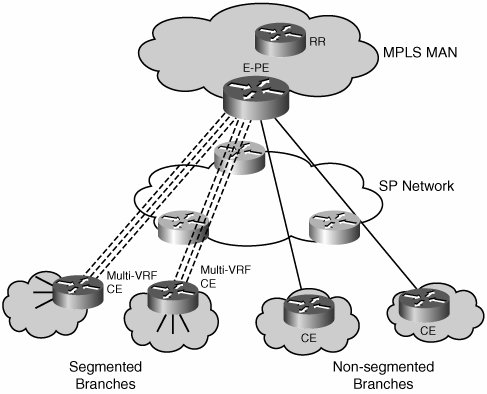
In this section, we analyze the different techniques from both perspectives (site interconnection and branch aggregation). Each of the options can address the scenario in which segmentation is required at some branches and not required at others, as depicted in Figure 7-6. Branches that do not require segmentation might have to be placed in their own VRF, the default common VRF, or the global table at the headend depending on the enterprise requirements. Figure 7-6. Segmented and Nonsegmented Branches Note As we analyze the different options, it is important to understand that all traffic is originally forwarded using the global routing table. As VNs are created, traffic that does not require segmentation can continue to use the global routing table, whereas segmented traffic can be assigned to VNs as needed. |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 128
- ERP Systems Impact on Organizations
- The Effects of an Enterprise Resource Planning System (ERP) Implementation on Job Characteristics – A Study using the Hackman and Oldham Job Characteristics Model
- Context Management of ERP Processes in Virtual Communities
- Distributed Data Warehouse for Geo-spatial Services
- A Hybrid Clustering Technique to Improve Patient Data Quality