Self Test
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
| 1. | Of the following, which one is not an example of formal communications?
| |
| 2. | Of the following, which one is an example of informal communications?
| |
| 3. | You are the project manager for the LKH Project. Management has requested that you create a document detailing what information will be expected from stakeholders and to whom that information will be disseminated. Management is asking for which one of the following?
| |
| 4. | Which one of the following will help you, the project manager, complete the needed Communications Management Plan by identifying the stakeholders and their communication needs?
| |
| 5. | You are the project manager for the JGI Project. You have 32 stakeholders on this project. How many communications channels do you have?
| |
| 6. | You are the project manager for the KLN Project. You had 19 stakeholders on this project. You have added three team members to the project. How many more communication channels do you have now than before?
| |
| 7. | A memo has been sent to you, the project manager, project team members, and the project customers from the project sponsor. In this instance, who is the encoder?
| |
| 8. | Which one of the following can use EVM in its preparation for management?
| |
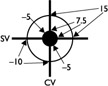
| 9. | What does the following figure mean?
| |
| 10. | Of the following, which term describes the pitch and tone of an individual’s voice?
| |
| 11. | You are the project manager of the KMH Project. This project is slated to last eight years. You have just calculated EVM and have a CV of –$3500. What type of report is needed for management?
| |
| 12. | In your Communications Management Plan, you have detailed administrative closure. At what point will administrative closure take place?
| |
| 13. | You are the project manager for OOK Project. You will be hosting project meetings every week. Of the following, which one is not a valid rule for project meetings?
| |
| 14. | The three basic elements needed for communication in project management are
| |
| 15. | Which one of the following is the method of analyzing project performance preferred in government projects?
| |
| 16. | What percentage of a message is sent through nonverbal communications, such as facial expressions, hand gestures, and body language?
| |
| 17. | Which one is not a filter for receivers of communication?
| |
| 18. | You are finalizing project completion. You will gather, generate, and disseminate project information. This is known as which one of the following?
| |
| 19. | Often in project management you will have to negotiate. Negotiations work best in which environment?
| |
| 20. | You are the project manager for the PMU Project. Your project has 13 members. You have been informed that next week your project will receive the seven additional members you requested. How many channels of communications will you have next week?
| |
| 21. | Which one of the following will result in the most productive results when negotiating?
| |
| 22. | Which one of the following is an output from performance reporting?
| |
| 23. | The process of sending information from the project manager to the project team is called which of the following:
| |
| 24. | George is the project manager of the 7YH Project. In this project, George considers the relation between himself and the customer to be of utmost important. Which one of the following is a valid reason for George’s belief in the importance of the relationship between the customer and himself?
| |
| 25. | Which one of the following means that communications occur?
| |
Answers
| 1. | þ B. Ad hoc conversations, while often effective, are not examples of formal communications, as they are impromptu meetings. ý A, presentations to groups, is an example of formal communication. C, contractual agreements, are a type of formal communication. Finally, D is incorrect; presentations to management are formal. |
| 2. | þ A. Memos are examples of informal communication. ý Choices B, C, and D are incorrect, as presentations, briefings, and speeches are formal communication. |
| 3. | þ C. Management is requesting a Communications Management Plan, which details the requirements and expectations for communicating information among the project stakeholders. ý A is incorrect; a roles and responsibilities matrix depicts who does what and who makes what decisions. B, the Scope Management Plan, is also incorrect; this plan explains how changes to the scope may be allowed depending on the circumstances. D is not a valid choice for the question. |
| 4. | þ D. A communication matrix is an excellent tool to identify the stakeholders and their requirements for communication. ý A, B, and C are incorrect, as these choices do not fully answer the question. A communication matrix is the best tool to identify stakeholders’ requirements for communication. |
| 5. | þ B. Using the formula N(N–1)/2, where N represents the number of stakeholders, there are 496 communication channels. ý Choices A, C, and D are incorrect; these values do not reflect the number of communication channels on the project. |
| 6. | þ C. This is a tough question, but typical of the PMP exam. The question asks how many more communication channels exist. You’ll have to calculate the new value, which is 231, and then subtract the original value, which is 171, for a total of 60 new channels. ý A. is incorrect; 171 is the original number of communication channels. B is incorrect as this value reflects the new number of communication channels. D is not a valid choice. |
| 7. | þ A. The project sponsor is the source of the memo, as this is the sender of the message. ý B, C, and D are all recipients of the memo, not the sender, so they cannot be the source of the message. |
| 8. | þ D. Status, trend, and performance reports can all use EVM as an input. ý Choices A, B, and C are all incorrect, as EVM can be used in each of these reports. |
| 9. | þ D. The figure is called a communications bull’s eye and is used to trigger communication needs to management when EVM results fall within the identified ranges. ý Choices A, B, and C are incorrect, as these choices do not accurately identify the illustration. |
| 10. | þ A. Paralingual is a term used to describe the pitch and tone of one’s voice. ý B, feedback, is a request to confirm the information sent in the conversation. C, effective listening, is the ability to understand the message through what is said, facial expressions, gestures, tone and pitch, and son on. D, active listening, is the process of confirming what is understood and asking for clarification when needed. |
| 11. | þ C. An exception report is typically completed when variances exceed a given limit. ý A is incorrect; progress reports describe the progress of the project or phase. B is incorrect, as this is not a valid answer. D, trends report, is an analysis of project trends over time. |
| 12. | þ B. Administrative closure should take place at the completion of each phase. ý A, while tempting, is incorrect; administrative closure will need to be completed prior to archiving the project records. C is also incorrect; administrative closure does not take place only at project completion and cancellation; it can happen at the end of each project phase. D is not a valid choice. |
| 13. | þ B. Project meetings should have a set time limit. ý A, B, and C are incorrect answers because these are good attributes of project team meetings. |
| 14. | þ D. The three parts to communication are sender, receiver, and message. ý Choices A, B, and C are all incorrect choices. |
| 15. | þ C. EVM is all about analyzing project performance. ý A. communications management, focuses on managing communications, not performance. B, management by walking around, is an effective management style, but it does reflect project performance. D, variance analysis, focuses on the root causes of variances within the project, but not solely on the project performance. |
| 16. | þ A. Greater than 50 percent of a message is sent through nonverbal communications. ý Choices B, C, and D are incorrect. |
| 17. | þ B Conflict is not a filter of communication—it is a communication hindrance. ý Choices A, C, and D are incorrect choices; culture, knowledge, and language are filters for receivers. |
| 18. | þ C. Administrative closure is the process of generating, gathering, and disseminating project information. ý A and B are incorrect, as project closure and project postmortem involve more than just generating, gathering, and disseminating project information. D, operational transfer, is the process of moving the project deliverable into operations. |
| 19. | þ D. Mutual respect and cooperation is the environment needed for fair and balanced negotiations. ý A, caution and yielding, is not a good environment for negotiations. B, while tempting, is not the best choice. C is incorrect, as the people in negotiations don’t necessarily need to admire one another. |
| 20. | þ C. The project currently has 13 team members and next week seven additional team members come aboard for a total of 20 team members. Using the formula N(N–1)/2 where N is the number of identified stakeholders the communication channels equal 190. ý A, B, and D are all incorrect choices. |
| 21. | þ C. Collaborating is the ideal method when negotiating. The goal of negotiations is to work together for the good of the project. ý A, yielding, is not working for the good of the project. B, forcing, exerts power over one party without properly negotiating. D, compromising, calls for both parties to give up something without necessarily working together for the good of the project. |
| 22. | þ D. Of all the choices, change requests is the only acceptable answer. Incidentally, there are two outputs of performance reporting: change requests and performance reports. ý A. Trend analysis is the study of project performance results to determine if the project is improving or failing. It is a tool used as part of performance reporting, but it is not an output of performance reporting. B and C are also tools used in performance reporting, but they are not an output of the process. |
| 23. | þ D. When information is sent, it is considered to be transmitted. ý A, B, and C are all incorrect choices. |
| 24. | þ D. George and the customer’s relationship can allow clearer communication on the project objectives than what may be expressed in the project contract. The contract should take precedence on any issues, but direct contact is often the best way to achieve clear and concise communication. ý A is an incorrect choice as the focus is on personal gain rather than the good of the project. B is incorrect as the customer does not necessarily need to be educated on the project management process. C is incorrect; the customer is not always right—the contract will take precedence in any disagreements. |
| 25. | þ A. The transfer of knowledge is evidence that communication has occurred. ý B and C do not necessarily mean the knowledge has originated from the source and been transferred to the recipient. D is incorrect; messages are transmitted, but knowledge is transferred. |
|
| < Day Day Up > |
|
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 209
- Chapter VI Web Site Quality and Usability in E-Commerce
- Chapter IX Extrinsic Plus Intrinsic Human Factors Influencing the Web Usage
- Chapter X Converting Browsers to Buyers: Key Considerations in Designing Business-to-Consumer Web Sites
- Chapter XVII Internet Markets and E-Loyalty
- Chapter XVIII Web Systems Design, Litigation, and Online Consumer Behavior