19-8 ip ospf demand-circuit
| < Free Open Study > |
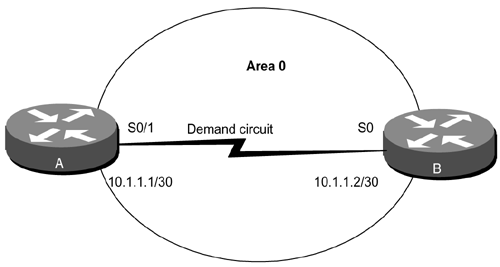
19-8 ip ospf demand-circuitSyntax Description: This command has no arguments. Purpose: On an OSPF demand circuit, periodic Hello messages are suppressed and periodic refreshes of LSAs do not flood the demand circuit. The ip ospf demand-circuit command allows the underlying data link layer to be closed when the topology is stable. In a point-to-multipoint topology, only the multipoint end must be configured with this command. This command is normally used on a tariff link such as ISDN. A tariff link is one that incurs a financial charge for every packet that is sent on the link. Configuring the link as a demand circuit will suppress periodic OSPF packets, reducing the line charges. Initial Cisco IOS Software Release: 11.2 Configuration Example: Configuring a Point-to-Point Link as an OSPF Demand CircuitConfigure the serial network in Figure 19-5 as an OSPF demand circuit. Figure 19-5. Configuring a Link as an OSPF Demand Circuit Will Suppress Hello Packets and Periodic Refreshing of LSAs Router A interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 ip ospf demand-circuit clockrate 64000 ! router ospf 1 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 1 _________________________________________________________________ Router B interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 ! router ospf 1 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 2 VerificationVerify that the serial interface has been configured as an OSPF demand circuit. rtrA# show ip ospf interface serial 0/1 Serial0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.1.1.1/30, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 64 Configured as demand circuit. Run as demand circuit. DoNotAge LSA allowed. Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 41, Retransmit 5 Hello due in 00:00:04 Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 2.2.2.2 (Hello suppressed) Suppress hello for 1 neighbor(s) Verify that the other end of the serial link is configured as a demand circuit even though the command ip ospf demand-circuit was not used on Router B. rtrB# show ip ospf interface serial 0 Serial0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.1.1.2/30, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 2.2.2.2, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 64 Configured as demand circuit. Run as demand circuit. DoNotAge LSA allowed. Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 41, Retransmit 5 Hello due in 00:00:04 Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 1.1.1.1 (Hello suppressed) Suppress hello for 1 neighbor(s) Verify that Routers A and B have established an OSPF neighbor relationship. rtrA# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 2.2.2.2 1 FULL/ - 00:00:35 10.1.1.2 Serial0/1 Troubleshooting
|
| < Free Open Study > |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 236
- Chapter V Consumer Complaint Behavior in the Online Environment
- Chapter VII Objective and Perceived Complexity and Their Impacts on Internet Communication
- Chapter VIII Personalization Systems and Their Deployment as Web Site Interface Design Decisions
- Chapter X Converting Browsers to Buyers: Key Considerations in Designing Business-to-Consumer Web Sites
- Chapter XIV Product Catalog and Shopping Cart Effective Design