4.1. How MapServer Applications Operate
| < Day Day Up > |
| MapServer usually works behind a web server application. The web server receives requests for maps and passes them to MapServer to create. MapServer generates the requested map image and hands it to the web server, which transmits it back to the user. Figure 4-1 shows how the user interacts with the web server which, in turn, makes requests to the MapServer program. MapServer's primary function is reading data from various sources and pulling these layers together into a graphic file, also known as the map image. One layer may be a Figure 4-1. A diagram showing the basic operation of a MapServer application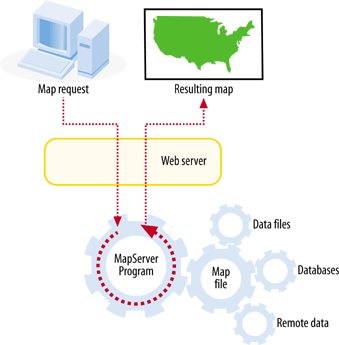 satellite image, another the outline of your country or points showing a major city. Each layer is overlaid or drawn on top of the others and then printed into a web-friendly graphic for the user to see. A good example of the results of the overlapping and mapping process can be seen in Figure 4-2. You can see a satellite image (from a remote server), road lines, and city locations; the city labels are dynamically generated by MapServer. This drawing process (a.k.a. rendering) occurs each time a request for a new map is made to MapServer, for instance, when a user zooms into the map for a closer look. This process also occurs when a user manually requests a redraw, such as when the content of one data layer changes, and the user wants to see the change. |
| < Day Day Up > |
EAN: 2147483647
Pages: 138